-
O&M
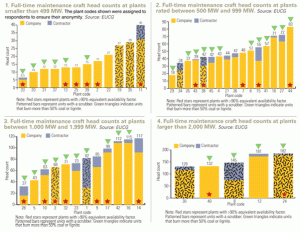
Who’s doing coal plant maintenance?
POWER has reported on several EUCG benchmarking studies over the past several years. This month we examine the maintenance staffing of 45 coal plants reported by 13 EUCG member utilities. If you benchmark your plants or fleet, as you should, some of the study’s results challenge what is considered conventional wisdom.
-
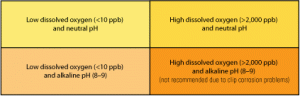
O&M
The case for cathodic protection
All fossil fuels carry some risk with their reward of an energy density that’s sufficient for producing electricity economically. For coal and natural gas, that threat is a fire or explosion. However, the risk of an explosion isn’t limited to gas-fired plants. Gas poses a threat to any plant that uses the fuel, even in small quantities for heating. Here’s an overview of what you should be doing to keep gas pipelines from corroding and exploding.
-
Distributed Energy
Aggregated backup generators help support San Diego grid
Last year, San Diego Gas & Electric tapped Boston-based EnerNOC Inc. to aggregate 25 MW of backup generators throughout SDG&E’s service area to relieve the grid when it’s stressed by peak demand for electricity. By combining stringent environmental controls with field-proven expertise managing distributed assets, EnerNOC has helped to improve grid stability in Southern California.
-
Commentary
What Congress can learn from Google
Chances are good that legislation to “cap and auction” greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions will become law as early as 2009. While many environmentalists, utilities, and energy companies agree that cap and auction is the right framework, huge differences remain. Environmentalists want an 80% reduction of GHG emissions by 2050, or sooner. Energy companies want more […]
-
Nuclear
U.S. a paper tiger in nuclear power
I was talking with a utility executive the other day about his recent vacation in India. It’s certainly not your usual holiday destination, but he’s the adventurous type, eager to mingle with different cultures and sample their cuisine. The exec did a lot more than tour the Taj Mahal and get a glimpse of endangered […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (February 2008)
FutureGen picks Mattoon, Ill./Duke applies for first greenfield COL/PPL to work with UniStar on another COL
/Areva seeks NRC certification of its reactor/Mitsubishi also in line at the NRC/PV project shines in Nevada/SunEdison commissions Colorado PV plant/Big concentrating solar plant proposed/Super Boiler celebrates first anniversary/Small fuel cell uses JP-8 jet fuel/POWER digest -
Water
Costlier, scarcer supplies dictate making thermal plants less thirsty
The Energy Information Administration estimates that U.S. thermoelectric generating capacity will grow from 709 GW in 2005 to 862 GW in 2030 to help meet annual demand increases of 2%. The makeup and cooling water needed by plants generating that increased capacity certainly won’t be available from withdrawal sources, so plant developers and owners will have to apply water-stingy technologies plantwide. As is usually the case, conservation saves money as well as the environment. Here’s a thumbnail economic analysis of some solutions to the water problem.
-
O&M
Eliminating oil whip–induced vibration after a steam turbine retrofit
Nobody expected driveline vibration to occur after a flawless retrofit of a 200-MW steam turbine. But when it did, Mitsubishi Power Systems and Exelon vibration specialists identified the symptoms and rapidly narrowed the list of possible causes. Confounding factors made the root cause difficult to identify, but the experts pinpointed the problem, made necessary hardware modifications, and placed the turbine back in service in a week.
-
O&M
Protecting plant equipment from voltage sags
Immunity from voltage sags is vital for reliable operation of our ever-more-sophisticated electronic controls and equipment. Every electrical product should be able to ride through typical voltage sags, but in many cases the first sag test occurs after equipment is installed and in operation. Select the appropriate sag immunity specification and equipment compliance testing, and you’ll be glad you did.
-
Business
Workforce analysis: Replacing management by fad with management certainty
The biggest problem facing industrial managers is ensuring that they’ll continue to have a skilled workforce. With so many people nearing retirement, organizational skills are at risk, which poses a direct threat to operations. Many companies are making big investments to capture the unique knowledge and experience of graybeards before they move on. But that is just one aspect of a far more complex issue.
-
Commentary
U.S. nuclear power’s time has come—again
In the U.S. today, there are continual discussions about energy independence, energy security, and ways to slow climate change. But meeting the nation’s projected 40% increase in electricity demand by 2030, while reducing overall power plant CO2 emissions, will require much more than talk. During the 1990s, American utilities increased their gas-fired generating capacity because […]
-
Nuclear
Renew Indian Point’s fission license
Early last month, Governor Eliot Spitzer and Attorney General Andrew M. Cuomo—both New York Democrats—asked the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) to reject Entergy Nuclear’s application to extend the operating licenses of Indian Point Units 2 and 3 for 20 years. The units, each rated at about 1,000 MW, are a major source of […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (January 2008)
Dominion applies for new Virginia reactor / ABB commissions world’s largest SVC / Google Earth adds air quality data / Alstom supplies integrated solar/CC project in Morocco / DOE updates coal plant database / Dam the Red Sea? / Complying with CWA Section 316
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (January 2008)
Single-window control of CHP plant’s energy converters / Safety stuffers entertain as they inform / Doubling up for a heavy load
-
Legal & Regulatory
One-size RPS does not fit all
The U.S. Congress continues to debate proposals that would mandate that a set amount of the nation’s electricity come from renewable energy sources such as wind, the sun, or biomass. These discussions about adopting a nationwide renewable portfolio standard (RPS) raise significant concerns for power providers and customers alike. Backers of a one-size-fits-all federal RPS […]
-
Coal
Regulatory risks paralyzing power industry while demand grows
In our second annual report on the state and future of the U.S. power generation industry, we combine the considerable experience of POWER’s editorial staff with the market savvy of Industrial Info Resources Inc. (see next story) to preview the industry’s direction in 2008. We anticipate that the specter of carbon control legislation will hobble coal and make renewables the hot ticket while nukes continue to inch forward in a generation market that is basically treading water.
