-
Coal
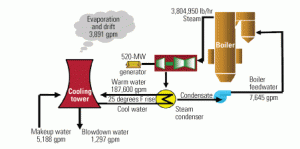
New coal plant technologies will demand more water
Population shifts, growing electricity demand, and greater competition for water resources have heightened interest in the link between energy and water. The U.S. Energy Information Administration projects a 22% increase in U.S. installed generating capacity by 2030. Of the 259 GW of new capacity expected to have come on-line by then, more than 192 GW will be thermoelectric and thus require some water for cooling. Our challenge will become balancing people’s needs for power and for water.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
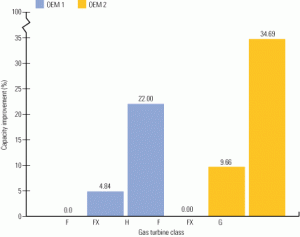
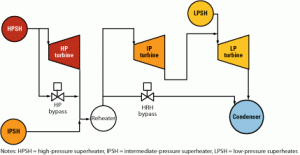
Turbine technology maturity: A shifting paradigm
Selecting the right turbine(s) for a specific power project is a complex process that poses two challenges. One is understanding which field experience cited by suppliers represents proven technology; the other is evaluating whether a turbine upgrade represents an evolutionary change or a revolutionary transformation that warrants further study before deploying it in the field. Here‘s how a leading EPC contractor makes technology-neutral equipment selection decisions on behalf of its customers.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
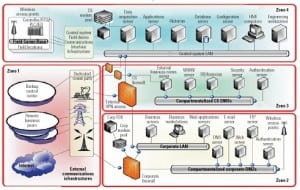
Time to get serious about security
Managing ongoing threats to power plants’ digital, telecommunications, monitoring, control, and automation systems is no longer just a good idea. It’s an essential element of superior plant operations and now a regulatory requirement as well, thanks to new critical infrastructure protection standards recently approved by FERC.
-
Gas
Castejon 2: Ready to reign in Spain
The new, 424-MW Castejon 2 combined-cycle plant designed and built by Alstom was recently given its provisional acceptance certificate. Alstom used its “Plant Integrator” approach to fast-track delivery of a plant just like Castejon 1, which averaged 98% availability during its first three years of operation. That kind of performance is crucial to generators operating in the Spanish merchant power market—or any market.
-
O&M
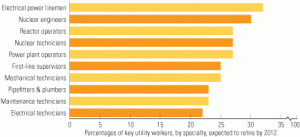
The aging workforce: Panic is not a strategy
Leaders in the utilities sector talk a lot these days about talent. On one hand, they express concern about facing a shortage of knowledgeable staff as 76 million baby boomers exit the workforce. On the other, they worry about where they’ll find enough qualified people to remain competitive in light of the fierce battle for engineering talent that globalization has created. The antidote to these worries lies in reconfiguring HR practices.
-
Business
ELECTRIC POWER 2008 offers access to the latest products and services
If you enjoy POWER magazine’s New Products department, you’re going to love the ELECTRIC POWER 2008 Exhibition. You’ll be able to see and feel the latest tools of the trade and talk to the folks who provide them to the generation industry. Here’s a sneak peak at what awaits you on the exhibit floor May 6 to 8 at the Baltimore Convention Center.
-
Conservation and the law of the jungle
—Dr. Robert Peltier, PE Editor-in-Chief Ever wonder why many utilities receive so little respect from the public? In America, open competition requires every business to earn customers’ trust before making a sale. Unfortunately, many utilities exploit their monopoly position to avoid the hazards of competition, including losses. It’s no wonder that public utilities, as a […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (March 2008)
DOE scraps FutureGen / U.S. nuclear plants have record year / Westinghouse wins TVA contract / UniStar Nuclear to file for COL / AEP ranks second in U.S. construction / China moving to the driver’s seat / New solar cycle poses risks / Dutch favor power from natural gas / POWER digest / Corrections
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (March 2008)
New CIP standards leave questions unanswered/Solving common analyzer problems/Qualifying rebuild shops
-
Legal & Regulatory
Congress failed to deliver a green Christmas
Renewable power proponents exuded great confidence as the U.S. Congress approached its near-annual end-of-year task of extending the production tax credit (PTC) for wind, solar, biomass, and geothermal power beyond its current December 2008 expiration. The debate promised to bypass the threshold issue of simply extending the PTC. It was expected to focus on […]
-
Gas
How to make a power plant a welcome neighbor
Developing power projects has become less a technical challenge and more an exercise in developing good relationships among all the stakeholders. If a community understands the need for a new plant and is involved in its development process, the odds of a successful project increase.
