Coal
-
O&M
The Role of Fireside Corrosion on Boiler Tube Failures, Part I
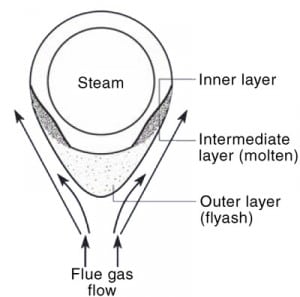
One of the primary challenges of reliably burning coal is managing the corrosion experienced by the furnace heat transfer surfaces. Fireside corrosion remains a leading cause of failure in superheater and reheater tubes. Three case studies examine the different failure modes experienced by tubes located throughout the furnace.
-
O&M
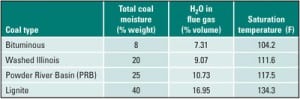
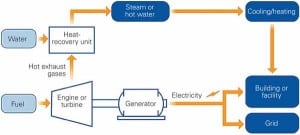
Power 101: Flue Gas Heat Recovery in Power Plants, Part I
Every power engineer must have a firm grasp of the rudiments of how fuel is processed to produce electricity in a power generation facility. With this article, we begin a series of Power 101 tutorials that present these fundamentals in a clear and concise way. First up are the essentials of recovering heat from flue gas.
-
Coal
New Coal Ash Rules May Focus on Conversion to Dry Storage
While the Environmental Protection Agency appears to have initially proposed to regulate power plant coal ash as hazardous waste, there are indications the Obama administration is preparing new federal rules that will at a minimum require utilities to convert coal ash impoundments from wet to dry storage to prevent leaks—a change that would cost tens of millions of dollars but also potentially increase regulated utilities’ rate base and earnings, a Wall Street firm says.
-
Coal
Congress, APPA Divided on EPA Greenhouse Finding
Highlighting a sharp division within the public power community, two senior House Democrats blasted the American Public Power Association for endorsing Sen. Lisa Murkowski’s effort to strip the Environmental Protection Agency of its Clean Air Act authority to regulate greenhouse gas emissions, with the lawmakers saying they have been informed that “numerous” APPA members oppose the endorsement.
-
Coal
New York Proposes Costly Retooling of Power Plant Cooling
In a move that could cost the state’s electricity generators an estimated $8.5 billion, New York regulators [have] issued a draft policy that would require the installment of closed-loop cooling systems at two dozen large power plants in the state, including oil, coal, nuclear and natural gas generators, to reduce fish kills and other harmful effects to wildlife in the water bodies that supply the plants’ cooling water.
-
O&M
The Unique Challenge of Controlling Biomass-Fired Boilers
Biomass has many advantages as a fuel for boilers: It’s inexpensive, readily available in many regions, CO2 neutral, and its use warrants government subsidies. The fuel also presents unique concerns to the designers, owners, and operators of biomass plants, especially in the design of the control system.
-
Coal
OPG Charts Move from Coal to Biomass
In response to Ontario’s provincial regulatory mandates to phase out the use of coal by the end of 2014, Ontario Power Generation (OPG) is exploring its capability to employ biomass feedstocks to displace coal in some units within the OPG thermal fleet. The primary fuels employed during the respective trials at its Nanticoke and Atikokan Generating Stations have been agricultural by-products and commercial grade wood pellets. The Canadian utility has learned valuable lessons about fuel supply and logistics, and the technical challenges of safely handling and firing high levels of biomass.
-
Coal
From GHG to Useful Materials
Could the transformation of carbon dioxide (CO2) into carbonates and oxides solve the problem of greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) from fossil-fired power plants? Some companies are betting that such processes could make everyone happy and even create new profits. Buzz has been growing about this approach, though the concept has been around for many years.
-
Coal
Big Bend’s Multi-Unit SCR Retrofit
Tampa Electric will soon complete a comprehensive selective catalytic reduction project on all four units at its Big Bend Power Station that will make Big Bend among the cleanest coal plants in the U.S. The project — the centerpiece of the company’s 10-year, $1.2 billion air quality improvement program — is on schedule to meet all of its air quality improvement goals by mid-2010.
-
Coal
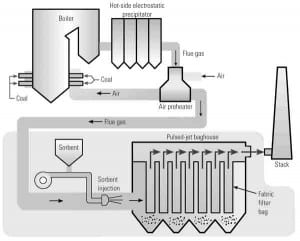
Big Stone Remodels ESP into Pulse Jet Fabric Filter
Short of replacement, what are your options when your original electrostatic precipitator fails to meet your current emissions and opacity requirements? The management of Big Stone Plant chose the unconventional, yet economic approach of building a pulse jet fabric filter inside the casing of the old electrostatic precipitator. The upgrades restored plant availability and prepare the plant to meet the next regulated reductions in particulate matter emissions.
