Water
-
Coal
Plant Efficiency: Begin with the Right Definitions
The race is on to claim the title of "most efficient coal-fired power plant" on the planet. However, it’s tricky identifying finalists because of the widespread misuse of the term "efficiency" and all those nagging assumptions. Let’s first establish clear definitions and then identify the title contenders.
-
O&M
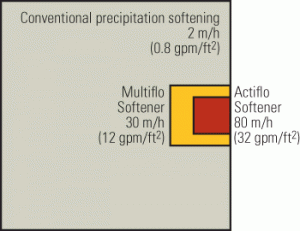
Avoid These 10 Mistakes When Selecting Your New Water Treatment System
There are a number of reasons why your plant might be looking at new water pretreatment equipment in the near future. One common reason is the addition of new generating capacity. Regardless of the type of new generation, you can be sure that it will require additional high-purity water for processes ranging from direct steam generation to power augmentation, NOx control, and washing the blades of the combustion turbines.
-
O&M
Accurate Online Silica Analyzers Ensure Boiler Performance, Add Boiler Life
One key area at the 800-MW Michoud power station where O&M excellence is evident is in maintaining plant water quality.
-
Water
Improved FGD Dewatering Process Cuts Solid Waste
In 2007, Duke Energy’s W.H. Zimmer Station set out to advance the overall performance of its flue gas desulfurization (FGD) dewatering process. The plant implemented a variety of measures, including upgrading water-solids separation, improving polymer program effectiveness and reliability, optimizing treatment costs, reducing solid waste sent to the landfill, decreasing labor requirements, and maintaining septic-free conditions in clarifiers. The changes succeeded in greatly reducing solid waste generation and achieving total annual savings of over half a million dollars per year.
-
O&M
Preventing Turbine Water Damage: TDP-1 Updated
ASME’s latest revision of its Recommended Practices for the Prevention of Water Damage to Steam Turbines Used for Electric Power Generation: Fossil-Fuel Plants, ASME TDP-1-2006, contains much important design and operating advice that is proven to protect steam turbines. However, many in the industry are not as familiar with the update as they should be. This article provides a concise overview of this critical design standard.
-
Gas
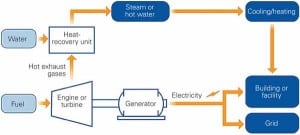
Qatar Starts Construction on Middle East’s Largest Power and Water Plant
The gas-rich Persian Gulf state of Qatar in May commenced construction of the region’s largest power and water plant, a massive project comprising eight gas turbine generators, eight heat-recovery steam generators, four steam turbine generators, and 10 desalination units.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Looking Downstream After the Cooling Water Case
In the wake of the recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling related to cooling water intake practices at large power plants, many utilities are relieved to be off the hook as far as implementing expensive control upgrades to protect fish and other aquatic organisms.
-
O&M
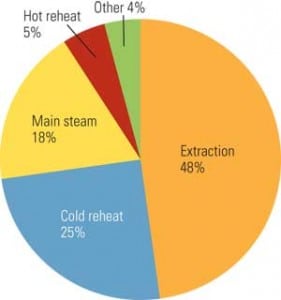
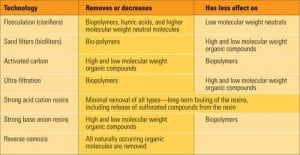
Focus on Organics in Steam
Organic compounds can enter the steam cycle from a number of sources, including water treatment chemicals, or as part of a manufacturing process. Regardless of the source of the organics, their effects range from fouling polisher resins to causing significant steam turbine damage. Conventional water pretreatment systems are available to remove organics from water, but removing organic compounds at their source is the best place to start addressing the problem.
-
Water
Reconsider Start-up Controls to Avoid Boiler Deposits and Underdeposit Corrosion
Water treatment programs for boilers and heat-recovery steam generator (HRSG) units appropriately focus on chemistry controls during normal operation. However, rates of corrosion product transport and deposition can be much greater in boilers and HRSG units during start-up than during routine operation. For that reason, in addition to standard programs for monitoring and control of corrosion product transport, deposition, and underdeposit corrosion, consider adding contingency plans for boiler water chemistry holds in the start-up process.
