O&M
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (October 2007)
Why bypass desuperheaters fail; DSSP, CAD, and fast casting salvage nearly totaled pump; Seals of approval; Making gas turbine plants quieter
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (September 2007)
Replace pumps, cut repair bills / New bolts show their stress level / Up a certain creek, without a filter / Hang up those cables and hoses
-
O&M
The Coal Patrol: Mine Safety Deserves More Than Lip Service
Every step forward in underground U.S. mine safety in the 20th and 21st centuries has been on the backs of mangled and dead coal miners. That grisly observation is unassailable. Following the August tragedy at the Crandall Canyon mine in Utah that killed six miners and three would-be rescuers, the federal Mine Safety and Health […]
-
O&M
Plant Economics: The Impact of Shortages on FGD Prices
Since ratification of the Clean Air Act (CAA) in 1970, U.S. utilities have made steady efforts to install pollution control equipment to curb power plant stack emissions. The CAA Amendments of 1990 raised concerns at the time about the industry’s ability to install a large number of flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems, or scrubbers, in […]
-
O&M
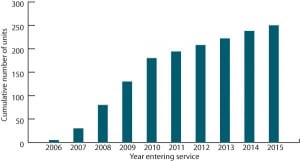
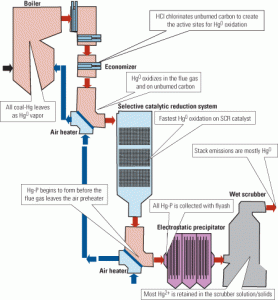
Mercury Control: Capturing Mercury in Wet Scrubbers: Part II
In Part I of this two-part report ( COAL POWER, July/August 2007, p. 22), we introduced the integrated R&D effort by the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Energy Technology Laboratory (DOE/NETL) to improve understanding of the mechanisms of mercury (Hg) capture and retention in flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems and the fate of Hg in […]
-
O&M
Finding and fixing leakage within combined HP-IP steam turbines: Part II
By design, combined HP-IP turbines have a small amount of internal leakage from the high-pressure turbine to the intermediate-pressure turbine. As turbines age, the leakage increases considerably and becomes excessive, creating a heat rate penalty and possibly a reliability problem. Last month we explored the symptoms and causes of steam leakage within GE steam turbines and how to correct the problem. In Part II, we examine the same issues for Westinghouse and Allis-Chalmers turbines from both theoretical and practical angles.
-
O&M
Use predictive techniques to guide your mercury compliance strategy
Several states have mandated faster and/or deeper reductions in plant mercury emissions than those called for by the Clean Air Mercury Rule. Unfortunately, differences between plants make accurate evaluation of control options difficult. In most cases, even statistically based Hg emission models don’t pass muster because they don’t account for the dynamic chemical behavior of Hg species in gas cleaning systems. This article describes one system evaluation tool that has been validated using Hg field test data from 50 full-scale flue gas cleaning systems. It is already being used by TVA and other utilities.
-
O&M
Detecting and solving lube oil varnish problems
Have you bought electrostatic or agglomeration equipment to rid your turbine oil of varnish deposits, but its varnish potential rating failed to improve? Or, after an initial drop, has the varnish potential returned to its previous level? Even worse, have you had recurring valve sticking problems after making a sizeable investment to "solve" this problem? Welcome to the world of soluble varnish caused by autodegradation. Read the unvarnished truth about varnish and how to get rid of it for good.
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (August 2007)
Stop valves from leaking money / Integrating plant and equipment models / Pricing priceless knowledge
-
O&M
MidAmerican’s Walter Scott, Jr. Energy Center Unit 4 earns POWER’s highest honor
MidAmerican Energy Co. and its project partners are convinced that supercritical coal-firing technology’s inherently higher efficiency and lower CO2 emissions no longer come with a price: reduced reliability. Their Walter Scott, Jr. Energy Center Unit 4, the first major new supercritical plant in the U.S. in more than 15 years, is POWER’s 2007 Plant of the Year.
