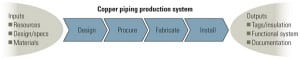
Gas
-
Gas
Top Plant: Langage Combined Cycle Power Plant, Plymouth, Devon, UK
The UK grid, focused on adding valuable renewable generation, will rely on natural gas–fired generation for many years to come. One of the most recent additions is the Langage Power Plant, designed for quick response and low load “parking” at night while remaining below air emissions limits. With an extraordinary architectural design that blends into the natural surroundings, Langage is now a local landmark.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Panoche Energy Center, Firebaugh, California
The Panoche Energy Center is a 400-MW simple-cycle power plant using four of General Electric’s GE LMS100s with fast-start capability. Dispatched by Pacific Gas & Electric to meet regional power and grid stabilization needs, the project entered commercial service two months earlier than planned. Panoche is the largest LMS100 peaking facility in the U.S.
-
Gas
High-Efficiency Gas Turbines Go to Market
This May, following two years of construction, Siemens Energy put into operation Irsching 5, an 847-MW advanced combined-cycle power plant near Ingolstadt, Germany. The plant’s owner, Gemeinschaftskraftwerke Irsching GmbH—a joint venture of E.ON, Mainova, and HEAG Südhessische Energie—features two SGT5-4000F gas turbines, one SST5-5000 steam turbine, three hydrogen-cooled generators, electrical systems, and Siemens’ SPPA-T3000 instrumentation and control system.
-
Coal
Breathing Added Life into Failing Heat Exchangers
When heat exchanger tubes—sometimes numbering a thousand or more per unit—begin to crack or wear, the effects can lead to a cascade of subsequent failures in adjacent tubes. If too many tubes are plugged, heat exchanger effectiveness is compromised, and power generation may be curtailed. If conventional mechanical plugs are used, they can break loose, leak, and fail. At that point, the replacement of a very costly heat exchanger is imminent.
-
Gas
Local Warming: Helsingin Energia Uses CHP to Heat a City
Power plant operators, especially those located in countries with enforceable carbon emissions standards, are concerned about their CO2 emissions. But for Helsingin Energia—which provides power, heating, and cooling for Helsinki, Finland’s 300,000 residents—the main concern is local warming, not global warming. In Helsinki, temperatures on midsummer afternoons only reach an average 21C, and for half the year daytime temperatures are below 10C.
-
Coal
Protect Your Stack Linings from Corrosion
Stacks at power generating stations may be low maintenance, but they are not no maintenance. The cost of preventing corrosion may be as little as $10,000, but the cost of repair or replacement could be many times that or even put your plant out of commission until the stack problem is corrected.
-
Coal
Luminant’s Oak Grove Power Plant Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
Luminant used remnants of the ill-fated Twin Oaks and Forest Grove plants (which were mothballed more than 30 years ago) to build the new two-unit 1,600-MW Oak Grove Plant. Though outfitted with equipment from those old plants, Oak Grove also sports an array of modern air quality control equipment and is the nation’s first 100% lignite-fired plant to adopt selective catalytic reduction for NOx control and activated carbon sorbent injection technology to remove mercury. For melding two different steam generators into a single project, adopting a unique and efficient “push-pull” fuel delivery system, assembling a tightly integrated team that completed the project on time and within budget, and for completing what was started almost four decades ago, Oak Grove Power Plant is awarded POWER magazine’s 2010 Plant of the Year award.
-
Coal
Lean Construction Principles Eliminate Waste
Eliminate waste in coal, gas, or nuclear power plant construction through a holistic application of lean principles.
-
Gas
Qatar Opens 2,000-MW Gas Plant
The gas-rich emirate of Qatar, holder the world’s third-largest gas reserves, inaugurated another massive 2,000-MW gas power plant in the industrial city of Mesaieed, south of the capital Doha this May.
-
Gas
Qatar Opens 2,000-MW Gas Plant
The gas-rich emirate of Qatar, holder the world’s third-largest gas reserves, inaugurated another massive 2,000-MW gas power plant in the industrial city of Mesaieed, south of the capital Doha this May.
-
History
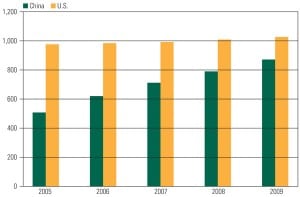
China: A World Powerhouse
It’s no surprise that China leads the world in recent power capacity additions. What may surprise you is the precise mix of options this vast country is relying upon to meet its ever-growing demand for electricity. As a result, this ancient civilization is fast becoming the test bed and factory for the newest generation and transmission technologies.
