Instrumentation & Controls
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Cation conductivity monitoring: A reality check
The ability to detect contaminated feedwater or steam before it can corrode the internals of a turbine or HRSG and cause a forced outage is worth millions. One knock against cation conductivity monitoring—still the most common technique for the early detection of contamination—is the difficulty of interpreting conductivity readings when the plant’s makeup contains significant levels of organics or CO2. Here are the pros and cons of cation conductivity monitoriting and some alternative monitoring methods.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
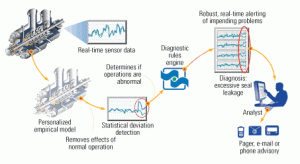
Making PM systems sweat the small stuff
Modern predictive maintenance systems can monitor the health of most plant equipment. By sorting through the wealth of information those systems deliver, operators can discern important trends, including the early signs of a system or component failure.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Turbine technology maturity: A shifting paradigm
Selecting the right turbine(s) for a specific power project is a complex process that poses two challenges. One is understanding which field experience cited by suppliers represents proven technology; the other is evaluating whether a turbine upgrade represents an evolutionary change or a revolutionary transformation that warrants further study before deploying it in the field. Here‘s how a leading EPC contractor makes technology-neutral equipment selection decisions on behalf of its customers.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
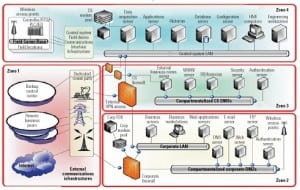
Time to get serious about security
Managing ongoing threats to power plants’ digital, telecommunications, monitoring, control, and automation systems is no longer just a good idea. It’s an essential element of superior plant operations and now a regulatory requirement as well, thanks to new critical infrastructure protection standards recently approved by FERC.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Wireless technologies connect two LCRA plants
Lower Colorado River Authority recently put two separate plants at its Lost Pines Power Park under one functional management system. The project has already deployed a layered wireless infrastructure that allows the two plants to communicate at a fraction of the cost of a wired solution while providing a platform for optimizing work processes and reducing operating costs. What’s not to like?
-
Coal
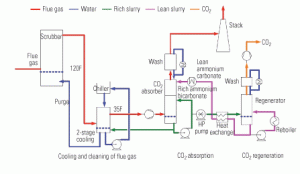
Alstom’s chilled ammonia CO2-capture process advances toward commercialization
Carbon dioxide emissions aren’t yet regulated by the EPA, but it’s likely they will be soon. There are many technically feasible, but as-yet-undemonstrated ways to reduce the considerable carbon footprint of any coal-fired plant, whether it uses conventional or unconventional technology. One promising approach to removing CO2 from a plant’s flue gas uses chilled ammonium bicarbonate to drive the separation process.
-
Coal
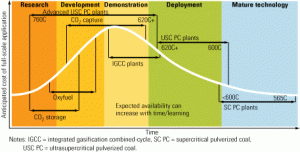
Accelerating the deployment of cleaner coal plants
The dearth of commercial operating experience for advanced coal-fired facilities is forcing their early adopters and builders to use long development cycles and pay high costs for unique engineering design studies. A broad-based industry collaborative effort fostered by EPRI to address this issue is beginning to show results.
-
O&M
The case for cathodic protection
All fossil fuels carry some risk with their reward of an energy density that’s sufficient for producing electricity economically. For coal and natural gas, that threat is a fire or explosion. However, the risk of an explosion isn’t limited to gas-fired plants. Gas poses a threat to any plant that uses the fuel, even in small quantities for heating. Here’s an overview of what you should be doing to keep gas pipelines from corroding and exploding.
-
Distributed Energy
Aggregated backup generators help support San Diego grid
Last year, San Diego Gas & Electric tapped Boston-based EnerNOC Inc. to aggregate 25 MW of backup generators throughout SDG&E’s service area to relieve the grid when it’s stressed by peak demand for electricity. By combining stringent environmental controls with field-proven expertise managing distributed assets, EnerNOC has helped to improve grid stability in Southern California.
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (January 2008)
Single-window control of CHP plant’s energy converters / Safety stuffers entertain as they inform / Doubling up for a heavy load
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (November 2007)
The NERC auditors are coming / Winning encore for on-line pH monitoring / Using baloons as temporary barriers / How data logging can cut power bills
-
O&M
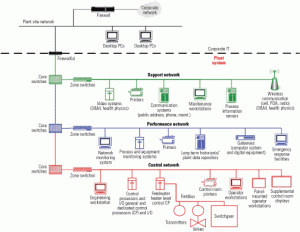
Plantwide data networks leverage digital technology to the max
To make the most of their digital devices and enable the sharing of data by different departments, new and old plants alike need a reliable digital data infrastructure.