-
Coal
Real-Time Control of Coal Quality Improves Reliability
Poor lignite fuel quality had plagued the Red Hills Power Plant since it began operation eight years ago. The solution: real-time measurement of coal properties that has allowed Red Hills Mine to carefully monitor fuel quality and adjust fuel collection processes to ensure that only high-quality fuel is delivered to the plant. Now all delivered fuel is consumed, and plant reliability is much improved. It’s a classic win-win project.
-
Coal
Determining Carbon Capture and Sequestration’s Water Demands
The U.S. Department of Energy’s National Energy Technology Laboratory is pursuing a new integrated energy-water R&D program that addresses water management issues relative to coal-fired power generation that takes into account the major impacts of CCS on water use. The goal of this research is to promote more efficient use of water in power plant operations and increase the availability of heretofore unusable waters for power plant use. Those practices can mitigate the impacts of CCS on power plant water use and allow for continued development of energy resources.
-
Coal
NETL, We Energies Successfully Complete TOXECON Demonstration
A three-year demonstration of the TOXECON process, a technology to reduce mercury emissions while increasing the collection efficiency of particulate matter (PM), was last year successfully completed at a Michigan coal power plant, the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL) reported in January.
-
O&M
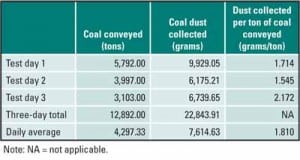
Conveyor Upgrades Increase Plant Availability, Reduce Airborne Dust
The loading and discharge of conveyor belts is the area where many, if not most, of the problems in solids conveying occur. Fortunately, a new technology provides chutes to accomplish conveyor loading and discharge without blockages while minimizing the dust generated: engineered-flow transfer chutes.
-
Coal
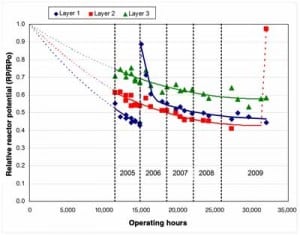
KnoxCheck Reports Reactor Potential and Catalyst Activity
Adding a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system to an operating coal-fired plant may be an expensive and time-consuming project, but the environmental benefits are without question. However, once construction is complete and operations staff assume control of the SCR, proper measurement tools are required to monitor the catalyst performance life cycle.
-
O&M
A Game Plan for Improving Boiler Operations
Operating a boiler is not difficult, but operating a boiler safely and efficiently requires skill and proper training. Following boiler operation best practices will keep your equipment in like-new condition for years to come. This game plan includes a compendium of best practices, with web links to a number of additional key resources you should be famililar with.
-
Coal
EPA Proposes To Tighten Ozone Standard
In one of the most far-reaching of numerous new air regulations expected from the Obama administration, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has proposed to tighten the primary federal standard for ground-level ozone, the principal constituent of smog, to within a range of 60 to 70 parts per billion, saying the tougher standard is needed to protect human health.
-
Coal
DOE Official Floats NSR ‘Carve-Out’ for Some Coal Plants
The Energy Department’s top fossil energy official said [in December that] he might seek exemption or relaxation of “new source review” requirements for certain U.S. coal-fired power plants that are boosting efficiency through retrofits if the plants are also good candidates for subsequent installation of carbon capture and storage systems.
-
O&M
Fuels Used for Power Generation Expected to Rebound in 2010
The Energy Information Administraion has predicted that, as the economy gathers steam this year, rising demand for gasoline, crude oil, coal, and natural gas is expected to push up energy prices, aided by a projected boost in crude oil production.
-
Coal
Digital Plant Controls Provide an Essential Edge
It’s a digital world, and even aging power plants are experiencing the benefits of digital controls technologies. The following cover stories provide insight into the latest options and inspiration for your own plant controls projects.
-
O&M
Can Your Boiler Feed Pump Handle a Deaerator Pressure Transient?
In a typical steam power plant, the boiler feedwater (BFW) pump takes suction from the deaerator (DA) and discharges high-pressure water to the boiler through the feedwater heaters. During normal operation, the DA is supplied with steam turbine extraction steam to mix with and heat the feedwater.
