-
O&M
Preventing Copper Deposition in Steam Turbines
Many large utility-scale units with copper alloy condensers and feedwater heaters lose generating capacity when copper and copper oxide deposits develop on high-pressure (HP) steam turbine blading. It is not unusual for a 400-MW unit to lose 10% of its generating capacity over a six-month period when water treatment processes aren’t properly tuned to prevent copper transport in the steam and condensate systems. In fact, one utility reported that it lost 20 MW of capacity in one month because of such deposits. The financial implications of such deposits, particularly in power markets where plants are pushed to their generating limits, are tremendous.
-
Commentary
Customers Know What Customers Know Best
Wish you could get inside your customer’s head? If so, forget data and go to the source.
-
Coal
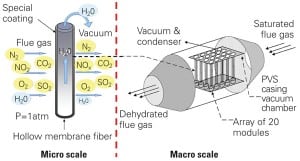
Large-Scale Tests Begin to Convert Flue Gas to Usable Water
Subsidized by the Dutch government, a number of Dutch utilities, the European Membrane Institute at the University of Twente, and Dutch consulting firm KEMA have, for over a decade, been testing membrane technology that promises to directly convert water vapor from power and other industrial plants’ flue gases into drinking water. The technology could provide a new source of large volumes of potable water.
-
O&M
Predictive Maintenance That Works
This series of articles focuses on the nuts and bolts of predictive maintenance (PdM), also known as condition-based maintenance. A well-defined and well-executed PdM program saves time and money by reducing unneeded time-based maintenance tasks and by identifying and fixing problems before they cause equipment failure or plant shutdown. In this article, we begin introducing condition-monitoring techniques commonly in use at power plants.
-
Commentary
Prudence: Who’s Minding the Store?
Regulators are asked to balance a societal need with the cost burden placed on those who pay for the service. Sometimes they forget that it’s other people’s money at stake.
-
Wind
Major Offshore Players Introduce Colossal Wind Turbines
Competition among offshore wind turbine vendors vying for market share went into overdrive in the first three months of 2011 as several key players announced gigantic new turbine models.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Is FERC Backstop Siting Authority Still Alive?
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit recently dealt another setback to the use of Section 216 of the Federal Power Act, which gives the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) “backstop” authority to site electric transmission lines. Although enacted in 2005, this authority has never been used by FERC, and it can be questioned whether it ever will be used.
-
Commentary
How to Hire an Honest Staff
It’s not just hard finding good help these days. It’s hard finding honest help, too.
-
Hydro
China Dam Gets World’s First Self-Closing Ring Gate Control System
A major technical advance in hydroelectric dam safety was achieved this March as Alstom’s Chinese arm, the Tianjin Alstom Hydro Co. (TAH), delivered what it called “the world’s first self-closing electronic ring gate control system” to the Ahai hydropower project in China.
-
Coal
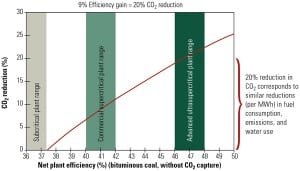
Research and Development for Future Coal Generation
If coal is to be a viable long-term fuel for a significant percentage of electricity generation, research and development is needed to increase thermal efficiency, demonstrate cost-effective and secure carbon dioxide capture and storage, further improve emission controls, and reduce water demands.
-
Environmental
Researchers Develop Supercritical CO2 Brayton Cycle Turbines
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories say a project that focuses on supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) Brayton cycle turbines is moving to the demonstration stage.
-
Coal
Added Regulatory Hurdles Will Accelerate Coal Plant Retirements
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is developing a number of new regulations for the power sector governing air emissions, cooling water intake structures, and coal combustion waste disposal methods. Combined, these regulations have the potential to drive as much as 40% of existing coal-fired generating units to retire in the next 10 years, representing about 51 GW.
-
Solar
Interest, Funding Buoys Floating Solar Power Plants
Like most forms of generation, solar power has its disadvantages. Two cited most by critics of photovoltaic (PV) or concentrating solar power facilities are that they require large expanses of land and that solar cell fabrication and maintenance costs are high. Several companies have been assessing a new approach to tackling these factors: installing solar plants on water.
-
Coal
Predicting U.S. Coal Plant Retirements
The question concerning coal plant retirements forced by looming regulatory rules, low gas prices, and moribund load growth has changed from “Why?” to “How many plants?” Many highly detailed analyses and reports have been written on the subject by superbly qualified analysts. This approach to estimating potential plant closures is much more qualitative, and much easier to understand. However, the results closely align: About 50 GW are threatened.
-
Business
POWER Digest (May 2011)
ABB, BHEL to Deliver $1.1B Multi-Terminal UHVDC Line in India. Zurich-based ABB and Indian state-owned company Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd. (BHEL) said on March 23 that they had been selected by Power Grid Corp. of India Ltd. (PGCIL) to deliver an ultrahigh-voltage direct current (UHVDC) transmission system to convey hydropower from northeastern India to the […]
-
Nuclear
Chernobyl: Twenty-Five Years of Wormwood
Twenty-five years ago last month, engineers and technicians were running low-power tests at the 1,000-MW Reactor No. 4 of the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant outside Kiev. They quickly, inexplicably, lost control of the light-water-cooled, graphite-moderated reactor. In an instant, the critical chain reaction flared out of control. The plant exploded like a small, dirty bomb, the graphite caught fire, and the worst catastrophe in civilian nuclear power was under way.
