-
Legal & Regulatory
Will Nuclear 2.0 Be Better, Faster, and Cheaper than Nuclear 1.0?
The nuclear renaissance has been in play for several years yet not a shovel of dirt has been turned. Why should anyone believe that Nuclear 2.0 will be an improvement?
-
Commentary
The Hidden Agendas Behind Citizen Suits
The enforcement mechanisms of the environmental statutes in the 1960s were both cumbersome and ineffective.
-
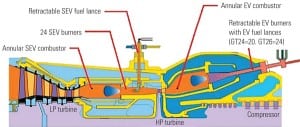
Gas
Flexible Turbine Operation Is Vital for a Robust Grid
Renewable electricity generation has many environmental advantages, but adding large amounts of far-flung renewable resources to a grid requires increased operating flexibility from dispatchable generators when the wind doesn’t blow or the sun doesn’t shine. One promising option: A combined-cycle plant based on Alstom’s GT24/GT26 combustion turbine can be “parked” at approximately 20% plant load while producing emissions comparable to those during baseload operation—with little loss in thermal efficiency. When demand returns, the combined cycle can return to baseload within minutes.
-
News
NRC Greenlights Licensing for Savannah River MOX Facility
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) last week released a report that deemed the mixed oxide (MOX) fuel facility at the Savannah River site near Aiken, S.C., safe. The 568-page document essentially allows licensing to proceed for the plant to make nuclear reactor fuel from plutonium waste.
-
Smart Grid
Addressing Smart Grid and Consumer Info
As state regulators examine whether the smart grid benefits consumers, a federal agency is looking at what information consumers need to take advantage of the technology.
-
News
TVA to Idle Nine Coal Units
Federal public utility Tennessee Valley Authority on Tuesday said it would idle nine coal-fired power units totaling nearly 1 GW at three power plants starting in 2011. Utility officials said the plans were part of a strategy to replace older and less-efficient coal-fired units with “low-carbon” and “carbon-free” generation.
-
News
New Jersey Act Calls for Offshore Wind State Mandates
A bill signed on Thursday by New Jersey’s Governor Chris Christie seeks to meet targets established in the state’s Energy Master Plan for the development of 3,000 MW of offshore wind by 2020.
-
News
FPL Demolishes Cape Canaveral Power Plant
Florida Power & Light this weekend demolished the most visible structures at its 42-acre Cape Canaveral Power Plant. A video shows the implosion of the 45-year-old plant’s red-and-white stacks. The company said it is preparing to build the Cape Canaveral Next Generation Clean Energy Center—a natural gas plant—which will open in 2013.
-
News
Oregon, Washington Fail to Pass Bills to Participate in Regional Cap-and-Trade Program
Oregon and Washington failed to pass bills before the end of their legislative sessions that would implement the Western Climate Initiative (WCI). That leaves only two U.S. states and three Canadian provinces to participate in the regional greenhouse gas (GHG) cap-and-trade program when it begins in 2012.
-
News
Turkey to Begin Privatizing Power Plants
Turkey will reportedly start privatizing power generation plants by the end of this month or in early September. Some of the first few plants up for sale include the Hamitabat power station, a 1,120-MW thermal plant that produces 7% of the country’s total electricity output.
-
News
DOE Says FutureGen 2.0 Still on Track, Solicits Storage Site Hosts
The Department of Energy, the state of Illinois, and parties affiliated with FutureGen 2.0 on Thursday outlined plans for the revamped Illinois carbon capture and storage project.
-
General
Fear Space Weather, Not Climate Change
By Kennedy Maize Washington, D.C., Aug. 23, 2010 — It’s time to stop fretting about climate change and start worrying about space weather. In an opinion article in the Aug. 15, 2010 New York Times, journalist Lawrence E. Joseph raises the issue of the havoc a major solar storm could have on modern electric power […]
-
News
EPA Proposes Two More GHG Rules
A rule proposed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Thursday would certify that 13 states lack the authority to apply Prevention of Significant Deterioration (PSD) permits to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions under their State Implementation Plans. A second rulemaking action, also issued last week, proposes a federal implementation plan (FIP) under which the EPA would assume the authority to issue PSD permits for GHG emissions in states that lack the authority to do so.
-
News
Interagency CCS Task Force Issues Recommendations
An interagency task force on Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) established by President Obama this February delivered a series of recommendations on overcoming barriers to the widespread, cost-effective deployment of CCS within 10 years.
-
News
FirstEnergy, Xcel to Cut Back Coal-Fired Capacity
FirstEnergy Corp. last week said it would cut back operations or idle 1,620-MW of coal-fired capacity in Ohio for up to a year to reduce operating costs, while Xcel Energy announced plans to shut down nearly 900-MW of coal-fired capacity to generate a savings of nearly $225 million. Reasons for the cutbacks included the continued slow economy, lower demand in electricity, and uncertainty related to proposed new federal environmental regulations.
