-
Commentary
The mother of all energy crises
POWER readers today face severe problems in the electricity supply business. But a much bigger problem will soon burst on the scene: the peaking of world oil production. Experts have forecast peaking since shortly after the first U.S. well began production in 1859, and many subsequent forecasts of peaking have proven incorrect. Oil reserves dip […]
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (December 2007)
The web: Ideal for skills development / Upgrading a New Orleans pumping station / Turn plant failures into successes
-
Legal & Regulatory
Rigid COD deadlines do more harm than good
A utility executive responsible for procuring renewable power recently lamented that, at the time of contract execution, renewable “projects” are typically at a very preliminary stage of development, offering scant information about project specifics. Regulatory or other objectives often cause the utility to require that the power purchase agreement be executed before critical permits have […]
-
Wind
Burbo Bank Offshore Wind Farm, Liverpool Bay, UK
POWER congratulates DONG Energy and Siemens Power Generation on the October 18 inauguration of their 90-MW Burbo Bank Offshore Wind Farm. This project was the first commercial application of Siemens’ new 3.6-MW wind turbine and exemplifies how the right developer and supplier team can quickly add much-needed offshore wind power to a country’s generation mix.
-
Waste to Energy
Central Vermont Public Service, Cow Power Program
Central Vermont Public Service developed the nation’s first farm-to-consumer renewable energy choice by using cow manure to generate electricity. CVPS gave beleaguered farms new economic hope; developed a generation system that provides clean, renewable energy; and helped solve numerous manure management environmental challenges. CVPS and Cow Power’s four member dairies are recognized as a 2007 Top Plant for generating renewable energy one cow at a time.
-
Solar
Nevada Solar One, Boulder City, Nevada
Concentrating solar thermal projects fell out of favor more than 15 years ago, when the last SEGS plant was commissioned. But advances in reflective mirror, thermal receiver, and tracking system technologies have significantly improved the systems’ energy conversion efficiency at a much lower capital cost. POWER recognizes Nevada Solar One as a 2007 Top Plant for pushing the limits of solar thermal technology and for being the first of a new generation of concentrating solar projects now being developed around the world.
-
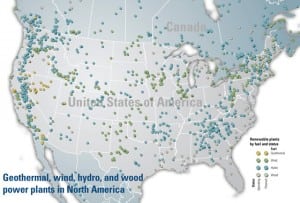
Geothermal
Raft River Geothermal Project, Malta, Idaho
Geothermal power is a unique renewable energy because it has the best potential capacity factor and is perhaps the only option for baseload power generation. U.S. Geothermal has constructed the first geothermal plant in Idaho in a generation by restoring an abandoned DOE demonstration project site that may possess a development potential of over 100 MW using proven power generation technology. The success of Raft River may well determine the future of geothermal energy production in Idaho.
-
Wind
Steel Winds Project, Lackawanna, New York
This year, for the first time, the U.S. wind power industry is poised to push past the 3,000 MW installed per year milestone. At 20 MW, Steel Winds may seem like a footnote, but its importance is measured in more meaningful terms than just size. Steel Winds is the first commercial deployment of the Clipper Windpower 2.5-MW Liberty turbine, the first installation on a former Superfund site, and is said to be the largest wind farm in the U.S. developed in an urban setting. In addition, the project anchors Lackawanna’s redevelopment of a former industrial site along Lake Erie for public use.
-
Wind
Developing wind projects in California—or anywhere
Acquiring capacity from renewable resources is now mandatory for many electric utilities, and nowhere is green generation being pursued with more vigor than in California. Regulators there want power from renewables to account for at least 20% of utilities’ annual sales by 2010, and Governor Schwarzenegger is proposing increasing the minimum to 33% by 2020. Wind power appears to have the lowest technical risks of the renewables options, but don’t ignore the rising development risks. Here’s a primer on developing wind projects in the Golden State—and elsewhere.
