O&M
-
O&M
Optimizing Outages with Outage Readiness Analysis
In order to ramp up the success of planned outages at its power plants and lower the risk of unexpected and costly problems, OG&E management has begun using the outage readiness index process. This method identifies and defines the scope of the work needed prior to the commencement of an outage and quantifies the amount of preparedness needed to implement the outage in the most cost-effective manner.
-
O&M
Enhancing Plant Performance Through Formal Outage Planning and Execution
By thoroughly planning their outage strategies well in advance, Southern Company personnel are better able to achieve a number of important objectives, including improving unit economic performance, reducing unplanned maintenance outage hours, completing outages on time and within budget, and ensuring that outage workmanship is of the highest quality.
-
O&M
The End of the Line for Pipe Cleaning with Natural Gas?
Piping at gas-fired plants has long been cleaned using compressed natural gas because of its easy availability. The big problem? It’s also explosive. The fatal 2010 blast at the Kleen Energy plant in Connecticut began a shift toward safer alternatives such as nitrogen and compressed air that is gathering increasing momentum.
-
O&M
Virtual Co-Driver to Improve Truck Safety
POWER recently talked with Erika Jakobsson, a project manager at Volvo Technology in Gothenburg, Sweden, who is responsible for developing intelligent trucks in response to European Union (EU) directives.
-
O&M
Condenser Backpressure High? Check Vacuum System Sizing
In a power plant, the primary use of vacuum systems is to remove air and other noncondensable gases from the shell side of the condenser in order to maintain design heat transfer and thus design vacuum. If holding condenser vacuum is a persistent problem, one often-overlooked cause is an inadequately sized vacuum system.
-
O&M
Avoiding Flow-Induced Sympathetic Vibration in Control Valves
Compressible fluid flow through control valves will inevitably cause some form of flow-induced vibration in the fluid system. Identifying the type and cause of the vibration requires detective work. Determining the design changes required in the valve and fluid system to prevent the vibration from occurring requires advanced analytical techniques.
-
O&M
Audit Your Coal Dust Prevention Program
The hazards of coal dust accumulation in power plants are familiar to coal-fired plant operators. Operators of plants that burn Powder River Basin coal are particularly aware of necessary housekeeping and fuel-handling practices, but any plant that allows excessive amounts of coal dust to accumulate is playing Russian Roulette with its staff and equipment.
-
O&M
Constructing and Managing Coal Ash Landfills
Creating a landfill to hold dry boiler ash is a challenging proposition these days. There’s more to the project than you might imagine, as you’ll learn from this article about the development of a typical new ash landfill.
-
O&M
Collecting Dust
Rules requiring removal of combustible dust from the workplace will undoubtedly improve worker safety and health. A survey of equipment suppliers finds a variety of dust collection systems are available to meet just about every dust collection need in the power house.
-
O&M
EPRI Bridges Industry R&D Gaps
The technologies used to generate and distribute electricity will be radically transformed during the coming decade. Amid that change, the power industry must continue to meet customer reliability, safety, and cost-of-service expectations. Achieving the right balance among these often-conflicting goals is the primary focus of every utility. The Electric Power Research Institute is helping utilities achieve that balance with R&D programs for many new and emerging technologies.
-
O&M
Real-time Proactive Safety in Construction
For each of the past 10 years, nearly 1,200 U.S. construction workers have died as the result of injuries received on the job. Of these fatalities, 25% involved heavy equipment—most categorized as struck-by incidents. Remote sensing and visualization technology promises to improve worker situational awareness on congested and busy work sites.
-
O&M
Level Switches Keep Electrostatic Precipitators Online
Measuring the level of dust and fly ash collected in electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) is a very difficult technical problem. At one utility, level switches were so unreliable that operators could not trust their readings because failures were so frequent. When a switch did fail, the precipitator would often clog up, costing the utility up to $100,000 in downtime and repair costs.