-
Nuclear
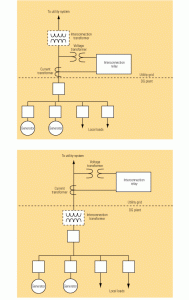
Defined scope, experienced team essential to nuclear I&C upgrade projects
Over the past few years, U.S. nuclear power plants have begun replacing their obsolete analog control systems with digital control systems. Many of these projects have been completed successfully, yielding a tidy return on investment in the form of increased generation. However, some have encountered difficulties, which resulted in cost overruns and schedule delays. This minority of projects may have eroded the industry’s confidence in digital upgrade projects, but a well-run project is still one of your best options for squeezing the last drop of performance out of your plant.
-
Nuclear
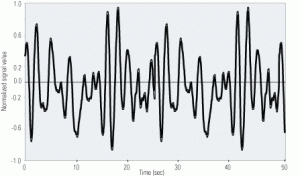
Accurately measure the dynamic response of pressure instruments
How do you know if a pressure transmitter is giving poor results? Unless the transmitter actually fails, most operators won’t notice a very slow loss in accuracy or response time. Fortunately, the noise analysis technique can identify such changes before they cause a problem. The technique has been used to effectively measure the dynamic response of nuclear power plant pressure sensors and their associated sensing lines. It also can be applied to any plant that relies on accurate instrumentation for control and monitoring plant performance.
-
Coal
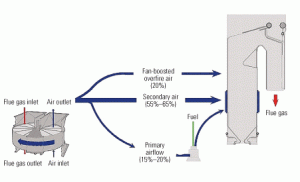
Managing air to improve combustion efficiency
The average pulverized coal–fired coal plant is more than 30 years old and has a heat rate in the neighborhood of 10,300 Btu/kWh operating with an "off-design" coal. Add a high load factor (or increased cycling service), squeezed maintenance budgets, reduced plant staff, and increased time between overhauls to meet the plant’s pro forma, and you’ve got major stress. Fortunately, there is a way to come in under your NOx budget and lower the stress. Breathe deeply and read carefully.
-
Coal
Harness detonation waves to clean boiler tubes
Air and steam sootblowers have been the power industry’s solution to the slagging and fouling of boiler convective passes caused by flyash and combustion products. Manual cleaning systems have been superseded by computers and neural nets, but the basic cleaning apparatus remained unchanged—until now. Say hello to detonation waves. They can knock those deposits loose while markedly improving boiler heat transfer efficiency.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Making the grade with stainless steel tubing
Tubing manufacturers have many alternatives for manufacturing and testing stainless steel tubing for feedwater heater and condenser applications. ASTM specifications are fairly generic in nature and only specify the minimum tube design and testing requirements—which may not be sufficient to provide the appropriate quality for a critical power plant application. To make the right material selections, it’s helpful to understand how welded stainless steel tubing is manufactured and its quality is checked.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Integrated software platform eludes many owner/operators
Ongoing research into experience with plant- and fleet-level software reveals that these applications work side by side but do not necessarily function as an integrated “knowledge management” system. On the supplier side, the industry continues to be fragmented, with individual programs governing a narrow part of the overall plant.
-
Gas
Global Monitor (August 2007)
PG&E mounts tidal power project / GE F-class turbine breaks record / Iowa welcomes ethanol-fed hog / NYPA upgrades pumped-storage plant / Bush blesses Browns Ferry 1 restart / Shearon Harris looks to live on / Nevada bets on solar thermal / Climate models questioned / POWER digest
-
O&M
Finding and fixing leakage within combined HP-IP steam turbines: Part II
By design, combined HP-IP turbines have a small amount of internal leakage from the high-pressure turbine to the intermediate-pressure turbine. As turbines age, the leakage increases considerably and becomes excessive, creating a heat rate penalty and possibly a reliability problem. Last month we explored the symptoms and causes of steam leakage within GE steam turbines and how to correct the problem. In Part II, we examine the same issues for Westinghouse and Allis-Chalmers turbines from both theoretical and practical angles.