-
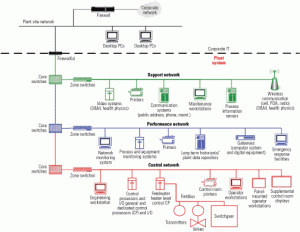
O&M
Plantwide data networks leverage digital technology to the max
To make the most of their digital devices and enable the sharing of data by different departments, new and old plants alike need a reliable digital data infrastructure.
-
O&M
Upgrade your BWR recirc pumps with adjustable-speed drives
The U.S. is home to more than 30 boiling water reactors of BWR-3 through -6 vintage. At one time or another, all have experienced obsolescence, reliability, or control problems with their reactor recirculation flow control systems and components. Temporary down-powers are often required for corrective maintenance. Exelon Nuclear plans to begin upgrading the recirculation pump motor drives at its BWRs in the spring of 2009. The upgrade project’s technical design and business case were developed in great detail before the project was approved. This article presents the results of all key internal analyses.
-
Nuclear
Defined scope, experienced team essential to nuclear I&C upgrade projects
Over the past few years, U.S. nuclear power plants have begun replacing their obsolete analog control systems with digital control systems. Many of these projects have been completed successfully, yielding a tidy return on investment in the form of increased generation. However, some have encountered difficulties, which resulted in cost overruns and schedule delays. This minority of projects may have eroded the industry’s confidence in digital upgrade projects, but a well-run project is still one of your best options for squeezing the last drop of performance out of your plant.
-
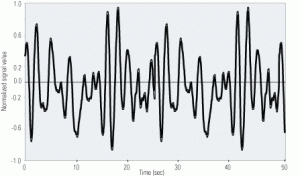
Nuclear
Accurately measure the dynamic response of pressure instruments
How do you know if a pressure transmitter is giving poor results? Unless the transmitter actually fails, most operators won’t notice a very slow loss in accuracy or response time. Fortunately, the noise analysis technique can identify such changes before they cause a problem. The technique has been used to effectively measure the dynamic response of nuclear power plant pressure sensors and their associated sensing lines. It also can be applied to any plant that relies on accurate instrumentation for control and monitoring plant performance.
-
Business
Milestones on the road to commercial operation
The electric power industry is capital-intensive, and it takes several years to build and commission a baseload plant for commercial operation. Owners seek contractors who are willing—given proper incentives—to build a plant for a lump-sum price with a guaranteed schedule and performance. Matching an owner’s wants with contractors’ needs is an exercise in allocating risk. Avoid the contract traps that can stall a project and cost millions to resolve.
-
Business
This month in POWER . . .
POWER began its life in October 1882 as a tabloid-size publication originally entitled Steam. About the same time, two young Boston advertising salesmen decided to launch a new magazine about textile mill steam plants, called POWER. They bought Steam prior to publishing POWER’s first issue, so early issues of this magazine carried the flag “POWER, […]
-
Commentary
Centralized markets are failing consumers
During my 30-year career at the American Public Power Association (APPA), I’ve had a front-row seat for most of the major events in our industry’s recent history. So it disturbs me when my view of our history is 180 degrees out of phase with how others perceive it. Such was the case with the preamble […]
-
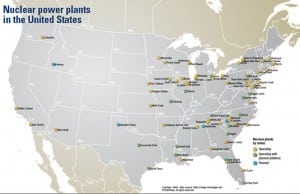
Nuclear
Do the math
The eyes of Texas—and the rest of the world—are upon NRG Energy after its September application for licenses for two new reactors at South Texas Project (see Global Monitor). The filing was the first of its kind in nearly three decades and the first of up to 30 like it expected over the next few […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (November 2007)
NRG applies for first COL / TVA green-lights Watts Bar 2 / Southern Co. and Florida muni launch IGCC project / UK approves wave energy "hub" / New Jersey-New York HV system launched / Membrane strips CO2 from methane faster / POWER digest
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (November 2007)
The NERC auditors are coming / Winning encore for on-line pH monitoring / Using baloons as temporary barriers / How data logging can cut power bills
-
Legal & Regulatory
Can FERC deliver transmission?