-
Water
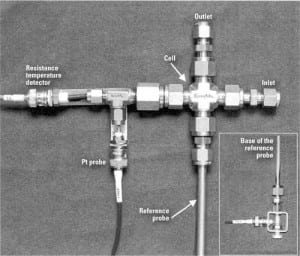
How to Measure Corrosion Processes Faster and More Accurately
Maintaining reliable and efficient plant operations requires good control of corrosion and corrosion product transport in power plant water systems. The Electric Power Research Institute recommends oxidation-reduction potential for passivator control in feedwater systems, as do many industry experts. Here’s how to turn that recommendation into a robust feedwater monitoring program.
-
Water
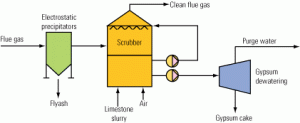
Flue Gas Desulfurization Wastewater Treatment Primer
Purge water from a typical wet flue gas desulfurization system contains myriad chemical constituents and heavy metals whose mixture is determined by the fuel source and combustion products as well as the stack gas treatment process. A well-designed water treatment system can tolerate upstream fuel and sorbent variation over time and consists of multiple process treatment steps arranged in just the right order to produce wastewater acceptable for discharge.
-
Water
Oak Creek Power Plant Upgrades Cooling Water System
Formed suction intake designs have been used in many large vertical pump stations in flood control projects. Space limitations at the Oak Creek Power Plant Expansion Project near Milwaukee, Wisconsin, created a unique opportunity to apply this technology to an 800,000-gpm cooling water system upgrade for the entire Oak Creek Power Plant.
-
O&M
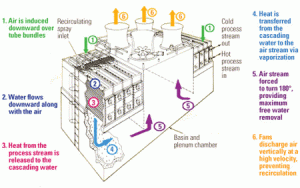
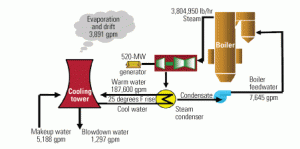
Conserve Water by Improving Cooling Tower Efficiency
Though an abundant supply of freshwater has been taken for granted in many parts of the world, its availability is becoming less certain, even in North America. Water is a valuable resource and commodity that needs to be efficiently managed to minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and control cost, especially for power generation. The industry must respond by seeking out more efficient ways to use water, such as by implementing water recycling and reuse strategies, especially for critical equipment like cooling towers.
-
Water
Invasive Species and Water Intakes
On October 21, a mass of basketball-sized jellyfish managed to accomplish what activists of every stripe had failed to do: Abruptly shut down Pacific Gas & Electric Corp.’s (PG&E) 1,118-MW Diablo Canyon Unit 2 reactor in San Luis Obispo County, Calif. (Figure 8).
-
Water
Cooling water intake structure regulations
In the wake of a recent federal case, large power plants are off the hook for now as far as complying with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) 2004 rule intended to protect fish and other aquatic organisms by controlling cooling water intake practices.
-
O&M
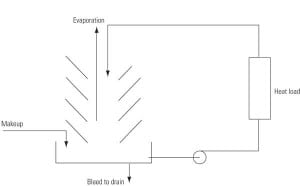
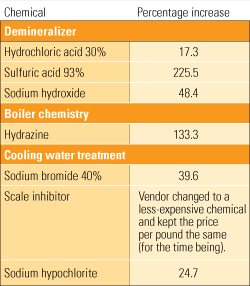
Put a lid on rising chemical costs
News reports tell us that rapidly growing economies, such as China’s, are importing more oil and raw materials each year, thereby pushing up commodity prices on the world market. One of the side effects of rising commodity prices is considerable increases in the cost of water treatment chemicals. Don’t be tempted to skimp on chemicals to save a buck but risk catastrophic damage. In the words of NASA’s former flight director, Gene Kranz: “Failure is not an option.”
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (September 2008)
Tackling substandard water sources / Control abrasive wear in scrubber piping / Sensors and final control elements
-
Water
Air-cooled condensers eliminate plant water use
River or ocean water has been the mainstay for condensing turbine exhaust steam since the first steam turbine began generating electricity. A primary challenge facing today’s plant developers, especially in drought-prone regions, is incorporating processes that reduce plant water use and consumption. One solution is to shed the conventional mindset that once-through cooling is the only option and adopt dry cooling technologies that reduce plant water use from a flood to a few sips.
