POWER
-
News
Energy industry needs a Sputnik
The 1940s and 50s are considered the golden age of science fiction literature. After my kids saw the movie, I, Robot, a few years ago, they were surprised to learn that Isaac Asimov—a giant of the genre with more than 500 books to his credit—had written a series of nine short stories with the same […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (October 2007)
Siemens ships first blade from U.S. plant; GE’s frames hit 1,000; Battery problems hit hybrid EV programs; Solar thermal rebounds in California;Peabody’s Illinois coal plant gets green light;EPA could sink 278-MW CFB unit; Longest-serving NRC commissioner dies at 58; POWER digest; Readers talk back; corrections
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (October 2007)
Why bypass desuperheaters fail; DSSP, CAD, and fast casting salvage nearly totaled pump; Seals of approval; Making gas turbine plants quieter
-
Commentary
What is resource adequacy?
Under its Resource Adequacy (RA) program, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) requires load-serving entities—both independently owned utilities and electric service providers—to demonstrate in both monthly and annual filings that they have purchased capacity commitments of no less than 115% of their peak loads. These purchase requirements are intended to secure sufficient commitments from […]
-
Coal
IGCC demonstration plant at Nakoso Power Station, Iwaki City, Japan
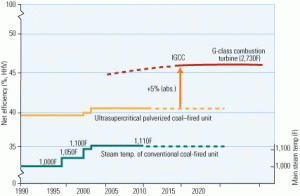
Integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) power plants are not yet standard designs. Although they use mature coal gasification processes and combustion turbines, disparate technologies and equipment still require custom, laborious interfacing at each site. Every major gas turbine vendor now can point to one or more power-producing IGCC projects based on its prime mover, but none yet offers a "reference" plant that has standardized the interfacing enough to justify confidence in two key metrics: $/kW and availability. With an air-blown demonstration plant based on one of its 130-MW turbines, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries is looking to change the rules of this game.
-
Coal
Pleasant Prairie Power Plant Air Quality Control Upgrade Project, Pleasant Prairie, Wisconsin
We Energies’ Pleasant Prairie Power Plant is a good example of how existing plants retrofitted with NOx and SO2 removal systems benefit from early planning and action. P4, as everyone calls it, recently completed a multiyear project to add a selective catalytic reduction system to one of its two units and a scrubber to both. The unique design and contracting aspects of the project make Pleasant Prairie one of POWER’s top coal-fired plants of 2007.
-
Coal
Polk Power Station Unit 1, Mulberry, Florida
Ten years ago, POWER selected Tampa Electric’s 250-MW Polk Power Station and its revolutionary integrated gasification combined-cycle demonstration project as the magazine’s 1997 Plant of the Year. Although no new commercial IGCC projects have been built since then, interest in deploying the coal-gasification technology is getting traction in some parts of the U.S. In 2007, POWER recognizes Polk Unit 1 as a Top Plant for developing trailblazing O&M practices and technical improvements that enable it to operate today as reliably as a modern pulverized coal plant, with lower pollutant emissions.
-
Gas
Tenaska Virginia Generating Station, Scottsville, Virginia
Not every facility that POWER singles out as a Top Plant has a unique design. Some, like this one, may be recognized for an excellent operations record and being a good corporate citizen. At Tenaska Virginia Generating Station, a formal program to make O&M personnel aware of best industry practices—and apply them on the job—has shortened the plant’s start-up time and elevated its availability, making it much more dispatchable and profitable.
-
Water
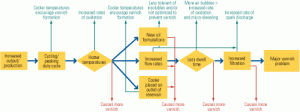
Biofouling control options for cooling systems
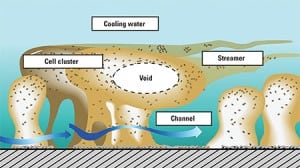
The infrequent or improper introduction of biocides into a plant cooling system may make fouling within it worse, by creating thick biofilms that can foster corrosion, reduce heat transfer, and increase water pumps’ operating costs. At the other end of the spectrum, overuse of biocides can waste expensive chemicals. Optimizing the quantity, frequency, and type of dosage can improve both the health of a cooling system and its plant’s bottom line.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Integrated software platform eludes many owner/operators
Ongoing research into experience with plant- and fleet-level software reveals that these applications work side by side but do not necessarily function as an integrated “knowledge management” system. On the supplier side, the industry continues to be fragmented, with individual programs governing a narrow part of the overall plant.
-
News
This month in POWER . . .
September 1886 Four years after this magazine was launched, the editors reviewed the latest improvements to industrial boilers, beginning with the Backus furnace (Figure 1). 1. The Backus furnace. “This furnace is provided with a brick arch placed just back of the fire-doors, that is intended to deflect the currents of air that are admitted […]
-
Commentary
It’s time to rebalance America’s electricity strategy
Not long ago, most utility investors considered California’s electricity policies too iconoclastic to support. Driven by far-left environmentalists and overzealous regulators, those policies have made it nearly impossible to build new power plants in the state, despite the urgent need for them. Now, however, with growing proof that global warming is real and with Americans […]
-
Nuclear
Nuclear plants: Something old, something new
The recent restart of Tennessee Valley Authority’s (TVA’s) Brown’s Ferry Unit 1 following a five-year renovation brings to 104 the number of nuclear plants operating in the U.S. Their 100 gigawatts of capacity represent about 20% of the nation’s electricity supply. If American electricity demand doubles by 2030 (as the U.S. Energy Information Administration predicts), […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (September 2007)
Constellation files partial COL / IAEA scrutinizes shaken Japanese nuke / Wave energy of the future? / New GE plant reigns in Spain / Solar house competition heats up / Oxygen-blown IGCC, at micro-scale / Turning corncobs into ethanol / Court blocks gas attack on coal project / New advanced energy initiatives / POWER digest
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (September 2007)
Replace pumps, cut repair bills / New bolts show their stress level / Up a certain creek, without a filter / Hang up those cables and hoses
-
Legal & Regulatory
Carbon-neutral status shouldn’t be for sale
While elected officials in Washington debate the politics of climate change, state legislators and regulators have been busy putting in place programs to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. For the most part, the goals of the programs reflect desired changes to power supply and consumption: increasing the efficiency of electricity generation and delivery, using less fossil […]
-
Gas
Al Ezzel Power Plant, Isle of Muharraq, Bahrain
Bahrain began privatizing its electricity and water-supply sectors three years ago, and the Al Ezzel Power Plant represents the first fruit of that strategic shift. The 950-MW plant, powered by two identical 2 x 1 combined-cycle units that burn natural gas, went commercial in May of this year. The plant now supplies about half of the national grid’s demand. The success of this fast-track project demonstrates the advantages of free markets and the wisdom of bringing in experts to build new capacity.