-
O&M
Marmaduke Award Trophy Presented
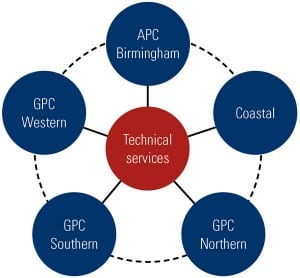
The 2011 Marmaduke Award winner was CTG Universidad, a two-unit combustion turbine plant built in the early 1970s in Monterrey, Mexico. The award was made to the plant in recognition of its upgrade of one 14-MW unit to operate as a synchronous condenser, thus relaxing power restrictions caused by a lack of sufficient reactive power production in the north of the city. More reactive power production by this urban plant also allows delivery of more power produced by efficient combined cycle plants located outside the city, because it reduces the amount of reactive power that must be moved over transmission lines.
-
O&M
Wet Booster Fans Optimize Power Station Performance with FGD and Wet Stack
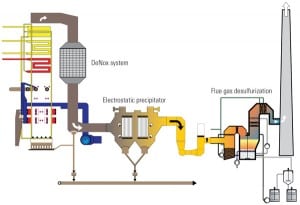
A Romanian lignite-fired power station wanted to minimize the operating cost of the flue gas desulfurization (FGD) system by placing the booster fans in the "wet position," between the wet FGD scrubber and the wet stack, where they would consume significantly less power. A number of combined environmental effects must be considered in this design.
-
O&M
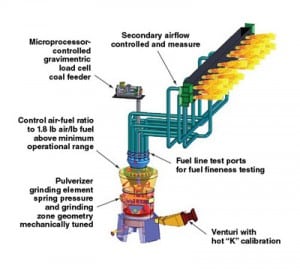
Pulverizers 101: Part III
Pulverizers prepare raw fuel for burning by grinding it to a desired fineness and mixing it with the just the right amount of air before sending the mixture to boiler burners for combustion. Part I of this three-part report examined the essentials of pulverizer design and performance; Part II discussed the importance of fuel fineness. This final article discusses the importance of air and fuel measurement.
-
O&M
Improved Performance from Priority-Based Intelligent Sootblower Systems
When sootblower operation frequency is too high, a plant risks losing power generation from tube leaks; but when sootblower frequency is too low, there is a risk of boiler pluggage. Intelligent sootblowing finds the right balance between tube erosion and plant economic operation.
-
O&M
Tools at Height
A structure or mechanical system that requires fasteners also demands tools to maintain it properly. In power sectors such as wind, fossil fuel, and nuclear, some work areas may be several hundred feet in the air. While working at those extreme heights, or even just 10 feet off the ground, it’s simply unacceptable to drop anything. That’s why the concept of “tools at height” is being embraced as a way to improve safety and efficiency on the worksite.
-
O&M
Microns Matter: Proper Design of Fogging Nozzles
Inlet fogging systems for combustion turbines achieve their effect at the molecular level: The cooling effect occurs by converting thousands of gallons of water into single evaporated molecules suspended in the air. The right fog pattern comes down to a matter of selecting the best nozzle design and proper placement in the inlet air stream.
-
O&M
Using Temperature- Measuring Indicators
Correct welding procedures are extremely important elements of the work done by the PSEG Central Maintenance Shop (serving Public Service Electric and Gas Co., PSEG, a New Jersey utility). We have, for example, a Critical Weld Inspection Program for high-temperature pressure piping whose goal is to identify cracks in high-temperature piping welds.
-
O&M
Steam Turbine Cleaning Using Chemical Foams
In the May issue, we discussed the importance of either preventing copper plating of the high-pressure (HP) steam turbine rotor or finding a good foam or mechanical removal means of restoring lost efficiency. In that article we noted that “copper deposits typically form on the stationary nozzle block or first-stage stationary blades” and that those deposits usually result in a steam turbine loss of capacity at a rate of about 2 to 3 MW per month. We also stated that the “general rule of thumb is that there is a reduction of about 1 MW of generating capacity for each 1 to 2 pounds of deposit that accumulates on the HP turbine.
-
O&M
Predictive Maintenance That Works
This is the fourth in a series of predictive maintenance (PdM) articles that began in the April “Focus on O&M” with an introduction to PdM as a process whereby maintenance is performed based on the condition of the equipment rather than on a predetermined interval. In the May and July issues, we began exploring specific PdM techniques, such as motor-current signature analysis and oil analysis.