-
Coal
Greater fuel diversity needed to meet growing U.S. electricity demand
Industrial Info Resources’ strengths are tracking capital projects and cost projections and providing intelligence about the power generation market, among others. IIR has used its large industry databases and numerous industry contacts to develop its outlook for 2008. Here’s what you should expect and plan for this year.
-
Commentary
Storming the Gates
Visiting power plants is one of the perks of being a COAL POWER editor. Some plants are located in metropolitan areas; others are closer to east nowhere, especially those mine-mouth plants. Each is unique and worth the travel time to visit and meet plant staff.
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: With Chaos Comes Opportunity
Combat veterans use the phrase "fog of war" to explain why carefully prepared battle plans are quickly overwhelmed by chaos once the first bullet is fired. Survivors often describe experiences that are markedly different from those of others standing only yards away. The fog of our industry’s battle to build new generating plants permeates the […]
-
Coal
The Coal Patrol: Growth in PRB Coal Use Will Be Fueled by New Projects
Production from Wyoming Powder River Basin (PRB) coal mines ended last year with a increase of only about 1.1%, reflecting a record 451.3 million tons, according to the Department of Energy’s Energy Information Administration. Production of PRB coal spiked with a record 10% growth in 2006 following two derailments on the PRB’s main triple-track line […]
-
O&M
The Coal Patrol: Court Rejects Industry Suit Targeting Miner Safety Rules
A federal appeals court has rejected a National Mining Association (NMA) suit seeking to throw out new regulations issued by the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA). The rules were to improve protection for miners in the wake of accidents at two West Virginia coal mines in January 2006 that killed 15. (See COAL POWER […]
-
Coal
Tech Notes: Giving PRB Coal the Respect It Deserves, Part 1
Use of Powder River Basin (PRB) coal for power generation set another record in 2007. In fact, PRB coal now accounts for about 40% of all the coal fired in the U.S. to produce electricity. Yet we have barely dented the estimated 800 billion tons of the fuel’s proven reserves in Wyoming. The size of […]
-
O&M
Coal Plant O & M: Condition Monitoring Cuts Mirant Mid-Atlantic’s Costs
Condition monitoring (CM) has become an increasingly important aspect of power plant maintenance philosophy. Today many utilities are using a variety of predictive maintenance (PM) techniques like CM to lower their operation and maintenance expenses. Over the years, gencos have developed a diverse collection of CM programs of various breadth, depth, and formality. All are […]
-
Coal
FutureGen: FutureGen Finds a Home But Can’t Pay the Mortgage
The FutureGen Industrial Alliance Inc. selected Mattoon, Ill., as the site of the $1.8 billion FutureGen project just before Christmas, but the plant may never move off the drawing board.. FutureGen, the proposed prototype of a near-zero-emissions coal plant, is to demonstrate advanced technologies for coal gasification, electricity production, emissions control, CO 2 capture and […]
-
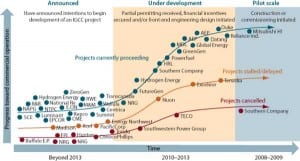
Coal
IGCC: IGCC’s Future Hinges on a Workable Carbon Framework
Integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) technology, a process of gasifying coal that allows the capture of carbon dioxide emissions, has tremendous potential for meeting future baseload generation demand. Though it is one of the leading alternatives for producing clean power from coal, IGCC faces a precarious future due to rising capital costs and regulatory uncertainty. We’re […]
-
O&M
Safety: Worker Health and Safety Now Top Priorities for Alabama Power
Employees of Alabama Power, a Southern Company subsidiary, routinely work near energized wires, intense heat, nuclear fuel, heavy equipment, moving vehicles, and pressurized equipment, as well as under other conditions that require exceptional safety attitudes and measures. Though it is vitally important to provide electricity to customers, neither company believes that doing so is worth […]
-
Water
Forgotten water: Stator cooling water chemistry
Stator cooling water treatment is often ignored—until the generator fails. Proper treatment and monitoring is essential to keeping the copper in your stators, where it belongs.
-
Business
This month in POWER…
During this 125th anniversary year, Retrospective has surveyed the evolution of the power industry as chronicled in POWER. The magazine’s original focus in the 1880s was to fill the fledgling industry’s technical information vacuum and share common operating experiences. Our goals today are remarkably similar, as technology continues to change and operators continue to learn […]
-
Carbon credits and debits
Carbon control legislation made it out of a subcommittee of the U.S. Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works in late October, but no one is happy with it. The bill, S. 2191, America’s Climate Security Act of 2007, would direct the U.S. EPA to establish a program to decrease emissions of greenhouse gases (GHGs). […]
-
Gas
Global Monitor (December 2007)
TVA may revive Bellefonte / GE’s globetrotting Jenbaches / Largest PV plant taking shape / When will PV be competitive? / Siemens goes to the wall with solar / Breakthrough in metamaterials / POWER digest
Search