-
Gas
Groton Generating Station, Groton, South Dakota
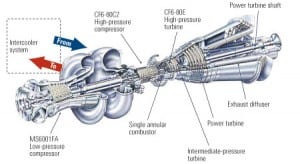
This plant’s main claim to fame: It marks the commercial debut of GE’s 100-MW LMS100 gas turbine-generator. According to Basin Electric, over the unit’s first year of service it has demonstrated top-notch operating flexibility in peaking, mid-range, and baseload service, thanks to capabilities such as 10-minute cold start-ups and minimal impact on heat rate at partial loads. In addition to hosting the first LMS100, Groton Generating Station earns recognition as one of POWER’s Top Plants for the attention its design pays to reliability and resource planning.
-
Gas
GTAA Cogeneration Complex, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada
When a blackout shuts down a factory, the impact isn’t apparent to the public. But lose power at an international airport, and thousands of angry travelers and the people waiting for them won’t be interested in excuses. The Greater Toronto Airports Authority learned that lesson in August 2003. Ten months later, it began building a 117-MW cogeneration plant that is now capable of supplying all of its energy needs—not just electricity, but space heating and chilled water as well.
-
Gas
Port Arthur II Integrated Hydrogen/Cogeneration Facility, Port Arthur, Texas
The rationale for a typical cogeneration plant is clear: Supply some power, and maybe some steam, to an industrial host and save energy dollars on both sides of the fence. But integrating a cogen plant that also produces hydrogen with a major refinery that operates 24/7 is a job best left to a company with diverse and proven technology skills. The Air Products Port Arthur II project proves that such a job can be done right. Accordingly, it is one of POWER’s natural gas–fired Top Plants of 2007.
-
Gas
Port Westward Generating Plant, Clatskanie, Oregon
Since going commercial this June, Port Westward Generating Plant has taken its rightful place as one of America’s most efficient power stations. It is now helping to satisfy Portland General Electric’s summer demand reliably and cost-effectively. What differentiates Port Westward is its pioneering use in the U.S. of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries’ G1 class combined-cycle combustion turbine.
-
O&M
Detecting and solving lube oil varnish problems
Have you bought electrostatic or agglomeration equipment to rid your turbine oil of varnish deposits, but its varnish potential rating failed to improve? Or, after an initial drop, has the varnish potential returned to its previous level? Even worse, have you had recurring valve sticking problems after making a sizeable investment to "solve" this problem? Welcome to the world of soluble varnish caused by autodegradation. Read the unvarnished truth about varnish and how to get rid of it for good.
-
Marmaduke
Marmy’s loose rivets
Steve Elonka began chronicling the exploits of Marmaduke Surfaceblow—a six-foot-four marine engineer with a steel brush mustache and a foghorn voice—in POWER in 1948, when he raised the wooden mast of the SS Asia Sun with the help of two cobras and a case of Sandpaper Gin. Marmy’s simple solutions to seemingly intractable plant problems remain timeless. This Classic Marmaduke story, originally published in 1958, illustrates that big problems often have simple, but ingenious, solutions.
-
News
Retrospective
August 1886 POWER reported on one of the first twin-cylinder "Otto" natural gas–fired engines that had recently appeared in the U.S. power market. The report notes that "engines of 100 horsepower are being now economically used where gas is low in price, as in England and other European countries" (Figure 1). 1. A twin-cylinder "Otto" […]
-
Commentary
Global warming "consensus" continues to melt away
We are witnessing an international awakening of scientists who are speaking out in opposition to former Vice President Al Gore, the United Nations, and the media-driven "consensus" on man-made global warming. In May, I released a report detailing scientists who were former believers in catastrophic man-made climate change but who have recently reversed themselves and […]
-
Synfuel
Fueling around
Europeans didn’t know that corn existed before Columbus "discovered" America. It had been cultivated by indigenous North Americans for thousands of years before the Italian brought home what was to become a favorite food for many. The more adventuresome even figured out how to distill corn into something more to their liking. Fast-forward five hundred […]
-
Gas
Global Monitor (August 2007)
PG&E mounts tidal power project / GE F-class turbine breaks record / Iowa welcomes ethanol-fed hog / NYPA upgrades pumped-storage plant / Bush blesses Browns Ferry 1 restart / Shearon Harris looks to live on / Nevada bets on solar thermal / Climate models questioned / POWER digest
-
Readers talk back and Corrections (August 2007)
Reaction to reactor comment On page 34 of your April article on nuclear power, the author mischaracterized the maturity of one of the new reactors that have been submitted for NRC approval. The statement, "None of the advanced reactors that the NRC has certified (by reviewing engineering documents) has a performance record," is incorrect. GE’s […]
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (August 2007)
Stop valves from leaking money / Integrating plant and equipment models / Pricing priceless knowledge