-
O&M
How to Measure Flyash Levels
Measuring the level of flyash in your silos is not an easy task, in part because the flyash collected at one plant can be remarkably different from that collected at another plant, even if both fire the same coal. Such variability means that selecting the right instrument for your application is important.
-
Coal
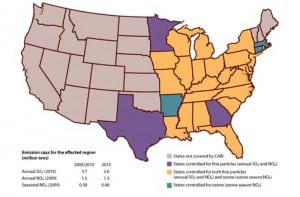
Court Kicks CAIR Rules to the Curb
A federal appeals court has struck down a key Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) program for reducing fine particulate and smog-causing emissions in the eastern half of the nation, saying the rules were riddled with “several fatal flaws,” including the agency’s failure to properly focus pollution cuts to prevent movement of air pollution from one state from worsening air quality in a downwind state.
-
Coal
EEI Leaders Say Promise of Carbon Capture and Storage “Overblown”
In a sobering assessment of a key technology that’s expected to help keep the coal industry viable in the face of likely greenhouse gas caps, several electric utility executives have expressed deep concern that the promise of carbon capture and storage for coal-fired power plants has been “overblown” and “oversold.”
-
Commentary
EPA Staff’s GHG Proposal Will Paralyze the U.S. Economy
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has announced that is it well on its way to regulating at least 85% of the energy used in America in the name of global warming (never mind the fact that temperatures have inexplicably not increased since at least 2001). If the proposal is enacted, any organization or person that emits more than miniscule amounts of CO2 will be required to obtain a permit, effectively bringing our economy to its knees in short order.
-
Commentary
Stymied on Coal, Jacksonville Goes Back to Gas
By Kennedy Maize
Stymied in its plans for new coal-fired generation, Florida’s Jacksonville Energy Authority is moving to natural gas. . . .
For several years, JEA was heavily involved in a multiple-utility plan for a $2.3 billion, 800-MW coal-fired plant to meet the region’s rapidly-growing electricity demand. But Florida Republican Gov. Charlie Crist (rumored to be on presumptive Republican presidential nominee John McCain’s vice presidential short list) clobbered the project and imposed a 20% renewable energy mandate on Florida utilities. “I worked on that for three years. In a flash of an eye, it got cancelled,” JEA project manager Mike Lawson told the Florida Times-Union. -
Commentary
The Madness of Gore
Is Al Gore out of his mind? Or is he simply issuing a difficult challenge that he knows can’t be met, but will stimulate the country toward a positive effort?
It’s hard to tell, given his speech in Washington last week, calling for the U.S. to replace all – that’s 100 percent, folks – of its electric generation with renewables in a decade. We’re talking 2018 here.
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (July 2008)
Protection against arc flash more important than ever; Laramie River Station uses new coating technology; Protecting power plant pipes: Basics you must know
-
Legal & Regulatory
Climate change: Policy via litigation?
By Steven F. Greenwald and Jeffrey P. Gray David Crane, the CEO of NRG Energy, was recently quoted in a widely disseminated publication as saying: “It is a moral imperative that we take steps to reduce CO2 concentration in the earth’s atmosphere.” One might expect those reacting to Crane’s comments (made in a February 2007 […]
-
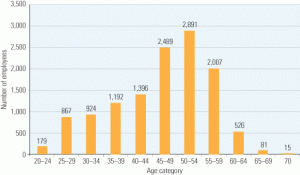
Business
Generation next: Strategies for recruiting younger workers
In our April 2008 issue, the article “The aging workforce: Panic is not a strategy” focused on how to reconfigure human resource practices in order to find enough well-trained new personnel to replace the large number of baby boomers who will be retiring in the next few years. This month we profile several utilities that are using innovative approaches to recruit younger technical staff and skilled craft labor to fill positions being vacated in growing numbers by retiring employees.
-
Coal
Luminant’s Big Brown Plant wins for continuous improvement and safety programs
Staff from Luminant’s Big Brown Plant accepted the PRB Coal Users’ Group’s top honor for innovative improvements to coal-handling systems and a sterling safety record. The numbers reveal their accomplishments: an average EFOR less than 4%, an availability factor averaging 90% for a plant that burns a lignite/PRB mix, and staff who worked more than 2.6 million man-hours since March 2000 without a lost-time injury.
