Plant Design
-
Coal
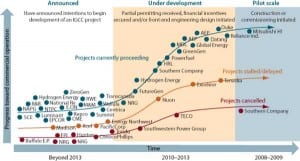
IGCC: IGCC’s Future Hinges on a Workable Carbon Framework
Integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) technology, a process of gasifying coal that allows the capture of carbon dioxide emissions, has tremendous potential for meeting future baseload generation demand. Though it is one of the leading alternatives for producing clean power from coal, IGCC faces a precarious future due to rising capital costs and regulatory uncertainty. We’re […]
-
Coal
Advanced Combustion: Cofiring Coal and Biomass or Non-Recyclable Waste
Burning biomass or nonrecyclable commercial, municipal, or industrial waste along with coal represents one of the nearest-term and lowest-cost options for reducing carbon dioxide (CO 2) emissions from existing utility power plants. At more than 150 plants worldwide, doing so has produced lower CO 2 emissions than burning coal alone. Indeed, with the number of […]
-
Coal
Coal Plant O&M: Retrofit Flyash-Handling System Pays Dividends
Like many older coal-fired plants, Westar Energy’s Jeffrey Energy Center (JEC) was built with traditional, pneumatic flyash-handling and removal systems. Such systems collect flyash in hoppers attached to the bottom of a unit’s electrostatic precipitator (ESP) and/or baghouse. Periodically, the hoppers are emptied into tanks and the flyash is conveyed away for disposal or beneficiation. […]
-
Coal
Safety: Detecting Fires on PRB Coal Conveyors
All conveyor systems are at risk of fire caused by the ignition of transported materials or equipment failure. But the propensity of Powder River Basin (PRB) coal to self-ignite introduces an exceptional hazard requiring special fire prevention and automatic detection and suppression efforts. To that end, this article discusses the technologies of linear heat detection […]
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: BACT to the Future
This August, Peabody Energy’s 1,600-MW Prairie State Energy Campus project in Illinois won a major federal appeals court decision, removing the last obstacle to groundbreaking. The six-year regulatory review process ended with an unsuccessful Sierra Club challenge to the $2.9 billion project’s air permit. The decision is sure to reverberate across the nation, and I […]
-
Coal
Coal Plant O&M: How Switching to PRB Lowered O&M Costs
Lansing Board of Water & Light (LBW&L), which has generated electricity since 1892 and steam since 1919 in mid-Michigan, primarily serves the city of Lansing’s business district and all state government buildings in the downtown area. But one of the municipal utility’s plants, Moores Park, has an additional and very important steam customer: General Motors’ […]
-
O&M
Plant Economics: The Impact of Shortages on FGD Prices
Since ratification of the Clean Air Act (CAA) in 1970, U.S. utilities have made steady efforts to install pollution control equipment to curb power plant stack emissions. The CAA Amendments of 1990 raised concerns at the time about the industry’s ability to install a large number of flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems, or scrubbers, in […]
-
Coal
The Coal Pile: Steam Blast Rocks Big Apple
This July, an underground steam pipe near Manhattan’s Grand Central Terminal ruptured and spewed a scalding brown geyser of steam and debris higher than the nearby 77-story Chrysler Building. The blast, which injured 30 people, created a 40-foot crater at street level that swallowed a tow truck. A similar explosion in 1989 killed three people. […]
-
O&M
Coal Plant O&M: Smart Sootblower Tailors Cleaning to Need for It / Blending’s Impact on Coal Quality
The 1990 amendments to the Clean Air Act require coal-fired power plants to reduce their emissions of the pollutant SO2. To do so, many have switched to, or are considering switching to, Powder River Basin (PRB) coal. Unfortunately, PRB coal has a tendency to leave excessive and tenacious deposits on boiler heat-exchange surfaces. Complicating the problem, the distribution of the deposits is far from uniform.
-
Coal
The Coal Patrol: Coal to Synfuels: Deal or No Deal?
