-
Commentary
Full-service utilities prove their value
During the past year, the debate over the structure of the nation’s electricity systems has continued at a steady clip. It seems that almost every month a new study or report is issued that proclaims the advantages or disadvantages of one market structure over another. Although a report or study may have value, the Community […]
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (April 2007)
Control pollution and slagging on a shoestring / Keeping HRSGs young, cool, and clean / Natural air conditioning
-
Legal & Regulatory
How direct access would improve electricity supply
The debate over retail choice has resurfaced, triggering in the minds of many consumer advocates California’s failed deregulation attempt and its fallout—rolling blackouts, bankrupt utilities, and government bailouts with crippling long-term consequences. Before allowing a chorus of "oh no, not again" to cloud the debate, state policy makers should realize that allowing generators to […]
-
Nuclear
Charlie Brown, nukes, and the football
The term "nuclear renaissance" is on the lips of many in the nuclear power industry today, for good reason. The federal executive branch is friendly to nukes; a nationwide shortage of baseload generation looms; the nuclear industry has vastly improved its performance in running its 20th-century plants; and a new generation of plant designs is ready for the road.
-
Coal
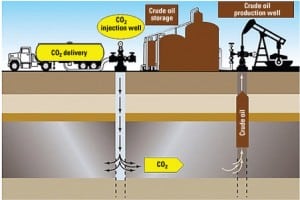
Exploring the many carbon capture options
Carbon capture and sequestration have many technical hurdles to leap in coming years. The capture and reuse of CO2 to enhance oil recovery preceded the current clamor over climate change, and that experience is often used as an example that the process is a viable way to handle this greenhouse gas. This article explores options for the first part of the process: CO2 separation and capture.
-
O&M
Adding cathodic protection to a hyperbolic tower
Hyperbolic cooling towers have a distinctive shape, but that form is subordinate to function—natural-draft cooling is cheaper than mechanical-draft cooling. The lower operating costs are offset to some degree by the higher cost of protecting internal tower surfaces from swings in humidity that foster corrosion damage. Learn how one utility added cathodic protection when it repaired its corroded hyperbolic tower, giving it a new lease on life.
-
O&M
Getting to the root of lube oil degradation problems
Doctors and engineers realize that solving a health problem is better done by identifying and eliminating its cause than by treating its symptoms. For machinery, the class of multidisciplinary methods known as root cause analysis (RCA) is an important tool for addressing chronic reliability problems. But RCA often is improperly applied to lubrication-related problems. Read on to learn how to use the technique correctly.
-
O&M
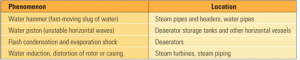
Water hammer and other hydraulic phenomena
The term "water hammer" encompasses a handful of hydraulic and thermohydraulic mechanisms. They include water hammer in steam and water piping, water piston, water induction, flash condensation and evaporation, and shock waves generated by transonic flow. All can lead to failures of steam and water cycle components and put plant operators and workers at risk. Proper design and O&M practices can keep water hammer and similar phenomena under control.
-
Gas
Will turbines require expensive retrofits to handle imported LNG?
With domestic reserves of natural gas declining and demand for gas rising, imported liquefied natural gas will increasingly fill the shortfall in U.S. pipeline supply. More than 40 LNG receiving/regasification terminals on three coasts are in various stages of development. Yet many questions about the operational and emissions impacts of the "hotter" LNG imports on today’s cleaner-burning gas turbines remain unanswered.
-
O&M
Practical guidelines for determining electrical area classification
A century ago, boiler explosions were an all-too-familiar event. But with the universal adoption of the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Codes in 1914, explosions caused by poor design or manufacturing became relics of history. Electrical classification codes had the same effect on safety. This article explains how designers and operators practically apply those standards. Code details and samples of area classification drawings for a gas turbine plant are included in an online supplement (see end of story).
-
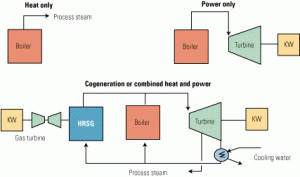
Gas
Balancing power and steam demand in combined-cycle cogeneration plants
The 2005 amendment to the 1978 Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act created some unique challenges for the design of cogeneration plants in general and combined-cycle cogeneration plants in particular. Because utilities are no longer obligated to buy electricity at "avoided cost" from qualifying facilities, plant owners must simultaneously balance power and thermal demand efficiently and economically. Here’s a prescription for your next plant design.