-
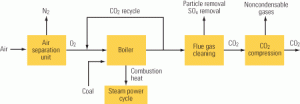
Coal
Options for reducing a coal-fired plant’s carbon footprint, Part II
A conventional coal plant’s CO2 emissions can be reduced either after combustion (see Part I of this article in POWER, June 2008) or before. In the latter case, typified by integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) plants, the fuel used is synthesis gas (syngas), which contains mostly hydrogen (H2) and CO. A water-shift reactor converts the CO […]
-
Coal
Woods and power company CEOs agree: “The state of the industry is cautious”
It is rare indeed to witness, at an otherwise staid industry forum, the public rebuke of the country’s most prominent supplier to the electric power industry. But at the Keynote session and Power Industry CEO Roundtable of the 2008 ELECTRIC POWER Conference & Exhibition in Baltimore this May, Milton Lee, general manager and CEO of […]
-
Coal
Carbon Constraint Conference: Dealing with the climate change conundrum
“Once it’s enacted, the impact of climate change legislation on the electric power industry will be ten times bigger than that of the Clean Air Act,” said Dan Adamson, an attorney with the law firm of Davis Wright Tremaine and chair of the opening session at the 2nd Annual Carbon Constraint Conference (Figure 1). 1. […]
-
Nuclear
A race for winning reactor designs and approvals
A week before the Preakness and two weeks after the Kentucky Derby, it was an atomic horse race in Baltimore. Reactor vendors trotted out their technologies at the ELECTRIC POWER Conference & Exhibition in sessions that filled the nuclear track’s 96-seat room at the Baltimore Convention Center. The reactor makers were also soliciting help from […]
-
Coal
PRB Coal Users’ Group enjoys growing interest in its concerns
The 2008 Powder River Basin Coal Users’ Group (PRBCUG) set new records for attendance again this year with more than 400 registered members for the three-and-a-half-day event, 268 of whom were from operating companies. The meeting’s Grand Sponsor was Benetech and its Plant Professionals group. The meeting began with the Power Plant Awards Banquet on […]
-
Water
New strategies for conquering environmental challenges
No doubt some power plant engineers feel that tackling environmental problems is a lot like dealing with the Hydra, the ancient mythological serpent monster with multiple heads. When an attacker would cut off one of the Hydra’s numerous heads, two new ones would grow back in place of the head that was removed. All too […]
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Digital technology spawns need for configuration management
Documenting changes to the distributed control system and other digital plant applications should be considered a critical element of managing risk—and of safe, efficient daily operations and maintenance. Coming up with a practical configuration management approach, though, isn’t easy.
-
Not a quarter’s worth of difference
What, if anything, distinguishes the three major presidential candidates on energy and environmental policy? Not much, based on papers posted on their web sites, public comments, and interviews reported on in the nation’s newspapers. Let’s split some hairs on the candidates’ energy and climate change policy positions.
-
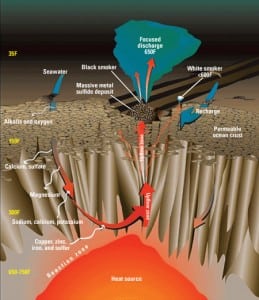
Geothermal
Tapping seafloor volcanic vents
Modern ocean power systems look to convert the mechanical energy of waves or tidal movement to electrical energy. But that’s not all the sea has to offer. It may also be possible to capture and convert the enormous quantities of heat produced by magma escaping through seafloor vents—an undersea version of geothermal energy.
-
It’s all about power
—Dr. Robert Peltier, PE Editor-in-Chief The Lieberman-Warner Climate Security Act (L-W) that proposes to cut carbon emissions by two-thirds by 2050 was delivered stillborn on the Senate floor in early June, as expected. Faced with public outcry over record-high gasoline prices, no senator was able to breathe life back into a bill that is estimated […]
-
Commentary
Kilowatt-hour tax is fairest approach
By Jim Rogers, Duke Energy Corp. The climate change debate has been dramatized in movies, on Hollywood’s red carpets, and in documentaries featuring melting ice caps. The collective effect is extraordinary, and positive. America now stands ready to address one of its toughest challenges since the industrial revolution—decarbonizing our energy supply and economy. Now the […]
-
Commentary
Deadlock: Bush’s Air Policy
After almost eight years, the Bush administration’s approach to air pollution policy—including global warming—ends up with bupkus. That’s a wonderfully-useful Yiddish word meaning, literally, “nothing,” but implying less than nothing, or the meaningless result of lots of apparent, but futile, effort.