-
Water
Wet surface air coolers minimize water use by maximizing heat transfer efficiency
Gas-fired power plant designers and operators are increasingly challenged to reduce their plants’ water consumption and improve their thermal efficiency. Closed-loop, evaporative cooling systems (known as wet surface air coolers, or WSACs) are a cost-effective heat transfer technology that can simultaneously achieve both goals. In addition to providing lower-temperature cooling and condensing while requiring less space and horsepower than conventional systems, WSACs can use poor-quality water as spray makeup.
-
O&M
Condensate polishers add operating reliability and flexibility
Many of today’s advanced steam generators favor either an all-volatile treatment or oxygenated treatment chemistry program, both of which require strict maintenance of an ultra-pure boiler feedwater or condensate system. Those requirements are many times at odds with the lower-quality water sources, such as graywater, available for plant makeup and cooling water. Adding a condensate polisher can be a simple, cost-effective solution.
-
Water
New strategies for conquering environmental challenges
No doubt some power plant engineers feel that tackling environmental problems is a lot like dealing with the Hydra, the ancient mythological serpent monster with multiple heads. When an attacker would cut off one of the Hydra’s numerous heads, two new ones would grow back in place of the head that was removed. All too […]
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (April 2008)
Tag-teamed seawater cleanup; New cooling towers to improve river’s health; Back to school
-
Coal
New coal plant technologies will demand more water
Population shifts, growing electricity demand, and greater competition for water resources have heightened interest in the link between energy and water. The U.S. Energy Information Administration projects a 22% increase in U.S. installed generating capacity by 2030. Of the 259 GW of new capacity expected to have come on-line by then, more than 192 GW will be thermoelectric and thus require some water for cooling. Our challenge will become balancing people’s needs for power and for water.
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (March 2008)
New CIP standards leave questions unanswered/Solving common analyzer problems/Qualifying rebuild shops
-
O&M
Maintaining water sample panels improves plant availability
Even comedian Rodney Dangerfield got more respect than many plant water sample panels do. But power plants ignore sample panels at their peril. Those sample panels, and readings of the on-line analyzers they support, identify when multi-million-dollar systems have a problem that demands immediate attention.
-
Water
Benefits of evaporating FGD purge water
In the U.S. and the European Union, scrubbers are installed on all new coal-fired power plants because their technology is considered the best available for removing SO2. A zero-liquid-discharge system is the best technology for treating wet scrubber wastewater. With the future promising stricter limits on power plants’ water use, ZLD systems that concentrate scrubber purge streams are sure to become as common as ZLD cooling tower blowdown systems.
-
Water
Costlier, scarcer supplies dictate making thermal plants less thirsty
The Energy Information Administration estimates that U.S. thermoelectric generating capacity will grow from 709 GW in 2005 to 862 GW in 2030 to help meet annual demand increases of 2%. The makeup and cooling water needed by plants generating that increased capacity certainly won’t be available from withdrawal sources, so plant developers and owners will have to apply water-stingy technologies plantwide. As is usually the case, conservation saves money as well as the environment. Here’s a thumbnail economic analysis of some solutions to the water problem.
-
Water
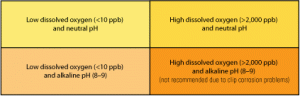
Forgotten water: Stator cooling water chemistry
Stator cooling water treatment is often ignored—until the generator fails. Proper treatment and monitoring is essential to keeping the copper in your stators, where it belongs.
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (September 2007)
Replace pumps, cut repair bills / New bolts show their stress level / Up a certain creek, without a filter / Hang up those cables and hoses
-
Water
Biofouling control options for cooling systems
The infrequent or improper introduction of biocides into a plant cooling system may make fouling within it worse, by creating thick biofilms that can foster corrosion, reduce heat transfer, and increase water pumps’ operating costs. At the other end of the spectrum, overuse of biocides can waste expensive chemicals. Optimizing the quantity, frequency, and type of dosage can improve both the health of a cooling system and its plant’s bottom line.