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (July 2007)
Hydro-demolition speeds reactor dome entry;
Tips for keeping your unit stable;
Air makes heavy move a breeze -
O&M
Safety, compliance, and then production maximizes bottom line
When injuries or accidents occur, the employer ultimately loses on two counts: increased medical costs and employee absences. A policy of "safety, compliance, and then production" is more than just good business; it’s also good stewardship of the health and safety of employees who deserve no less.
-
O&M
Coal Plant O&M: Smart Sootblower Tailors Cleaning to Need for It / Blending’s Impact on Coal Quality
The 1990 amendments to the Clean Air Act require coal-fired power plants to reduce their emissions of the pollutant SO2. To do so, many have switched to, or are considering switching to, Powder River Basin (PRB) coal. Unfortunately, PRB coal has a tendency to leave excessive and tenacious deposits on boiler heat-exchange surfaces. Complicating the problem, the distribution of the deposits is far from uniform.
-
O&M
Lignite Drying: New Coal-Drying Technology Promises Higher Efficiency Plus Lower Costs and Emissions
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and Great River Energy are testing a new coal-drying technology that could dramatically reduce the emissions of lignite-burning power plants. The project was selected for funding during Round I of the DOE’s Clean Coal Power Initiative (CCPI), a series of competitions to demonstrate a range of promising clean-coal technologies. […]
-
O&M
PRB Tech Notes: Lawrence Energy Center Showcases Winning Plant
Lawrence Energy Center (LEC) proudly hosted about 60 representatives of the Powder River Basin Coal Users’ Group (PRBCUG) at its July 24th open house, luncheon, and plant tour. LEC was named the PRBCUG’s 2007 Plant of the Year at this year’s ELECTRIC POWER Conference and Exhibition in Chicago, May 1 – 3. Traditionally, the winning […]
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (June 2007)
Ready for your NERC close-up? / Synthetic oils for industrial applications
-
O&M
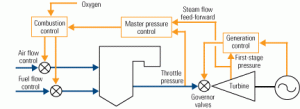
Drum pressure the key to managing boiler stored energy
At the heart of most boiler combustion control systems (and most coordinated boiler/turbine control systems as well) is throttle pressure correction, usually applied by the "master controller." Throttle pressure is considered a key variable to control because it represents the energy balance between the boiler and the turbine. When throttle pressure is constant, the boiler […]
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (May 2007)
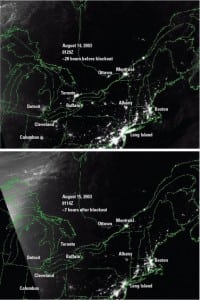
Cyber security and the grid; Harnessing the Yangtze;
Hydraulic system overhaul;
O&M problems not caused by cycling;
-
O&M
Coal Plant O&M: River Locks and Barges Are an Aging Workforce, Too
During 2005, about 150 million tons of coal were transported to power plants by hopper barges plying U.S. inland waterways. With coal-fired plants expected to continue producing 50% of America’s electricity, coal barge traffic is not likely to fall off. In fact, it may increase, for two reasons. One is cost. Shipping coal by barge […]
-
O&M
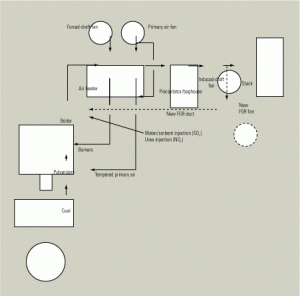
Pollution Control: LCRA Fayette Lowers NOx Below 0.10 lb/mmBtu
The Fayette Power Project (FPP, aka the Sam K. Seymour Power Station) is a three-unit, coal-fired generating plant sited near La Grange, Texas (Figure 1). Units 1 and 2, each with a nominal rating of 600 MW, are co-owned by the Lower Colorado River Authority (LCRA) and Austin Energy (AE). LCRA is a conservation and […]
-
O&M
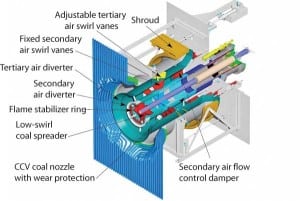
Pollution Control: Low-NOx Combustion Retrofit Options
Reducing NOx emissions from large utility coal-fired boilers has been a primary focus of the U.S. power generation industry since passage of the 1970 Clean Air Act and subsequent legislation. By the early 1990s, nearly all such boilers had installed some form of low-NOx burner (LNB) technology and/or overfire air (OFA) — the least expensive […]
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (April 2007)
Control pollution and slagging on a shoestring / Keeping HRSGs young, cool, and clean / Natural air conditioning
-
O&M
Adding cathodic protection to a hyperbolic tower
Hyperbolic cooling towers have a distinctive shape, but that form is subordinate to function—natural-draft cooling is cheaper than mechanical-draft cooling. The lower operating costs are offset to some degree by the higher cost of protecting internal tower surfaces from swings in humidity that foster corrosion damage. Learn how one utility added cathodic protection when it repaired its corroded hyperbolic tower, giving it a new lease on life.
