Instrumentation & Controls
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Innovative boiler master design improves system response
A quick and nimble boiler distributed control system can end up moving at the speed of molasses in winter after a low-NOx retrofit. In one utility fleet, several units—despite being equipped with a modern DCS—were experiencing firing system time lags and degraded dynamic loading capability. Swinging steam pressures and opacity excursions were forcing operators to constantly remove the unit from the load dispatch. Read how a new boiler master design read the riot act to those unruly steam generators.
-
Nuclear
Tow nuclear power I&C out of the "digital ditch"
One expert has called it the "digital delta"—the seemingly endless challenges in refurbishing U.S. nuclear plants with digital instrumentation and controls. But it appears more like a deep ditch, where even those seeking to license new reactors could get stuck. Here’s the latest on the issues, experience, and results—plus recommendations for getting the industry out of the mud and back on the road.
-
Gas
Global Monitor (Nov/Dec 2006)
Renewables require rethinking just about everything/Torque-splitting drive train improves wind turbine reliability/Waste gas–burning engines reach milestone/Hybrid power plant targets pipeline losses/Power from paint/Gulf Coast Power Association conference report/Pat Wood talks about the challenges facing ERCOT
-
Instrumentation & Controls
The long and short of last-stage blades
The use of longer steam turbine last-stage blades (LSBs) reduces the number of low-pressure casings and, thus, a turbine’s total installed cost. In many cases longer blades extract more energy from low-pressure steam before it enters the condenser and improve a turbine’s overall thermodynamic efficiency. But creating longer blades requires forsaking conventional design techniques for complex aerodynamic analysis of stationary vanes and rotating blades. Has the market push for longer LSBs exceeded current technology limits? Does the industry conduct proper analysis to determine when using longer blades is beneficial or not?
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (October 2006)
Upgrading to digital–twice / Lower-cost turbine monitoring / Pros and cons of remote process control / Nuts about Superbolt
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Cleaning and inspection of stainless steels and nickel alloys for FGD service
Stainless steels and nickel alloys of the C-family are major materials of construction for flue gas desulfurization systems. Both types of materials depend upon the presence of thin, passive, chromium-rich, surface-oxide films to provide the desired corrosion resistance. Corrosion resistance is optimized by proper cleaning before and after fabrication. Here are some guidelines for keeping those materials clean.
-
Nuclear
ISA/EPRI conference offers a smorgasbord of control cuisines
This year’s main course, as usual, was instrumentation and controls. Side dishes of digital nuclear plant controls, plant controller and IT security, corrosion monitoring, and model predictive control added their own distinctive flavors. There was something for every taste, from the theoretical to the practical.
-
Gas
Arcos de la Frontera Grupo III Combined-Cycle Plant, Cádiz, Spain
Iberdrola is rapidly making a name for itself on the world stage for building large, very efficient combined-cycle plants and for being the largest owner and operator of wind power plants. The utility’s most recent achievement was the successful commissioning of the Arcos de la Frontera Group III project, which marks the commercial debut of General Electric’s Frame 9FB gas turbine.
-
O&M
Computer-based hydro plant scheduling
Hydroelectric power plant managers face unique scheduling challenges. They have a finite amount of water in their reservoirs available for energy production, and they need to schedule generation according to market demand to maximize profits from their limited “fuel” supply. Hydro power plants are capable of producing products other than electricity. Among them are ancillary […]
-
Water
Focus on O&M (May 2006)
Desalination, Italian style; How to minimize DI operating costs; Advanced flow meter works with shorter pipe runs; Why tubing beats piping.
-
Coal
Curbing the blue plume: SO3 formation and mitigation
Understanding why stack emissions become opaque leads to better choices of systems for controlling SO3 and other pollutants, based on current and future plant operating configurations.