-
Business
ELECTRIC POWER Conference set for record year
ELECTRIC POWER 2007, sponsored by POWER magazine, will be presented at the Donald E. Stephens Convention Center in Rosemont, Ill., May 1 through May 3, 2007. A full agenda of preconference workshops and tutorials is scheduled for Monday, April 30.
-
News
This month in POWER …
March 1886 POWER reported on the latest development of a new and improved engine: "The chief feature of the Corliss engine [from Kendall & Roberts, Cambridgeport, Mass.] is the valve gear, which consists of four cylindrical valves, two each for admission and exhaust, operated from a central swing or stud plate; the steam valves being […]
-
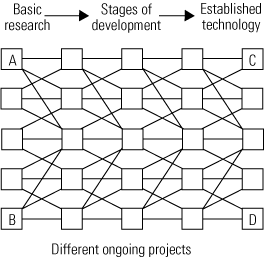
Commentary
A vision for speeding up science and technology developments
As David Wojick explains in his article, "Mapping technology chaos," on page 36, power engineers are under the gun to innovate. The president and Congress are calling for dramatic new advances in power technology. They are even considering legislating progress in areas such as efficiency and emissions control. Turning data into information Power engineers know […]
-
Unequivocal bragging rights
The new congressional leadership has promised a "new" agenda for fighting climate change based on reducing the quantities and rate of growth of greenhouse gases (GHG) discharged to the atmosphere. My first question to the Democrats: Where have you been the past few years? My second: How much are you willing to spend to make […]
-
Gas
Global Monitor (March 2007)
Winter storms ravage Nebraska grid / Waste-fired plant coming to Arizona / Wartsila lands jobs in Azerbaijan, Sweden / Yet another controversial LNG project / Siemens lands two-gasifier order in China / IndyCars drink nothing but ethanol / New Otto/diesel engine to debut in Russia / POWER digest / Readers talk back
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (March 2007)
The critical subset / Aging workforce challenges / Tighter tolerances in retrofits / Writing sensible start-up and shutdown procedures
-
Legal & Regulatory
Why raising renewable portfolio standards won’t work
Almost half of U.S. states now insist that their investor-owned electric utilities serve a specified percentage of their load with electricity from renewable resources by a date certain. Utilities struggling to comply with their mandate increasingly warn that they will be unable to achieve the required level on time. Yet even as utilities express these […]
-
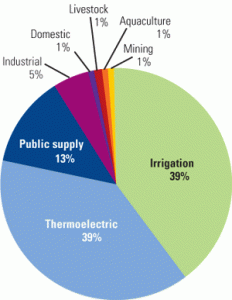
Water
Reclaimed cooling water’s impact on surface condensers and heat exchangers
Because water is more precious than power in many regions of the U.S., plant designers are more frequently specifying the use of treated wastewater for plant cooling. Using "gray water" poses its own challenges for critical service equipment like condensers and heat exchangers. Some problems—like corrosion—are familiar, whereas others are rare. But so far, none has been a match for the ingenuity of multidisciplinary design experts.
-
Business
Mapping technology chaos
Power engineers are in a predicament: Technology is advancing at a dizzying pace, but we are unsure how to mine information from disparate sources or predict the next big thing. Becoming expert at finding technology hones your competitive edge in both the workplace and the marketplace. Bring your pick and shovel, and we’ll show you where to start digging.
-
Business
U.S. Commercial Service helps suppliers go global
Successful exporting of goods and services is essential for U.S. companies seeking to exploit the increasingly open world economy. In the export business, the challenge is learning the ropes without getting hung out to dry when entering a potentially lucrative but unfamiliar market. Take advantage of the significant experience of the U.S. Commercial Service—its people really are here to help.