-
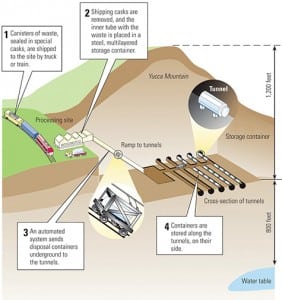
Coal
Global Monitor (July 2008)
Yucca Mountain plan sent to NRC/ CPV cells get cooling chips from IBM/ StatoilHydro to pilot test first offshore floating wind turbine/ U.S. rivers next massive power source?/ Siemens delivers 500-MW gasifiers/ Algae: A green solution/ POWER digest
-
Coal
New Source Review Update
The mere mention of the words "New Source Review" (NSR) will immediately capture the full attention of any utility executive and might cause the cancellation of even the best power plant "upgrade" project. The effects of those three words have nothing to do with project economics or whether a project increases or decreases emissions. It’s all about the lawsuits.
-
Commentary
Welcome to the New COAL POWER
Welcome to our new format for COAL POWER, brought to you by the editors of POWER magazine. This new web site and “webzine” contains in-depth information specifically for the coal-fired power generation market.
-
Commentary
Ups and Downs in Coal Markets
Earlier this month, blogger and Contributing Editor Kennedy Maize took a look at some significant developments on the coal front, including the fate of proposed new plants in Indiana and Kansas and the booming demand for coal mine workers.
-
Coal
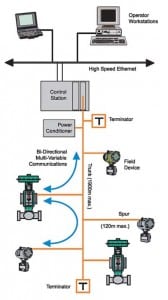
A Fieldbus Primer
Many automation engineers are coming face to face with real fieldbus applications for the first time. Fieldbus (the use of digital communications networks for distributed instrumentation and control) is a wonderful technology with many benefits, but fieldbus installation requires some additional considerations over and above normal 4-20 mA projects. In this article, I present some of those issues and show you how to deal with them.
-
Coal
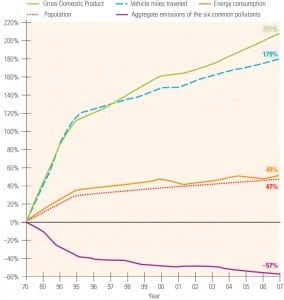
Debate on the Cost of Carbon Control Begins
Senate legislation to cap U.S. greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions beginning in 2012 would have generally modest cost impacts on the national economy, leading to reductions in gross domestic product (GDP) by 2030 that range from 0.2%, or $444 billion, to 0.6%, or $1.3 trillion, according to an Energy Information Administration analysis.
But the analysis, which concluded that the costs of the legislation would depend largely on the availability of advanced nuclear and coal-fired generation technologies, drew criticism from Republicans for its projection of a massive buildup of nuclear generation.
-
Coal
Designing Material-Handling Systems for FGD Projects
Reducing NOx, SO2, and other air pollutants continues to be a challenge for the power generation industry. The technologies are well-understood, but the devil is always in the details, especially when a complex treatment system is retrofitted to an existing plant.
The most common method for reducing SO2 from plant emissions is the conventional lime- and limestone-based flue gas desulfurization (FGD) system. Material-handling systems for limestone and gypsum present specific challenges and opportunities that differ from those of coal-handling systems. This article looks at factors to consider before and during the design of a new material-handling system. The choices you make about these many variables will determine the cost and longevity of your system.
-
Commentary
Wishful Thinking
By Editor-in-Chief Dr. Robert Peltier, PE
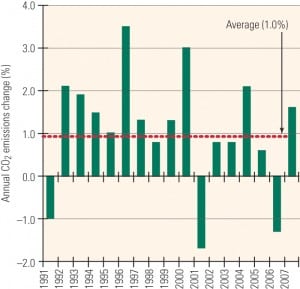
Zhou Dadi, director general (emeritus) of the Energy Research Institute at China’s National Development and Reform Commission, recently spoke at a panel discussion sponsored by the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Zhou boasted that China has set aggressive short-term goals for improved energy efficiency and that his country understands that it needs to make significant reductions of CO2 in the future. This is a remarkable statement considering that China installed over 100 GW of new coal-fired generation in 2006 and another 75 GW in 2007.
Search