O&M
-
O&M
TECO’s San José Plant Models Safe and Sustainable Practices
In operation since 2000, TECO Energy Inc.’s 132-MW San José Power Station was the first coal-fired power plant built in Central America and is still the largest one. Used as a baseload plant, the facility successfully combines high availability with a business model that promotes sustainable environmental practices and a safe workplace.
-
O&M
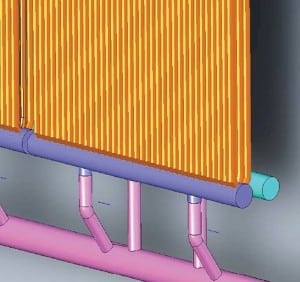
Proper Sizing of Steam Header Drains Prevents Water Induction
Steam turbines convert the thermal energy in motive steam to rotating mechanical energy, and the generator converts that energy into electrical power. One important requirement for safe and reliable operation is preventing water induction in the steam turbine and avoiding water hammer in the steam piping system. ASME standards present the design guidelines for removing moisture from steam lines; this article explains a practical design process.
-
O&M
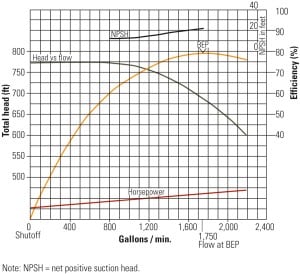
Deferred Maintenance Increases Pump Failures
If your facility has recently seen an upsurge in bearing failures on boiler feedwater (BFW) pumps, you are not the only plant experiencing these unnecessary and costly failures. The failure causes are often elusive, which is why plants have so many unresolved repeat failures.
-
O&M
Power 101: Improving the Performance of Boiler Auxiliaries, Part II
Efficient boiler operation requires boiler auxiliary equipment to operate in harmony. The air preheater, for example, though it has few moving parts, is vital to maintaining efficient boiler performance. In this second installment of our Power 101 series, we examine performance degradation caused by corrosion and fouling of the air preheater that results from the combustion of coal plus the effects of ammonia and sodium bisulfite injection for SO3 mitigation.
-
O&M
Designing Large Package Boilers
Designing large package boilers rated at over 400,000 lb/h steam production is a challenge because of shipping limitations within the U.S. and Canada.
-
O&M
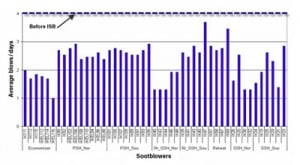
Clinker Minimization at San Miguel Electric Co-Op
San Miguel Electric Cooperative selected and installed an automatic sootblowing system for its Unit 1 to minimize clinkers in the boiler that caused semi-annual unscheduled outages. New boiler surface-cleaning equipment and intelligent cleaning software eliminated these expensive outages.
-
O&M
Increasing Generation Ramp Rate at Morgantown Generating Station’s Coal-Fired Units
At Morgantown Generating Station, plant personnel used innovative methods to combine model predictive control with distributed control system–based process control algorithms to improve waterwall temperature control and main steam temperature control and to enhance unit ramp rate capability. The previous heat rate and NOx optimization performance gains were retained. Focusing beyond basic loops of feedwater, air, and O2, the project considered issues such as PID controller override configuration and limitations. The techniques used to overcome these challenges improved unit ramp rate capability beyond any previous unit performance.
-
O&M
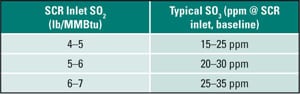
Continuous SO3 Monitoring Can Reduce Sorbent Consumption
An unintended consequence of employing selective catalytic reduction and wet flue gas desulfurization to reduce nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide levels at coal-fired power plants has been unwanted sulfur trioxide (SO3) emissions. Picking the right sorbent in the right amount can eliminate that problem.
-
O&M
New Tools for Diagnosing and Troubleshooting Power Plant Equipment Faults
The Electric Power Research Institute has developed a pair of diagnostic tools that combine and integrate features from multiple sources of plant information. The Diagnostic Advisor and the Asset Fault Signature Database will improve diagnostics for and troubleshooting of equipment faults by providing a holistic view of the condition of plant equipment.
-
O&M
EPRI Identifies Four Breakthrough Technologies for 2011
The Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) has identified four breakthrough technologies and funded them through its Strategic Research and Development Portfolio. EPRI expects to accelerate development of these innovations because they are likely to have significant effects on how electricity is generated and delivered.