-
O&M
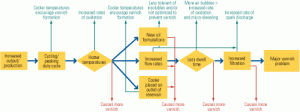
Getting to the root of lube oil degradation problems
Doctors and engineers realize that solving a health problem is better done by identifying and eliminating its cause than by treating its symptoms. For machinery, the class of multidisciplinary methods known as root cause analysis (RCA) is an important tool for addressing chronic reliability problems. But RCA often is improperly applied to lubrication-related problems. Read on to learn how to use the technique correctly.
-
O&M
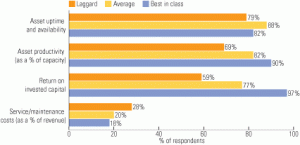
Utilities surpass other industries in asset maintenance practices
Want some good news about your predictive maintenance program for a change? A recent research report by the Aberdeen Group found the electric utility industry benchmarks exceptionally well against other industries in its PDM practices. In fact, the research found that best-in-class companies outperformed industry peers in improving asset availability by up to a three-to-one margin. In a web exclusive, the Aberdeen Group has provided its report for download from powermag.com as a service to our readers.
-
O&M
SO3’s impacts on plant O&M: Part III
Part I of this three-part series (POWER, October 2006) explored the negative impacts of sulfur trioxide (SO3) on the operations and maintenance of back-end plant equipment. Part II (February 2007) listed and quantified the likely and potential benefits of limiting the concentration of SO3 in flue gas to 3 ppm at the entrance to the air heater. This final part describes the characteristics of an optimal SO3 removal technology and details the operating experience of a patented process that has worked successfully at a half-dozen plants for up to three years.
-
O&M
Blades, better than new
The challenge for suppliers of aftermarket turbine blades is that their starting point is an existing blade and nothing else. There are no CAD models, drawings, measurements, tolerances, or inspection data associated with it. However, thanks to the latest in computer tools, a blade now can be digitally recreated to exact specifications and built using the latest design and manufacturing practices. Here’s an inside look at how turbine blades are captured, reconstructed, inspected, and remade to be better than the originals.
-
O&M
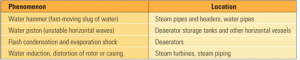
Water hammer and other hydraulic phenomena
The term "water hammer" encompasses a handful of hydraulic and thermohydraulic mechanisms. They include water hammer in steam and water piping, water piston, water induction, flash condensation and evaporation, and shock waves generated by transonic flow. All can lead to failures of steam and water cycle components and put plant operators and workers at risk. Proper design and O&M practices can keep water hammer and similar phenomena under control.
-
O&M
Practical guidelines for determining electrical area classification
A century ago, boiler explosions were an all-too-familiar event. But with the universal adoption of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Codes in 1914, explosions caused by poor design or manufacturing became relics of history. Electrical classification codes had the same effect on safety. This article explains how designers and operators practically apply those standards. Code details and samples of area classification drawings for a gas turbine plant are included in an online supplement (see end of story).
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (March 2007)
The critical subset / Aging workforce challenges / Tighter tolerances in retrofits / Writing sensible start-up and shutdown procedures