-
Environmental
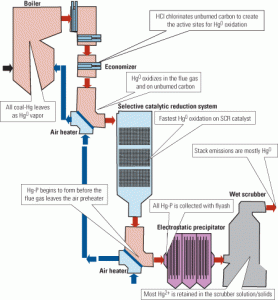
Field experience with mercury monitors
With U.S. mercury regulations pending and control technologies in the full-scale demonstration stage, accurate and reliable measurement of mercury in flue gas is becoming more important than ever. This article compares the results of field measurements of commercially available mercury monitors to approved reference methods. A key but not-so-surprising finding: Not all mercury monitors are created equal.
-
O&M
Use predictive techniques to guide your mercury compliance strategy
Several states have mandated faster and/or deeper reductions in plant mercury emissions than those called for by the Clean Air Mercury Rule. Unfortunately, differences between plants make accurate evaluation of control options difficult. In most cases, even statistically based Hg emission models don’t pass muster because they don’t account for the dynamic chemical behavior of Hg species in gas cleaning systems. This article describes one system evaluation tool that has been validated using Hg field test data from 50 full-scale flue gas cleaning systems. It is already being used by TVA and other utilities.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Finding and fixing leakage within combined HP-IP steam turbines: Part I
By design, combined HP-IP turbines have a small amount of internal leakage from the high-pressure turbine to the intermediate-pressure turbine. When turbines are new, the amount of this leakage is close to the design heat balance. But as turbines age, the leakage increases considerably, causing a heat rate penalty and possibly a reliability problem. In Part I, we explore the symptoms and causes of excessive leakage within GE steam turbines and how to correct the problem. Part II, in next month’s issue, will examine the same issues for Westinghouse and Allis-Chalmers turbines.
-
Coal
Dynamic classifiers improve pulverizer performance and more
Keeping coal-fired steam plants running efficiently and cleanly is a daily struggle. An article in the February 2007 issue of POWER explained that one way to improve the combustion and emissions performance of a plant is to optimize the performance of its coal pulverizers. By adding a dynamic classifier to the pulverizers, you can better control coal particle sizing and fineness—and increase pulverizer capacity to boot.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Old plant, new mission
Since 1999, the Texas grid operator ERCOT has given plant owners economic incentives to upgrade and extend the life of their generating units. Lower Colorado River Authority has seized the opportunity to modernize the control systems of its 1970s-vintage Sim Gideon natural gas–fired steam plant. Sophisticated control schemes now calculate the toll taken by running units under severe service conditions—including the high ramp rates that a plant must execute to sell ancillary services.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Water chemistry an important factor to consider for cycling HRSGs
Operators of combined-cycle plants that have been pressed into cycling service should make sure that the aqueous diet of their steam generators—especially heat-recovery steam generators—fits the plants’ more active lifestyle. Following are some tips for keeping your HRSGs’ water treatment regimen in tip-top shape. These prescriptions can keep the units vital longer and make them subject to fewer unexpected failures.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
DG interconnection standards remain elusive
The state of interconnection standards for distributed generation plants remains disconcerting to many prospective owners of such plants. IEEE 1547 has been in place for several years and appears to be the best option in a field of competing standards. But IEEE 1547 is an imperfect standard; it holds at least six holes. Here are some suggestions for filling them.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Controlling shaft voltages
Contrary to public belief, the most common electrical phenomenon produced by a power plant’s steam turbines, turbine-driven compressors, and pumps isn’t sparks or lightning bolts. It’s static electricity. The physical effects of static electricity—greater vibration and higher temperatures—can damage bearings, shaft journals, couplings, and gears enough to cause a forced outage. A few inexpensive instruments in the hands of a well-trained technician can prevent "frosting" and "worm tracks" in your babbitt bearings. We’ll start the training right now.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
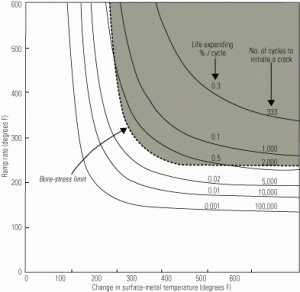
Reduce stress with proper on-line rotor temperature monitoring
On-line temperature monitoring of steam turbine rotors must be based on modeling thermodynamic processes—not direct temperature measurements. Good operating decisions can significantly extend the life of aging turbines, particularly those that are routinely cycled or operated at their maximum ramp rates.
-
Nuclear
Arc flash protection should be job No. 1
Arc flash is arguably the most deadly and least understood hazard faced daily by plant personnel. Research indicates that even the best safety plan, training regimen, and protective equipment may be no match for the heat and blast effects of an arc flash. Consider this article a wakeup call to retrofit every switchgear cubicle in your plant with a properly designed remote racking system. Forewarned is forearmed.