-
Coal
Plant Efficiency: Begin with the Right Definitions
The race is on to claim the title of "most efficient coal-fired power plant" on the planet. However, it’s tricky identifying finalists because of the widespread misuse of the term "efficiency" and all those nagging assumptions. Let’s first establish clear definitions and then identify the title contenders.
-
O&M
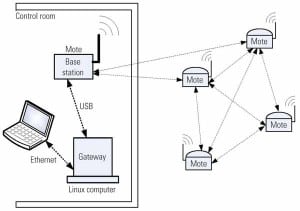
Low-Cost Wireless Sensors Can Improve Monitoring in Fossil-Fueled Power Plants
As equipment ages in fossil-fueled power plants, component wear leading to machinery failure increases as a result. Extending equipment life requires increased attention to maintenance, and one way to improve maintenance planning is to detect faults prior to failure so maintenance can be scheduled at the most cost-effective, opportune time. This type of strategy benefits from the use of additional sensors, and wireless ones can often be installed with the least time and cost.
-
Coal
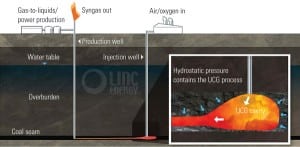
The Resurrection of Underground Coal Gasification
News this past November that Australian company Cougar Energy had begun developing a pilot project to generate power from coal still underground has reignited interest in the 100-year-old alternative energy technology. The company’s planned A$8 million program — expected to be started in the first quarter of 2010 — will be conducted 10 kilometers south of Kingaroy, in southern Queensland. If it is successful, it could lead to the establishment of a 400-MW baseload power station, Cougar Energy officials say.
-
O&M
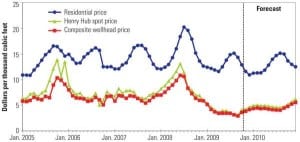
The U.S. Gas Rebound
"It’s déjà vu all over again," said Yogi Berra. The Hall of Fame catcher could easily have been predicting the coming resurgence of natural gas – fired generation. Yes, a few more coal plants will be completed this year, but don’t expect any new plant announcements. A couple of nuclear plants may actually break ground, but don’t hold your breath. Many more wind turbines will dot the landscape as renewable portfolio standards dictate resource planning, but their peak generation contribution will be small. The dash for gas in the U.S. has begun, again.
-
Coal
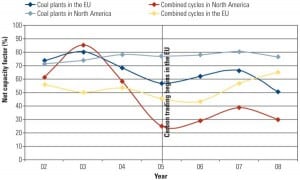
The Impact of Carbon Trading on Performance: What Europe’s Experience Can Teach North American Generators
The European carbon trading system experience suggests that North American generators should expect severely altered coal-fired power plant operating profiles if cap-and-trade legislation becomes law. In a groundbreaking study, Solomon Associates predicts the reduction in mean run time that North American generators should expect. The trends outlined in this study provide an overview of some of the broad challenges facing generators in moving to a carbon-constrained market environment.
-
Coal
Brazil: Latin America’s Beacon
With the eighth-largest economy in the world, Brazil has a clear need for power, but balancing supply and demand has proven tricky in recent decades. Even in a country where over 80% of generation capacity comes from renewables, planning for future capacity additions isn’t straightforward or easy.
-
Coal
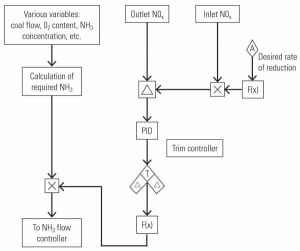
Tuning Ammonia Flow to Optimize SCR Performance
The selective catalytic reduction system has become ubiquitous throughout the world of power plants. Emission control requirements are ever-more stringent, and the cost of excursions is becoming increasingly high. The key to staying under the regulators’ radar is precisely controlling the ammonia injected into the boiler. A new control strategy does precisely that.
-
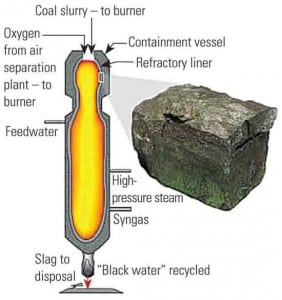
Coal
Advanced Refractory Lining Improves Gasifier Reliability
Successful testing of a new refractory lining material developed by the Office of Fossil Energy’s National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL) could lead to higher reliability and improved economics of gasification technology.
-
Coal
EPA Tightens Emissions Rules for Coal Processing, Preparation Plants
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has adopted final rules tightening emissions limits for coal preparation and processing plants and imposing new reporting requirements on those facilities.