-
O&M
Exelon Enjoys Benefits of Online Transformer Monitoring
In all of these cases, frequent oil analysis monitoring and preestablished action plans were able to allow for transformer replacement before the occurrence of a catastrophic failure. Exelon’s experience, as well as that of other power utilities across the grid, has spawned a report by the Institute of Nuclear Power Operations (INPO) of Atlanta, Georgia, that recommends that performance monitoring and trending be applied to all large transformers in order to establish a baseline for transformer maintenance strategies.
-
O&M
Selecting a Specialty Accumulator
Sudden bumps and shocks are great fun when you are off-roading or are riding on a rollercoaster. But when you are operating a piece of equipment, you want it to be running as smoothly as a Cadillac rolling down the interstate. Sudden changes in pressure produce vibration, cavitation, and water hammer and generally lower the lifespan and reliability of fluid systems.
-
O&M
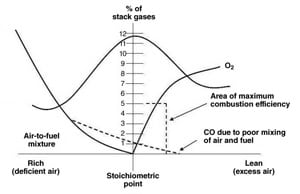
Flue Gas Analysis as a Furnace Diagnostic Tool
Combustion flue gas analysis has been used to optimize the boiler air/fuel ratio for decades. Measuring the amount of excess oxygen and/or carbon monoxide in combustion flue gases gives an indication of boiler efficiency and, thereby, plant operating economics. New sensors make those measurements simple and accurate.
-
O&M
Keeping Condensers Clean
The quality of the cooling water intake and the amount of debris in that water affects the operation and performance of the condenser and therefore the thermal performance of the typical steam plant.
-
O&M
Expanding the Use of Predictive Maintenance as a Business Strategy
The Linde Group is a world-leading gases and engineering company operating in more than 100 countries. It’s no surprise that the company uses a variety of advanced monitoring techniques and equipment to keep its plants operating reliably. In the U.S. and UK particularly, Linde plants have used online machine condition monitoring for a number of years. At its Shanghai headquarters, Linde has formed a large and impressive remote operations center where it monitors and tracks the process operations of all its major gas plants in China 24 hours a day.
-
O&M
Power 101: Improving the Performance of Boiler Auxiliaries, Part I
Boiler auxiliary equipment often receives no respect for the role it plays in maintaining efficient boiler performance. In this second installment of our Power 101 series, we examine the design and performance of the air preheater.
-
O&M
CSB Releases Hot Work Safety Notice
The Chemical Safety Board (CSB)—an independent federal agency charged with investigating serious chemical accidents such as equipment failure, as well as inadequacies in regulations, industry standards, and safety management systems—recently released multiple reports that should be made part of every power plant’s safety training program.
-
O&M
NFPA Gas Purging Rules Updated
The CSB has made urgent recommendations to the NFPA and the International Code Council to prohibit indoor purging and require companies and installers to purge flammable fuel gases to safe locations outdoors, away from workers and ignition sources.
-
O&M
Abrasion-Resistant Pipe Handles Ash Slurry
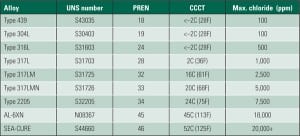
Steel piping systems are widely used at coal-fired power plants for a variety of purposes, including the conveying of coal ash slurry to nearby settling ponds, the transfer of limestone slurry to absorber spray towers for removal of SO2 and dilute hydrochloric acid from flue gases, and for transporting away the calcium sulfate by-product of the flue gas desulfurization process.
-
O&M
Air Casters Speed Equipment Moves
When it comes to moving megaton items like feedwater heaters or recirculating pumps, conventional moving tools such as wheel rollers, cranes, hoists, and come-alongs may be virtually useless. In some cases, moving large components is dangerous in a space-constrained location surrounded by delicate process control equipment. Feedwater heater and recirculating pump removal and replacement are […]
-
O&M
Retrofitting BWR Recirculation Pumps with Adjustable-Speed Drives
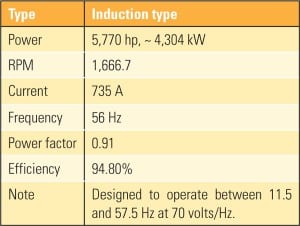
Exelon Nuclear recently replaced the original motor-generator sets for its boiling water reactor (BWR) recirculation pumps at its Quad Cities Generating Station Unit 1 with adjustable-speed drives. We examine the actual energy savings, motor-starting characteristics, control accuracy and stability, and motor and cable thermal behavior of this retrofit project.