-
Coal
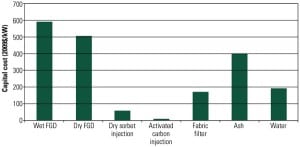
Coal-Fired Generation Cost and Performance Trends
Increasing regulatory requirements and a focus on reducing carbon emissions in the U.S. have significantly reduced the number of new coal-fired plants under development compared with past years. In addition, projected capital costs for new coal-fired plants have risen sharply in the past year, while those for natural gas combined-cycle and combustion turbines have stayed relatively flat. In order to keep coal a viable energy source, many countries, including the U.S., are seeking ways to improve plant efficiency while reducing carbon emissions.
-
Coal
Proactive Strategies for Dealing with Combustible Dust
The challenges of using Powder River Basin (PRB) coal are as significant as the rewards. The subbituminous coal contains lower amounts of sulfur dioxide than bituminous coal but can be prone to combustible dust explosions if it is not properly managed. To eliminate such hazards, plant personnel need to establish best practices for the safe operation and maintenance of PRB coal-handling and -storage systems based on best available technologies.
-
Hydro
New York City Backs Tidal Power
The Roosevelt Island Tidal Energy (RITE) pilot project used six full-scale hydrokinetic turbines to capture the power of river tides and currents and convert it into electricity. Located in New York City’s East River, it is the first and only grid-connected tidal array project in the world. RITE project developers are seeking approval to install up to 30 additional turbines in the near future.
-
Commentary
Disaster Management
The events in Japan, including the catastrophic destruction of a major nuclear power station, remind us of something we don’t like to think about: how to manage a physical disaster. But manage we must.
-
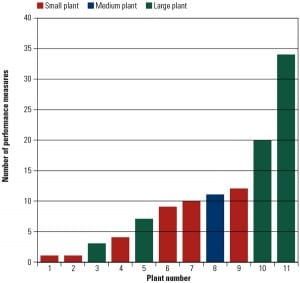
Coal
Benchmarking Fossil Plant Performance Measures, Part III: Metrics Used for Compensation
In Part III of this three-part report, we look at plant- and fleet-level metrics used to determine compensation. As expected from this EUCG-sponsored benchmarking survey, there is broad use of quantifiable metrics to set portions of compensation, but the metrics selected vary substantially across the surveyed utilities. More surprising was the number of utilities that used no performance metrics as part of their employee compensation packages.
-
Supply Chains
TREND: Markets and Critical Materials
While China seems determined to exploit its current control over the market for rare earths and other minerals critical to high-tech and green energy technologies, and while governments engage in conventional hand-wringing and head-scratching, markets appear to be reacting in the ways that markets are supposed to react.
-
News
Self-Propelled Spent Fuel Cask Transporter
The new Wheelift Self-Propelled Modular Transporter increases safety in spent fuel cask transport and alignment for NUHOMS-type ISFSI installations by reducing worker exposure because only one person is needed to operate the transporter from between 30 feet and 50 feet away. The transporter’s omni-directional steering and 10-inch lift capability enables the same operator to perform […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
The Energy Efficiency Conundrum
For many energy analysts and policy makers, efficiency is the Holy Grail, the universal solvent, the way to effortlessly reconcile supply and demand while simultaneously serving the needs of the environment. Don’t build new power plants, says policy guru Amory Lovins; gather "negawatts" instead. President Obama says that Americans "can save as much as 30% of our current energy usage without changing our quality of life."
-
News
NOx Burner Optimization Kit for All Burners
Hamworthy Peabody Combustion’s new Q-jet Low NOx Burner Optimization Kit can be retrofitted to practically any existing burner, regardless of manufacturer, to increase efficiency and reduce maintenance. In addition, the Q-jet Kit eliminates the need to replace complete burner assemblies just to meet emissions requirements, saving time and money. A key feature is that the […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Supreme Court Expands Employee Rights
U.S. Supreme Court rulings in two recent cases further advance the rights of employees in disputes with employers, continuing a long-term trend in federal law on employment discrimination.
-
News
Forged Ball Valves
Valve-maker Conval announced that its popular Camseal zero-leakage ball valves now have forged bodies. These new forged ball valves are available in half-inch through 4-inch sizes with top entry, socket weld, butt weld, and flanged ends. Pressure classes range from ASME 900 through 4500. Camseal forged ball valves feature zero body leakage, zero seat leakage, zero seal […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Japan, Critical Materials, and Weak Links in Supply Chains
The devastation in Japan has focused new attention on supply chain issues and the impact of the partial collapse of that country’s manufacturing infrastructure on both Japanese imports and exports.
-
News
Nuclear Sneak Attack
A renewed attack on nuclear power immediately followed the March 11 catastrophe at the six-unit Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power complex in Japan. At least one legislator and a multitude of anti-nuclear groups have demanded that the U.S. cease approval of all new nuclear plants for the foreseeable future and/or close our Mark I boiling water reactor (BWR) plants. This knee-jerk response adds nothing substantive to the nuclear safety debate. (Be sure to read our cover story for more on this issue.)
-
Commentary
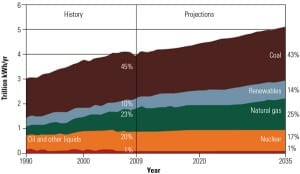
Solving the Challenges of Growing Energy Demand
The electric power generation landscape in both America and the rest of the world is poised to undergo a fundamental transformation in the next several decades. Global energy consumption is projected to rise dramatically by 2035, and the methods by which we generate electricity and the fuels we choose to use will begin to change as well.
Search