Coal
-
Coal
Research and Development for Future Coal Generation
If coal is to be a viable long-term fuel for a significant percentage of electricity generation, research and development is needed to increase thermal efficiency, demonstrate cost-effective and secure carbon dioxide capture and storage, further improve emission controls, and reduce water demands.
-
Coal
Added Regulatory Hurdles Will Accelerate Coal Plant Retirements
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is developing a number of new regulations for the power sector governing air emissions, cooling water intake structures, and coal combustion waste disposal methods. Combined, these regulations have the potential to drive as much as 40% of existing coal-fired generating units to retire in the next 10 years, representing about 51 GW.
-
Coal
Predicting U.S. Coal Plant Retirements
The question concerning coal plant retirements forced by looming regulatory rules, low gas prices, and moribund load growth has changed from “Why?” to “How many plants?” Many highly detailed analyses and reports have been written on the subject by superbly qualified analysts. This approach to estimating potential plant closures is much more qualitative, and much easier to understand. However, the results closely align: About 50 GW are threatened.
-
Coal
Coal-Fired Generation Cost and Performance Trends
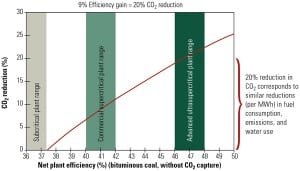
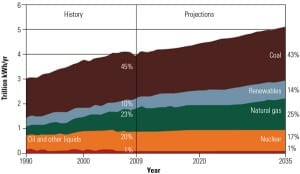
Increasing regulatory requirements and a focus on reducing carbon emissions in the U.S. have significantly reduced the number of new coal-fired plants under development compared with past years. In addition, projected capital costs for new coal-fired plants have risen sharply in the past year, while those for natural gas combined-cycle and combustion turbines have stayed relatively flat. In order to keep coal a viable energy source, many countries, including the U.S., are seeking ways to improve plant efficiency while reducing carbon emissions.
-
Coal
Proactive Strategies for Dealing with Combustible Dust
The challenges of using Powder River Basin (PRB) coal are as significant as the rewards. The subbituminous coal contains lower amounts of sulfur dioxide than bituminous coal but can be prone to combustible dust explosions if it is not properly managed. To eliminate such hazards, plant personnel need to establish best practices for the safe operation and maintenance of PRB coal-handling and -storage systems based on best available technologies.
-
Coal
Benchmarking Fossil Plant Performance Measures, Part III: Metrics Used for Compensation
In Part III of this three-part report, we look at plant- and fleet-level metrics used to determine compensation. As expected from this EUCG-sponsored benchmarking survey, there is broad use of quantifiable metrics to set portions of compensation, but the metrics selected vary substantially across the surveyed utilities. More surprising was the number of utilities that used no performance metrics as part of their employee compensation packages.
-
Coal
EPA Requiring Three Oklahoma Coal Plants to Scrub or Use Gas
In an unusual ultimatum, the Environmental Protection Agency said that it is proposing to take over visibility portions of the Oklahoma Clean Air Act implementation plan to require three coal-fired power plants in the state either to switch to natural gas or install sulfur dioxide scrubbers within three years.
-
Coal
Air Rules Could Risk 11% of PJM Generation
Anticipated clean air regulations could force the retirement of as much as 19,000 MW of coal capacity in the Mid-Atlantic—or 11% of the region’s generation—unless power prices rise to levels that make operation of the plants profitable, according to the independent market monitor for PJM Interconnection.
-
O&M
Condenser Performance Improvement Through Innovative Cleaning and Leak Detection Technologies
One of the largest returns on investment a plant can achieve is the improved condenser performance that results from an effective condenser tube cleaning. Perhaps it is time to reevaluate your choice of cleaning technologies, establish an optimal cleaning schedule, and add routine air and water in-leakage surveys to your plant’s maintenance schedule.
-
Coal
Turning Flue Gas Carbon into a Raw Material for Manufacturing
Bayer in February brought online a pilot plant at Chempark Leverkusen, Germany, to recycle carbon dioxide (CO2) scrubbed from the flue gas of a 1,000-MW RWE lignite-fired unit and convert it into a raw material and petroleum substitute for plastic manufacturing. The Bayer facility (Figure 4) essentially produces a chemical precursor into which CO2 is incorporated and then processed into polyurethanes that are used for many everyday items.