-
O&M
Pulverized Coal Pipe Testing and Balancing
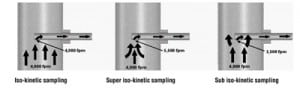
If you want the most accurate test results, it’s worth the extra effort to take isokinetic coal samples from coal pipes when collecting fuel and air measurements. Together, the data collected will allow more accurate balancing of coal pipes, measure fuel fineness, and improve the combustion efficiency of your steam generator.
-
O&M
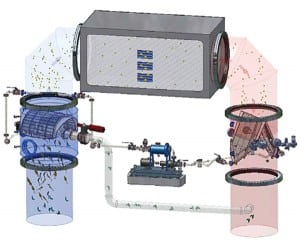
Innovative Cleaning of Air Preheater Coils with Pressurized Liquid Nitrogen
Cleaning air heaters in power plants or recovery boilers has traditionally involved using high-pressure water, chemicals, or steam. These techniques, though effective on moderate airside fouling of heat exchange surfaces, are usually ineffective on the more tenacious deposits that can develop in coal-fired plants. If these deposits are not removed by periodic cleaning, heat transfer in the heaters is reduced, which in turn reduces boiler efficiency and increases a unit’s heat rate. Severe fouling on air preheaters (APHs) can even reduce a unit’s power output.
-
O&M
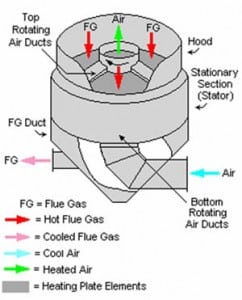
Air Preheater Seal Upgrades Renew Plant Efficiency
The air preheater is a critical, yet often overlooked, component of the boiler combustion air system. Evaluating and optimizing a heater’s performance is difficult given how entwined it is with the entire combustion system and the lack of standardized calculation tools. Reducing leakage by using modern seal technology will improve combustion efficiency, maintain fan performance, and keep your downstream air quality control equipment operating within spec.
-
O&M
Taming Condenser Tube Leaks, Part II
In Part I of this two-part report we examined the various chemical forces at work in condenser tube leaks, the steam plant components placed at risk, and the suite of instrumentation most capable of providing early warning of a leak. Assuming you were able to repair the leak and quickly resume operation, the next step is to identify the damage mechanisms that caused the problem so you can minimize future leaks.
-
O&M
FBC Control Strategies for Burning Biomass
As a boiler fuel, biomass has shown great promise while suffering from a slow development history. One factor limiting its use has been the combustion system. For the most part, conventional grate-fired boilers have been the only option. Today, the most efficient approach to burning biomass to produce electricity and steam is fluidized bed combustion (FBC). Whether you choose FBC or grate, biomass presents unique challenges to control system designers.
-
O&M
Ten Years of Experience with FAC in HRSGs
We first reported on combined-cycle plant reliability concerns due to erosive wear and flow accelerated corrosion (FAC) in heat-recovery steam generator (HRSG) pressure parts at the 1999 EPRI Maintenance Conference. More than 10 years later, these damage mechanisms remain significant contributors to forced outages, pressure part repairs, and major component replacement.
-
O&M
Taming Condenser Tube Leaks, Part I
Summer peaks are still with us, and every unit on your system must be prepared to operate at a moment’s notice. Spot power prices are so high that you expect phone calls asking for a few more megawatts from your units. Then your plant chemistry lab calls to report a condenser tube leak. Your options are few: Shut down immediately and get charged with a forced outage, ignore the leak and keeping running until fall, or schedule a maintenance outage next weekend and hope the leak can be found and fixed. In Part I, we examine what you need to know in order to make an informed decision. In Part II, we’ll explore the actual damage mechanisms.
-
O&M
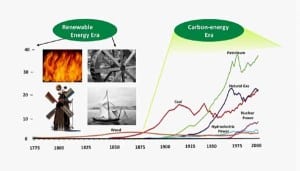
Wind Integration: Does It Reduce Pollution and Greenhouse Gas Emissions?
Many claim that wind generation is beneficial because it reduces pollution emissions and does not emit carbon dioxide. This isn’t necessarily the case. When wind is introduced into a generation system that uses carbon technologies to back up the wind, it actually reduces the energy efficiency of the carbon technologies.
-
O&M
Power 101: Flue Gas Heat Recovery in Power Plants, Part III
Every power engineer must have a firm grasp of the rudiments of how fuel is processed to produce electricity in a power generation facility. With this article, we conclude our three-part series on the essentials of recovering heat from flue gas to dry and process coal, with the goal of improving overall plant operating efficiency.