Synfuels’ political bubble has burst in Washington, but the market may step in where Congress fears to tread. When coal industry interests, in the form of the CTL Coalition, got a bill with strong federal support for coal-to-liquids technology before the Senate this spring, it appeared that the political skids were greased for some kind […]
-
O&M
Lignite Drying: New Coal-Drying Technology Promises Higher Efficiency Plus Lower Costs and Emissions
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and Great River Energy are testing a new coal-drying technology that could dramatically reduce the emissions of lignite-burning power plants. The project was selected for funding during Round I of the DOE’s Clean Coal Power Initiative (CCPI), a series of competitions to demonstrate a range of promising clean-coal technologies. […]
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: IGCC Sticker Shock
Former Illinois Senator Everett Dirksen once observed, "A billion here and a billion there, and pretty soon you’re talking real money." The same can be said about skyrocketing estimated costs of integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) plants as their designs are fleshed out. The higher price tags shouldn’t be a surprise — the more you learn […]
-
O&M
PRB Tech Notes: Lawrence Energy Center Showcases Winning Plant
Lawrence Energy Center (LEC) proudly hosted about 60 representatives of the Powder River Basin Coal Users’ Group (PRBCUG) at its July 24th open house, luncheon, and plant tour. LEC was named the PRBCUG’s 2007 Plant of the Year at this year’s ELECTRIC POWER Conference and Exhibition in Chicago, May 1 – 3. Traditionally, the winning […]
-
Coal
PRB Tech Notes: Pay Me Now or Pay Me Later
Money is always spent with the best intentions. We look for the best deal, often identifying it by the lowest price. Sometimes, our choice works out and we save money and get a great product. When it doesn’t work out, however, we find ourselves spending more and more money to repair or replace our "great […]
-
O&M
Coal Plant O&M: River Locks and Barges Are an Aging Workforce, Too
During 2005, about 150 million tons of coal were transported to power plants by hopper barges plying U.S. inland waterways. With coal-fired plants expected to continue producing 50% of America’s electricity, coal barge traffic is not likely to fall off. In fact, it may increase, for two reasons. One is cost. Shipping coal by barge […]
-
O&M
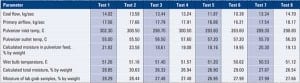
Pollution Control: LCRA Fayette Lowers NOx Below 0.10 lb/mmBtu
The Fayette Power Project (FPP, aka the Sam K. Seymour Power Station) is a three-unit, coal-fired generating plant sited near La Grange, Texas (Figure 1). Units 1 and 2, each with a nominal rating of 600 MW, are co-owned by the Lower Colorado River Authority (LCRA) and Austin Energy (AE). LCRA is a conservation and […]
-
O&M
Pollution Control: Low-NOx Combustion Retrofit Options
Reducing NOx emissions from large utility coal-fired boilers has been a primary focus of the U.S. power generation industry since passage of the 1970 Clean Air Act and subsequent legislation. By the early 1990s, nearly all such boilers had installed some form of low-NOx burner (LNB) technology and/or overfire air (OFA) — the least expensive […]
-
Coal
The Coal Patrol: Coal-to-Liquids Resurfaces after 20 Years
It’s déjà synfuels all over again. With crude oil prices seemingly interminably pegged at over $60 a barrel, the old, beguiling notion of turning coal into liquid fuel — a task accomplished by the Nazis in the 1940s and the South Africans in the 1970s and 1980s — is once again front-page political news in […]
-
O&M
Speaking of Coal Power: Coal in a Carbon-Constrained World
Carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) have elbowed their way into the nation’s lexicon with the rise in concern over climate change. But few of the journalists who are hyping global warming have taken the trouble to learn the ins and outs of producing affordable electricity from coal. Citizens of the industrialized world now wring their […]
-
Coal
The Coal Patrol: Glaciers and New Coal Plants
The big buzz still echoing through world of coal-fired generation is the move by two big-bucks private equity investors to take TXU Corp. off the public market, including scuttling announced plans for eight new pulverized coal – fired plants. That leaves alive plans for three new units at TXU’s existing Sandow and Oak Grove sites. […]
-
Coal
PRB Tech Notes: New Plant/Old Plant: Are We Applying What We’ve Learned?
In the last issue of COAL POWER, I urged readers to give coal handling the priority it deserves. The coal yard warrants as much attention as boilers and combustion systems, turbine-generators and auxiliaries, and postcombustion emissions control — the other three "zones" within the plant perimeter — because it is an equally valuable business unit. […]
-
Coal
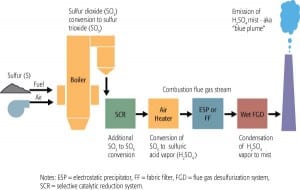
SO3 Control: AEP Pioneers and Refines Trona Injection Process for SO3 Mitigation
Using a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system to reduce the emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) from a coal-fired power plant is rapidly becoming the norm, rather than the exception. But for many plants, adding an SCR system has unintended consequences: greater oxidation of sulfur dioxide (SO2) to sulfur trioxide (SO3), and a rise in stack […]
-
O&M
SO3 Control: Dominion Demonstrates CleanStack Technology
Dominion Generation (DG) has installed selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems on many of the large coal-fired generating units it operates. The catalyst used has an SO2 to SO3 oxidation rate of about 1%, which roughly doubles the SO3 concentration at the outlet of the boiler economizers. The magnitude of the increase was proportional to the […]
-
O&M
SO3 Control: How Many Coal Plants Might Have Opacity Issues Due to SO3 Emissions?