-
O&M
Respect Your Refractory
Because refractory is out of sight inside the gas flow path of a steam generator and its auxiliaries, it’s also often out of mind. That is, until the refractory fails and causes a forced outage.
-
Coal
Biomass Cofiring: A Promising New Generation Option
Biomass cofiring has the potential to cut emissions from coal-fueled generation without substantially increasing costs or infrastructure investments. Research shows that when implemented at relatively low biomass-to-coal ratios, energy consumption, solid waste generation, and emissions are all reduced. However, mixing biomass and coal does create some challenges that must be addressed.
-
O&M
Power 101: Improving the Performance of Boiler Auxiliaries, Part III
Efficient boiler operation requires boiler auxiliary equipment to operate in harmony. In this third and last installment of our Power 101 series, we examine ways to decrease the auxiliary power requirements of boiler auxiliaries.
-
Coal
Benchmarking Fossil Plant Performance Measures, Part II: Fleet-Level Metrics
Part II of this three-part series moves up the typical utility organization to consider important fleet-level fossil plant operating metrics. This portion of the EUCG-sponsored benchmarking survey found that utilities favor fleet-level metrics that are similar to plant-level metrics but assign them different priority. Utilities generally agreed on what were important metrics in the eight categories examined, although none were favored by a majority of the surveyed utilities.
-
Coal
House Panel Hustles Through Bill Blocking EPA Climate Rules
In an anti-climactic markup that featured little new debate and no amendments by opposing Democrats, the House Energy and Power Subcommittee approved Republican legislation to block Obama administration action on climate change by stripping the Environmental Protection Agency of its Clean Air Act authority to regulate carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
-
Coal
U.S. and China Push Forward with Cleaner Coal Projects, Amid Setbacks
In his January State of the Union speech, President Barack Obama called on Congress to pass legislation that would allow the U.S. to source 80% of its electricity from “clean energy” sources by 2035—including traditional renewable sources like wind and solar as well as nuclear and “clean coal.” That broadened definition of “clean energy” was designed to inspire bipartisan interest, as was widely reported. But, as was also widely pointed out, the speech followed a visit to Washington from Chinese government officials and a series of key agreements aimed at increasing “clean energy” cooperation between the two countries.
-
O&M
TECO’s San José Plant Models Safe and Sustainable Practices
In operation since 2000, TECO Energy Inc.’s 132-MW San José Power Station was the first coal-fired power plant built in Central America and is still the largest one. Used as a baseload plant, the facility successfully combines high availability with a business model that promotes sustainable environmental practices and a safe workplace.
-
Coal
Canada’s “Clean” Image Extends to Clean Power
Canada’s extensive natural resources are the driver of its powerful economy, and energy is Canada’s single most important export. Yet policy makers across the nation are currently dealing with the consequences of a generation of under-investment in the electricity system and deciding what the new grid and supply mix should look like. Several provinces are competing to lead the charge in renewable energy and grid intelligence. Policy makers hope that such efforts will not only provide for Canada’s electricity needs but also create the green economy jobs that will drive the nation’s next generation of economic development.
-
Coal
Canada’s Provincial Power Strategies
In Canada, as in the U.S., where you live determines the type of generation technology that provides your power. Here’s how the four most energy-intensive provinces in Canada are responding to the challenge of providing reliable and cheap power in a sustainable way.
-
Coal
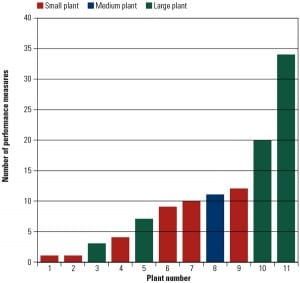
Benchmarking Fossil Plant Performance Measures, Part I: Station-Level Metrics
How does your company prepare and share fossil plant performance data? What data are important, and how much effort is required to collect and report the data? What are the most important statistics for reporting key fossil plant operations? The latest EUCG benchmarking survey reveals the favored fossil performance metrics at several of the largest utilities in eight key categories.