-
O&M
Optimizing Condenser Tube Selection
Selecting the most economical tube for a new condenser, or the retrofit of an existing one, is much more complex than mere price shopping. Each material has unique performance characteristics that affect the operating economics of the entire plant. A case study illustrates the importance of carefully choosing the tube material that is right for your plant.
-
O&M
Condenser Tube Failure Mechanisms
The operating environment within a condenser is extremely harsh, and in spite of the designer’s best intentions, sometimes tubes made of the best materials fail. The most important tube failure mechanisms typically result from different forms of corrosion and erosion. When it’s time to select new condenser tube material, you’ll need to consider the projected operating environment and failure mechanisms that material will be subjected to.
-
O&M
Condenser Retubing
Once the condenser tubes are designed, selected, and purchased, the final step in a retubing project is to remove the old tubes and install the new ones. The success of this project is very dependent upon attending to quality control, following proper procedures, using the right tools, and having a highly skilled workforce.
-
O&M
Improving Condenser O&M Practices
Losses attributed to condenser tube leaks, fouling, and failures continue to climb, costing the power generation industry an estimated half-billion dollars annually in maintenance costs and loss of production. Investing in an effective condenser maintenance program will reduce those expenses in short order.
-
O&M
Improved Coal Fineness Improves Performance, Reduces Emissions
Utilizing engineering ingenuity and today’s developing computational fluid dynamics tools, a new classifier design is now available that significantly improves fineness from pulverizers without the heavy costs associated with dynamic classification or any downsides on pulverizer capacities, maintenance, and parasitic power. Instead, operational flexibility and improved emission control options are enhanced.
-
O&M
JEA Increases Power Output Through CFB Improvements
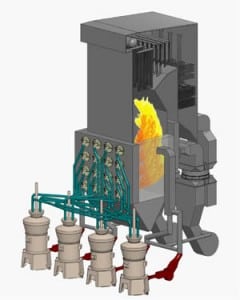
JEA’s Northside Generating Station in Jacksonville, Fla., Units 1 and 2 were built in 1966 and 1972, respectively, although the Unit 2 boiler had not operated since 1983. Both were heavy oil– and natural gas–fired steam units rated at about 300 MW. The utility “repowered” those two units by removing the old boilers and adding new circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers (Figure 1) that entered service in 2002. At that time, they were the world’s two largest CFBs, and the plant won POWER’ s Plant of the Year Award.
-
O&M
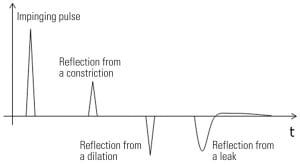
Applying Acoustic Pulse Reflectometry in a Geothermal Plant
Acoustic pulse reflectometry (APR) is a tube inspection method that has been gradually gaining acceptance as a tool for heat exchanger inspection. Different types of heat exchangers operating in different operating environments have different failure mechanisms, making some of them more suited than others for inspection by APR. Finned tube heat exchangers are a typical example of heat exchangers particularly conducive to APR inspection.
-
O&M
Enhanced Capture of Mercury Using Unique Baghouse Filter Media
Several states have already instituted mercury emission limits in expectation of tightening mercury emission rules that will require reductions of up to 91%. Coal-fired plants searching for an economical way to meet the new limits may need to look no further than replacing their baghouse filter elements.
-
O&M
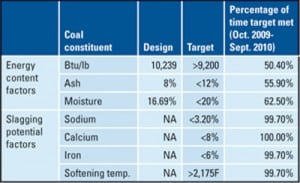
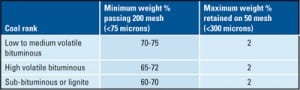
Pulverizers 101: Part II
Pulverizers prepare the raw fuel by grinding it to a desired fineness and mixing it with the just the right amount of air before sending the mixture to boiler burners for combustion. In Part I of this three-part report, we examined the essentials of pulverizer design and performance. In the second part, we discuss the importance of fuel fineness. In the final article, we will discuss the importance of air and fuel measurement.