This May, the Arizona Corporation Commission (ACC) rejected a proposal by Southern California Edison (SCE) to build Devers-Palo Verde No. 2 (DPV2)—a 230-mile-long, high-voltage transmission line connecting California and Arizona. The line, approved by the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) four months earlier, would enable SCE to import additional low-cost electricity from Arizona. The ACC’s rejection of DPV2 highlights a significant challenge for state and regional resource planners—weighing state interests against the regional benefits of interstate electricity commerce.
-
Nuclear
Browns Ferry Nuclear Power Plant, Athens, Alabama
TVA’s 1,155-MW Browns Ferry Unit 1 returned to service on May 22 after sitting idle since 1985, when all three units were shut down to address management and operational concerns. Units 2 and 3 returned to service in 1991 and 1995, respectively, after extensive upgrades to controls, electrical systems, pumps, motors, and more. The return of Unit 1 began in 2002 with a five-year $1.8 billion restart plan to make all three units essentially identical, and that goal was accomplished in style. Welcome back, Unit 1.
-
Nuclear
Comanche Peak Steam Electric Station, Glen Rose, Texas
A Luminant-Bechtel team completed replacement of four steam generators and the reactor vessel head—plus almost 200 other work packages—in a short, 55-day outage at Comanche Peak Unit 1. Matching or exceeding this schedule will become the goal for those who follow.
-
Nuclear
Fermi 2 Power Plant, Newport, Michigan
Detroit Edison teamed with Washington Group International to complete a first-of-its-kind nuclear retrofit project: replacing two moisture separator reheaters during a single 35-day outage with a perfect safety record. POWER recognizes this significant accomplishment by naming Fermi 2 Power Plant a 2007 Top Plant.
-
Nuclear
Fort Calhoun Nuclear Generating Station, Omaha, Nebraska
Just under a year ago, Omaha Public Power District completed perhaps the most complex nuclear power plant renovation in the history of the industry in a scant 85 days—five fewer days than the original plan called for. POWER recognizes Fort Calhoun Nuclear Generating Station as a Top Plant for packing more work into one outage than was thought possible, and then executing the plan ahead of schedule and below budget.
-
O&M
The Coal Patrol: Demand Growth — and Reliability — Are Still Supply-Limited
While noting marginal improvements since last year, America’s power reliability watchdog recently warned that the nation’s growing thirst for electricity will still far exceed planned increases in generation capacity over the next 10 years, and that reserve margins could dip below optimal levels within two or three years in California, the Rocky Mountain states, New […]
-
Coal
Advanced Combustion: Cofiring Coal and Biomass or Non-Recyclable Waste
Burning biomass or nonrecyclable commercial, municipal, or industrial waste along with coal represents one of the nearest-term and lowest-cost options for reducing carbon dioxide (CO 2) emissions from existing utility power plants. At more than 150 plants worldwide, doing so has produced lower CO 2 emissions than burning coal alone. Indeed, with the number of […]
-
Coal
The Coal Pile: Dreaming of a Green Christmas
On November 20, New York City Mayor Michael R. Bloomberg and top executives of the real estate company Tishman Speyer announced several energy conservation measures to be implemented at Rockefeller Center this holiday season. One is the outfitting of its famous Norway Spruce Christmas tree with 30,000 light-emitting diodes (LEDs) strung on five miles of […]
-
Coal
Coal Plant O&M: Retrofit Flyash-Handling System Pays Dividends
Like many older coal-fired plants, Westar Energy’s Jeffrey Energy Center (JEC) was built with traditional, pneumatic flyash-handling and removal systems. Such systems collect flyash in hoppers attached to the bottom of a unit’s electrostatic precipitator (ESP) and/or baghouse. Periodically, the hoppers are emptied into tanks and the flyash is conveyed away for disposal or beneficiation. […]
Search