-
Coal
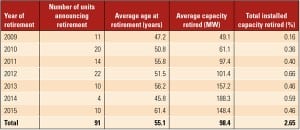
Reaching Retirement
A recent Washington Post article attacks coal as a fuel with a dim future. The author points to the large number of plant retirements as evidence of its impending demise. Checking the actual data reveals a much different story.
-
O&M
Increasing Generation Ramp Rate at Morgantown Generating Station’s Coal-Fired Units
At Morgantown Generating Station, plant personnel used innovative methods to combine model predictive control with distributed control system–based process control algorithms to improve waterwall temperature control and main steam temperature control and to enhance unit ramp rate capability. The previous heat rate and NOx optimization performance gains were retained. Focusing beyond basic loops of feedwater, air, and O2, the project considered issues such as PID controller override configuration and limitations. The techniques used to overcome these challenges improved unit ramp rate capability beyond any previous unit performance.
-
Coal
Designing Fuel Systems for Large Biomass Plants
Compared with other solid fuel–fired plants, the systems and components required for handling and processing biomass appear quite familiar, but important fuel differences must be considered. A successful biomass plant design must provide flexibility for handling the expected wide range of biomass fuel properties and characteristics.
-
O&M
Power 101: Improving the Performance of Boiler Auxiliaries, Part II
Efficient boiler operation requires boiler auxiliary equipment to operate in harmony. The air preheater, for example, though it has few moving parts, is vital to maintaining efficient boiler performance. In this second installment of our Power 101 series, we examine performance degradation caused by corrosion and fouling of the air preheater that results from the combustion of coal plus the effects of ammonia and sodium bisulfite injection for SO3 mitigation.
-
Commentary
Pre-Combustion Technologies: A Key Environmental Compliance Tool
Arizona Public Service’s (APS) plan to close three older coal-fueled units at the Four Corners Power Plant in New Mexico and buy out Southern California Edison’s 48% share of the two remaining units is a creative means of surviving the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) committed action against coal-fueled generation.
-
O&M
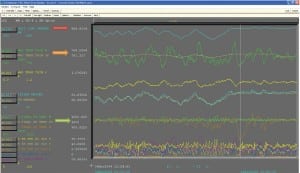
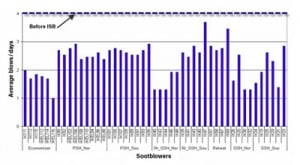
Clinker Minimization at San Miguel Electric Co-Op
San Miguel Electric Cooperative selected and installed an automatic sootblowing system for its Unit 1 to minimize clinkers in the boiler that caused semi-annual unscheduled outages. New boiler surface-cleaning equipment and intelligent cleaning software eliminated these expensive outages.
-
Coal
Duke, Progress Energy Merging into Biggest U.S. Power Utility
Duke Energy and Progress Energy announced January 10 that they are combining to create the nation’s biggest electric utility. The $13.7 billion deal is likely to draw tough scrutiny from federal and state regulators—and some protests from big power buyers—given the companies’ overwhelming market dominance in North Carolina and more modest operational overlap in South Carolina.
-
Coal
Coal Groups Blast Colorado’s Dash to Natural Gas
In a decision blasted by the coal industry as making the state "dangerously reliant" on natural gas, the Colorado Public Utilities Commission has approved an emissions-reduction plan for Xcel Energy that further expands the utility’s already extensive shutdown of coal-fired power plants in favor of gas-fueled generation.
-
Coal
Illinois Lawmakers Block Clean Coal Plant
Ringing what may be the death knell for the $3.5 billion Taylorville IGCC project, the Illinois Senate voted 33-18 in early January against authorizing construction of a coal gasification and power generating plant proposed in the state by Tenaska.
-
O&M
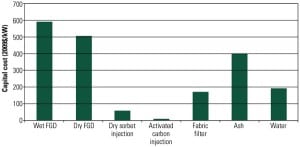
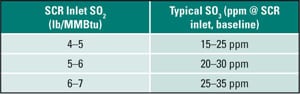
Continuous SO3 Monitoring Can Reduce Sorbent Consumption
An unintended consequence of employing selective catalytic reduction and wet flue gas desulfurization to reduce nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide levels at coal-fired power plants has been unwanted sulfur trioxide (SO3) emissions. Picking the right sorbent in the right amount can eliminate that problem.