-
O&M
Maintaining water sample panels improves plant availability
Even comedian Rodney Dangerfield got more respect than many plant water sample panels do. But power plants ignore sample panels at their peril. Those sample panels, and readings of the on-line analyzers they support, identify when multi-million-dollar systems have a problem that demands immediate attention.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Wireless technologies connect two LCRA plants
Lower Colorado River Authority recently put two separate plants at its Lost Pines Power Park under one functional management system. The project has already deployed a layered wireless infrastructure that allows the two plants to communicate at a fraction of the cost of a wired solution while providing a platform for optimizing work processes and reducing operating costs. What’s not to like?
-
O&M
Desuperheating valves take the heat
Hot reheat steam bypass actuators are some of the most critical, yet least understood components in a typical combined-cycle plant. If you’re using pneumatic actuators to stroke your main steam or hot reheat bypass valves in a cascading bypass system, you’re behind the times. Here’s a way to get better control of the bypass process, shorten unit start-up and train blending times, and decrease your plant’s heat rate—all at the same time.
-
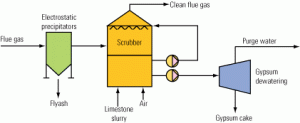
Water
Benefits of evaporating FGD purge water
In the U.S. and the European Union, scrubbers are installed on all new coal-fired power plants because their technology is considered the best available for removing SO2. A zero-liquid-discharge system is the best technology for treating wet scrubber wastewater. With the future promising stricter limits on power plants’ water use, ZLD systems that concentrate scrubber purge streams are sure to become as common as ZLD cooling tower blowdown systems.
-
O&M
Extend EOH tracking to the entire plant
Predicting combined-cycle system longevity and determining optimal maintenance intervals at the same time is difficult: It requires balancing repair costs against the risk of trying to squeeze that last bit of life out of some component before it fails. One solution to the problem is to extend coverage of an equivalent operating hours (EOH) preventive management program for turbines to the entire plant.
-
Business
ELECTRIC POWER celebrates 10th anniversary in Baltimore
At this juncture our industry is faced with greater uncertainty and opportunity than ever before. That’s why you won’t want to miss all the information, ideas, and networking available at the power generation industry’s premier event in May.