Flyash and condensed sulfur trioxide (SO3) are the major components of flue gas that contribute to the opacity of a coal plant’s stack emissions (stack opacity). Estimates are that 75% to 85% of bituminous coal-fired plants with selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and/or wet flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems are likely to produce enough SO3 vapor […]
-
Coal
PRB Tech Notes: Give Coal Handling the Priority It Deserves
Over the past 17 years — dating back to the 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments and including the introduction of retail competition — coal-fired power plants have become much cleaner and more efficient. Utilities have spent many billions of dollars to install pollution controls for regulatory reasons, and only slightly less to upgrade turbine-generators and […]
-
Coal
Coal Plant O&M: Coal Drying Reduces Pulverizer Start-up Costs
If coal leaving a pulverizer isn’t dry, it may plug up the coal pipes leading to the boiler. The coal-drying process in a pulverizer is similar to that used by flash dryers. Certain coals should be preheated to make them more combustible. Generally, preheating is done on higher rank coals — those with a low […]
-
O&M
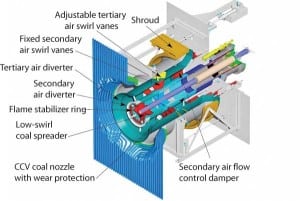
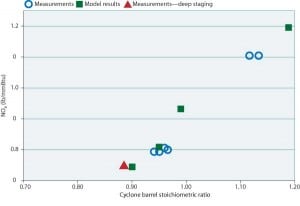
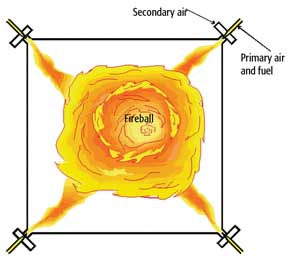
Emissions Control: Layered NOx Reduction on a 500-MW Cyclone-Fired Boiler
Historically, cyclone-fired boilers have been characterized as big emitters of NOx due to the very high temperatures in their primary combustion zone. Uncontrolled levels from 0.8 to 1.9 lb/mmBtu have been typical. The design of cyclone-fired units makes them impossible to retrofit with standard low-NOx burners. Prior to 1997, the conventional wisdom was that cyclone […]
-
O&M
Emissions Control: Cost-Effective Layered Technology for Ultra-Low NOx Control
Layering NOx control technologies can reduce a coal-fired unit’s NOx emissions to levels achievable by selective catalytic reduction alone. Advanced Combustion Technology Inc. (ACT) (www.advancedcombustion.net) has demonstrated that using several in combination can cut emissions from boilers firing eastern bituminous coal or No. 6 oil to less than 0.15 lb/mmBtu. The following two case studies […]
-
Coal
Emissions Control: User-Designed Large-Particle Ash Screens Minimize SCR Fouling
Large-particle ash (LPA), also called popcorn ash (Figure 1), is a serious concern for many coal-fired utility boiler operators who have retrofitted their unit(s) with a high-dust selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system. LPA formed in the boiler can easily carry over into the SCR reactor (Figure 2), where it often causes catalyst erosion damage and […]
-
Coal
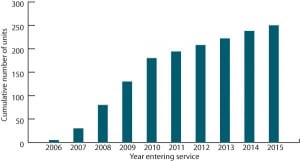
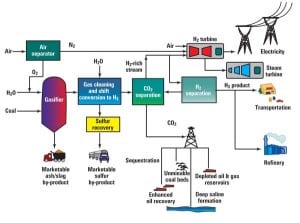
Cover Story: FutureGen: Zero-Emission Power Plant of the Future
In early 2003 the United States announced its plans to build a zero-emission prototype of the fossil fuel power plant of the future called FutureGen. It is one of the boldest steps toward a pollution-free energy future ever taken by the U.S. It has the potential to be one of the most important advances in […]