-
News
Shaw Group to Support Two More Chinese AP1000s
The Shaw Group on Monday announced it has signed an initial contract for two new AP1000 units at the Xianning nuclear power plant project in Hubei province with a subsidiary of China’s State Nuclear Power Technology Corp. (SNPTC).
-
News
GDF Suez-International Power Merger to Create World’s Largest IPP
French company GDF Suez formally announced last week it will merge its international business with UK company International Power. The new firm, New International Power, is expected to have over 66 GW in gross operation capacity and 22 GW in the pipeline.
-
News
Blackstone to Acquire Dynegy for $4.8 Billion
Houston-based Dynegy is to be acquired by an affiliate of private equity firm Blackstone Group in a $542 million deal that includes billions in debt assumption. Under a separate agreement between Blackstone and NRG Energy, NRG Energy could acquire four natural gas-fired assets owned by Dynegy for about $1.36 billion.
-
News
OSHA Issues $16.6 M in Fines After Fatal Kleen Energy Explosion
The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) on Thursday cited three construction companies and 14 site contractors for 371 alleged workplace safety violations, and issued a total of $16.6 million in penalties. The fines follow an investigation into the causes of February’s deadly natural gas explosion at the Kleen Energy power plant construction site in Middletown, Conn. The explosion killed six workers and injured 50 others.
-
News
Concern Mounts About Edwardsport IGCC Project Cost Overruns
An Indiana state agency representing utility ratepayer interests in cases before regulatory commissions said it has “serious concerns” regarding cost overruns at Duke Energy’s 618-MW integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) facility at Edwardsport.
-
News
Xcel Energy: Wind-to-Battery Project Tests Show Technology Works
Xcel Energy claims that preliminary tests of a 1-MW battery-storage technology system shows the technology works. The company announced on August 3 that its wind-to-battery project showed it was possible to reduce the need to compensate for the variability of wind generation.
-
News
EPA Sues DTE Energy for Alleged Clean Air Violations
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency filed suit against Michigan’s largest energy company, DTE Energy, for alleged violations of the federal Clean Air Act at that company’s coal-fired Monroe Power Plant in Michigan.
-
News
BrightSource’s Ivanpah CSP Project Garners Key Approvals
California-based BrightSource Energy in the past week received two key approvals for its 392-MW Ivanpah concentrating solar power (CSP) plant in the Mojave Desert. The California Energy Commission’s (CEC’s) siting committee issued a proposed decision recommending approval, and on Friday, the U.S. Bureau of Land Management (BLM) issued its Final Environmental Impact Statement (FEIS) for the project.
-
News
UK Sees Increased Attacks on Distribution Network
A massive increase in organized “attacks” on the distribution power network in central England has resulted in more than a dozen downed wooden poles and thousands of customers without power in a week, E.ON UK said last week.
-
News
Constellation Energy Eyes 3,000-MW New England Fleet
Constellation Energy on Monday said it had signed an asset purchase agreement to acquire Boston Generating’s 2,950-MW fleet, consisting of mainly natural gas–fired plants, for about $1.1 billion, or roughly $372/kW.
-
News
DOE to Support Revamped FutureGen Plans
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) on Thursday announced it would award $1 billion in Recovery Act funds to a revamped FutureGen proposal. The so-called “FutureGen 2.0” project contemplates repowering of an existing Ameren 200-MW coal unit in Meredosia, Ill., using oxyfuel technology—not construction of an integrated gasification combined-cycle facility at Mattoon, Ill., as originally envisioned. The new project still calls for use of the original Mattoon geologic storage site
to sequester carbon dioxide—however, the city of Mattoon has declined participation
in the project.
-
General
Quacks like a duck; Poops like a duck; Limps like a duck
By Kennedy Maize Washington, D.C., Aug. 9, 2010 – Washington is abuzz with talk of a lame-duck session of Congress after the November mid-term elections. Many pundits seem to assume that the Democratic leadership will call the solons into session after the elections (with the Democrats having done very poorly, possibly losing their control of […]
-
Commentary
For Grid Expansion, Think “Subregionally”
When—not if—we pass climate legislation, we will put the U.S. on a path toward a low-carbon electric generation sector. As part of this shift, we’ll need more transmission, including lines to wind and solar power plants that are sometimes located far from today’s power grid. The question is: How do we plan for these new lines and how should we pay for them?
-
Commentary
Bill Gates and the Energy Research Dilemma
There is an idea that has been around for a long time, at least since the fall of 1973: All that stands between the U.S. and an abundant energy future is a lack of spending on research and development. It is as though the Knights Templar could find the Holy Grail, if only the Pope would commit just a few more resources to the hunt.
-
Coal
Fourth Circuit Scuttles NC Air “Nuisance” Suit
Scuttling a high-profile “public nuisance” lawsuit, a federal appeals court has reversed a lower court ruling that required the Tennessee Valley Authority to accelerate plans to install pollution controls at four TVA coal-fired power plants to reduce the amount of pollution blowing into western North Carolina, saying the lower court decision could lead to other public nuisance suits that would wreak havoc on federal and state regulatory regimes for combating air pollution.
Search