-
Commentary
Markets, not government, must set energy prices
By J. Bennett Johnston It is fashionable these days for policymakers, particularly those running for office, to somberly suggest that America needs an energy policy—thus implying that America has no energy policy. As one of the prime architects of an energy policy that has served America well, I could not disagree more. The fact that […]
-
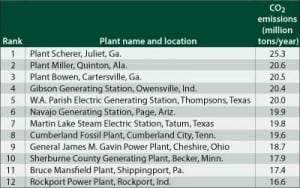
Coal
The Coal Patrol: Ranking the CO2 Emissions of the World’s Power Plants
The Environmental Integrity Project, a Washington-based advocacy group, announced in March that CO 2 emissions from U.S. power plants increased 2.9% last year over 2006 levels. The group used 2006 and 2007 CO 2 emissions data from the U.S. EPA and the DOE’s Energy Information Administration. It’s hard to normalize CO 2 numbers — and […]
-
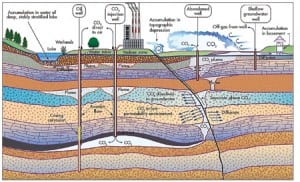
Coal
The Future of Coal Power: Modeling Geological Sequestration of CO2
Everyone in the power generation business knows that coal will continue to be a necessary fuel source for the foreseeable future. Many of those same people are beginning to understand that, politics aside, coal plant operations in the foreseeable future won’t look like the operations of yesterday or today. But what exactly will the future […]
-
Coal
The Future of Coal Power: Development and Siting Obstacles for New Coal Plants
In recent years, Sargent & Lundy has evaluated many potential sites for new coal-fueled generation. Some of the sites studied were lands adjacent to existing power plants (brownfield sites); others were undeveloped greenfield sites. The numerous technical, environmental, economic, and regulatory issues that bear on power plant siting generally apply to both brownfield and greenfield […]
-
Coal
Emissions: Unintended Consequences of Problem-Solving
Most folks probably don’t think that power plants burning coal and ethanol — the latter touted as a having a smaller carbon footprint — have much in common. But at least one ethanol plant — Blue Flint Ethanol in Underwood, N.D. — is co-located with a coal-fired power plant in order to use its excess […]
-
Coal
Plant Design: Trends in Coal Pile Design
An optimal coal pile design takes into account the site-specific (and often conflicting) needs of a new power plant early in its design — rather than using whatever land is available after the plant layout has been finalized. Determining site requirements necessitates a detailed analysis of all potential coal-fueling options. A coal pile designer should […]
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: The True Costs of Going Green
Three of the best-kept secrets in the U.S. today have nothing to do with national security in the traditional sense. They all involve costs: the cost of fulfilling campaign promises, a valid estimate of the cost of carbon control legislation (S. 2191) expected to reach the Senate floor in a few months, and the real […]
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (February 2008)
Survey captures industry’s carbon concerns; Sequestering coal plant emissions; Comparing mercury measurement methods
-
Legal & Regulatory
California constrains competition again
Given a chance to make a positive change in California’s wholesale generation market, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) in December opted instead to maintain the state’s existing “hybrid” market model. That decision will further restrict meaningful opportunities for independent power producers (IPPs) and increase the likelihood that future generation will consist of utility ratebase […]
-
O&M
TVA’s Shawnee Fossil Plant Unit 6 sets new record for continuous operation
Shawnee’s new 1,093-day long-run record is a testament to the plant’s highly qualified and trained staff, excellent operations and maintenance processes, and the quality leadership required to keep all the moving parts pointed in the right direction. If running a power plant is a team sport, then the staff of Shawnee are in a league of their own.
-
O&M
Alliant Energy sweeps EUCG Best Performer awards
The Fossil Productivity Committee of the EUCG conducts an annual analysis of its member plants’ operating results and selects the Best Performer in the categories of small and large coal plants. For 2007, Alliant Energy’s Lansing and Edgewater Generating Stations took the top spots—the first time in recent history that a single utility claimed both awards.
-
Coal
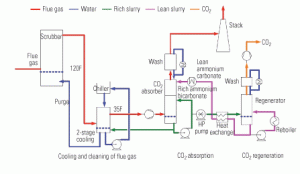
Alstom’s chilled ammonia CO2-capture process advances toward commercialization
Carbon dioxide emissions aren’t yet regulated by the EPA, but it’s likely they will be soon. There are many technically feasible, but as-yet-undemonstrated ways to reduce the considerable carbon footprint of any coal-fired plant, whether it uses conventional or unconventional technology. One promising approach to removing CO2 from a plant’s flue gas uses chilled ammonium bicarbonate to drive the separation process.
-
Coal
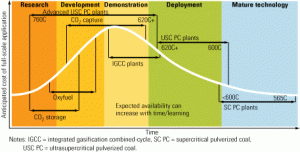
Accelerating the deployment of cleaner coal plants
The dearth of commercial operating experience for advanced coal-fired facilities is forcing their early adopters and builders to use long development cycles and pay high costs for unique engineering design studies. A broad-based industry collaborative effort fostered by EPRI to address this issue is beginning to show results.
Search