-
Water
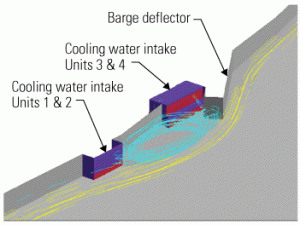
Fish and cooling water intakes: Debunking the myths
Thermal power plants are required to use fish protection technologies or make changes in plant operation to protect aquatic organisms. We intuitively understand that some organisms in the water drawn in to cool a power plant can be injured or killed when they hit a screen or enter the circulating water system. You have options for compliance with EPA rules; some are extremely expensive and burdensome, whereas others are brilliant in their simplicity. This article debunks several fish impingement myths and gives practical advice for successful compliance.
-
O&M
Speaking of Coal Power: Coal in a Carbon-Constrained World
Carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) have elbowed their way into the nation’s lexicon with the rise in concern over climate change. But few of the journalists who are hyping global warming have taken the trouble to learn the ins and outs of producing affordable electricity from coal. Citizens of the industrialized world now wring their […]
-
Coal
The Coal Patrol: Glaciers and New Coal Plants
The big buzz still echoing through world of coal-fired generation is the move by two big-bucks private equity investors to take TXU Corp. off the public market, including scuttling announced plans for eight new pulverized coal – fired plants. That leaves alive plans for three new units at TXU’s existing Sandow and Oak Grove sites. […]
-
Coal
PRB Tech Notes: New Plant/Old Plant: Are We Applying What We’ve Learned?
In the last issue of COAL POWER, I urged readers to give coal handling the priority it deserves. The coal yard warrants as much attention as boilers and combustion systems, turbine-generators and auxiliaries, and postcombustion emissions control — the other three "zones" within the plant perimeter — because it is an equally valuable business unit. […]
-
O&M
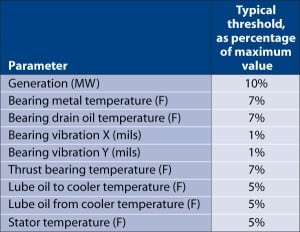
Coal Plant O&M: Continuous On-line Monitoring Cuts Downtime, Costs
As gencos seek to improve plant reliability and availability, many are turning to on-line condition monitoring for help. Huge advances in the capabilities of on-line diagnostics have occurred over the past five years. By using this technology, plant personnel can spot early warning signs of impending equipment failure and take action to correct the underlying […]
-
Coal
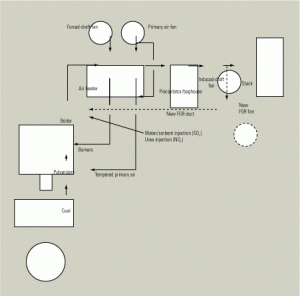
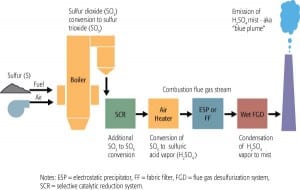
SO3 Control: AEP Pioneers and Refines Trona Injection Process for SO3 Mitigation
Using a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system to reduce the emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) from a coal-fired power plant is rapidly becoming the norm, rather than the exception. But for many plants, adding an SCR system has unintended consequences: greater oxidation of sulfur dioxide (SO2) to sulfur trioxide (SO3), and a rise in stack […]
-
O&M
SO3 Control: Dominion Demonstrates CleanStack Technology
Dominion Generation (DG) has installed selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems on many of the large coal-fired generating units it operates. The catalyst used has an SO2 to SO3 oxidation rate of about 1%, which roughly doubles the SO3 concentration at the outlet of the boiler economizers. The magnitude of the increase was proportional to the […]
-
O&M
SO3 Control: How Many Coal Plants Might Have Opacity Issues Due to SO3 Emissions?
Flyash and condensed sulfur trioxide (SO3) are the major components of flue gas that contribute to the opacity of a coal plant’s stack emissions (stack opacity). Estimates are that 75% to 85% of bituminous coal-fired plants with selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and/or wet flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems are likely to produce enough SO3 vapor […]
-
Coal
The Coal Pile
This month’s photo was submitted by David Carter, power generation supervisor at Springerville Generating Station. Readers of POWER may recall that Springerville Unit 3 — the first pulverized coal – fired unit built in the U.S. in more than a decade — was that magazine’s 2006 Plant of the Year. Located in northeastern Arizona, the […]
Search