-
Coal
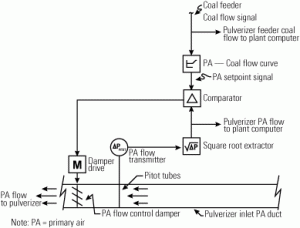
How accurate primary airflow measurements improve plant performance
Primary airflow has a major impact on the efficiency, capacity, and cleanliness of pulverized coal–fired generation. Inaccurate measurements that underestimate primary airflow levels can lead to negative operational outcomes that include increased boiler gas temperatures, flyash loss-on-ignition, excessive NOx emissions, and higher-than-necessary fan power consumption. We remind you how to avoid those headaches.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
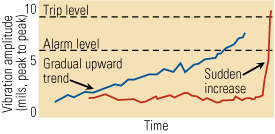
Solving plant vibration problems
Solving insidious vibration problems in rotating equipment may sometimes seem like a black art that requires the right incantation. But identifying the root cause of the vibration is actually a science. By using cutting-edge vibration measurement tools in concert with computer simulations, plant operators can arrive at a permanent, cost-effective solution to virtually any vibration […]
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Air heater leakage: Worse than you think
Rotary regenerative air heaters capture and recycle about 60% of the heat energy exiting the boiler—energy that would otherwise go up the stack. For a 500-MW coal-fired plant, the recycled energy amounts to about 1.5 billion Btu per hour, and reusing it reduces fuel consumption by about 1,500 tons per day. Although most performance engineers […]
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Siemens units keep pace
Earlier this February, Siemens Power Generation’s (SPG’s) factory in Berlin delivered its 500th gas turbine. The SGT5-4000F (Figure 2), formerly called the V94.3A, is nominally rated at 270 MW and weighs in at about 300 metric tons. With this shipment, the Berlin facility can boast of having built gas turbines with a cumulative capacity of […]
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Steam turbine upgrading: Low-hanging fruit
In 1500, Leonardo Da Vinci drew sketches of a device that rotated when hot air going up a chimney passed through a set of fan-like blades. Leonardo called his invention a "chimney jack," and although it only turned a roasting skewer, it gave birth to the idea of mounting blades on a shaft to convert […]
-
Instrumentation & Controls
A permanent solution to generator vibration problems
Remember the slogan, "Never trust anyone over thirty?" Chances are you’ve joined the ranks of the over-thirty generation and are dealing with your own personal "maintenance" issues—not unlike the fleet of generators at larger U.S. power plants, whose average age is about 30. Given the continuing growth in U.S. electricity demand and the cost and […]
-
Instrumentation & Controls
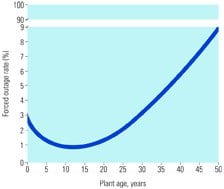
Brain surgery breathes new life into aging plants
Age is wreaking havoc on the U.S. generation industry, especially the coal-fired sector. Industry conferences are replete with hand-wringing over the "brain drain," the lack of skilled personnel, the meager number of students pursuing engineering degrees, and the accelerated retirement of the older workers who make up the industry’s experience base. On top of this, […]
-
Instrumentation & Controls
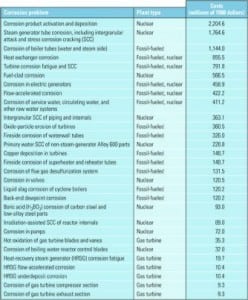
Designing steam cycles to avoid corrosion
U.S. power producers and owners of industrial steam systems each spend about $15.4 billion annually to combat corrosion in their plants. Scale and deposits are thought to be responsible for another $20 billion a year in reduced plant efficiency and lost generation capacity. Corrosion is the primary cause of every other forced outage, and the […]
-
-
Coal
Constant and sliding-pressure options for new supercritical plants
Sliding-pressure, supercritical plants are all the rage. They generally include certain design features developed for markets and operating environments outside the U.S., where new coal-fired plants have been built in recent decades. U.S. market conditions are different, and considerable capital cost savings—with negligible operating cost differences—are possible if technology options are considered for the next wave of supercritical and ultra-supercritical steam plants.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Understanding refractory failures
Compared to most pieces of a power plant, refractory costs very little to install. Yet, if improperly manufactured, specified, stored, mixed, installed, cured, or dried, refractory may cause problems that can significantly decrease a plant’s operating efficiency and flexibility. Like Rodney Dangerfield, refractory design and installation deserve more respect.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
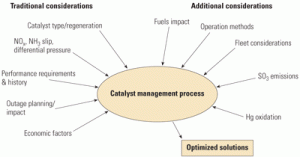
Long-term catalyst health care
Now that many U.S. selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems are in their fifth or sixth year of operation, a number of utilities are shifting their attention from implementing the technology to operating and maintaining it. Catalyst management and performance are key to the successful operation of any SCR system.
-
Coal
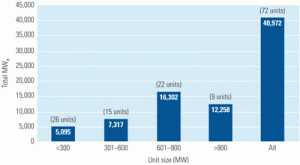
Estimating SCR installation costs
The EUCG surveyed 72 separate installations of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems at coal-fired units totaling 41 GW of capacity to identify the systems’ major cost drivers. The results, summarized in this article, provide excellent first-order estimates and guidance for utilities considering installing the downstream emissions-control technology.