-
Coal
Industry Pivots on Natural Gas, Hails Cap and Trade
At the opening ELECTRIC POWER 2010 plenary session, both the keynote speaker’s address and discussion among the Power Industry Executive Roundtable participants pointed to the renewed appeal of natural gas and proposed cap-and-trade legislation as being potential game-changers for the U.S. power industry.
-
O&M
Improving SCR Performance on Simple-Cycle Combustion Turbines
Austin Energy replaced the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalyst twice over five years for its four peaker turbines. The duct modifications and injection grid redesign, combined with new catalyst, are producing high NOx reduction and low ammonia slip, and the catalyst is now expected to last at least five years.
-
O&M
Real-Time Monitoring of Natural Gas Fuel Cleanliness
Gas turbines require clean gas to operate efficiently. Particulate contamination fouls fuel nozzles, causes increases in flue stack emissions, and occasionally causes unplanned plant outages. Now a new real-time natural gas cleanliness monitoring and web-based alarm system is providing valuable protection for natural gas–fired power plants. The adaptation of laser light–scattering technology for the purpose of contaminant measurement in high-pressure gaseous pipelines provides a method of monitoring liquid and solid contamination levels.
-
Gas
DOE Expedition Confirms Resource- Quality Gas Hydrate in the Gulf of Mexico
Gas hydrate, a potentially immense energy resource, occurs at high saturations within reservoir-quality sands in the Gulf of Mexico, an expedition by the U.S. Department of Energy has discovered.
-
Gas
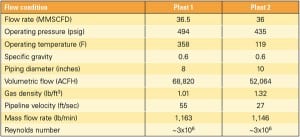
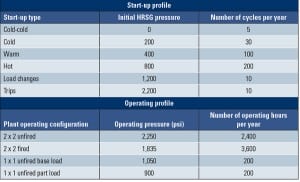
Economic Operation of Fast-Starting HRSGs
Fast-starting combined-cycle plants are designed for a certain operating life based on a customer-specified set of operating scenarios. During that design phase, periodic inspection and maintenance procedures to benchmark equipment actual wear and tear should be developed, but seldom are. Without an accurate assessment of remaining equipment life for components subjected to fast and frequent […]
-
Gas
Kawasaki Plant Claims Efficiency Record
Tokyo Electric Power Co.’s new Kawasaki Thermal Power Plant claims the title of having the highest combined-cycle efficiency in the world: 59.1%. The new gas-fired facility is equipped with three 500-MW single-shaft combined-cycle blocks. Each block is based on the MHI M701G2 gas turbine, which is the largest gas turbine currently in commercial operation.
-
O&M
Natural Gas Piping: It’s Time for Better Risk Control
At least 10 workers have died from natural gas piping explosions in the past 12 months. The most recent disaster, which occurred during gas system purging at the Kleen Energy Systems plant, claimed five lives and injured 27 workers. It’s time the industry understood the unique design and safety requirements for working with and purging natural gas piping.
-
Coal
Adding Desalination to Solar Hybrid and Fossil Plants
Shrinking water supplies will unquestionably constrain the development of future power plants. A hybrid system consisting of concentrated solar thermal power and desalination to produce water for a plant, integrated with a combined cycle or conventional steam plant, may be the simple solution.
-
Gas
Brazil Beings Operation of Ethanol Power Plant
Brazil’s state-owned oil producer, Petrobras, on Dec. 31, 2009, said it had inaugurated the world’s first power plant to run exclusively on ethanol.
-
Coal
Plant Efficiency: Begin with the Right Definitions
The race is on to claim the title of "most efficient coal-fired power plant" on the planet. However, it’s tricky identifying finalists because of the widespread misuse of the term "efficiency" and all those nagging assumptions. Let’s first establish clear definitions and then identify the title contenders.
-
O&M
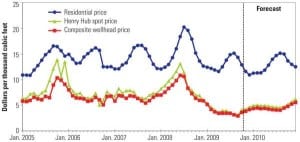
The U.S. Gas Rebound
"It’s déjà vu all over again," said Yogi Berra. The Hall of Fame catcher could easily have been predicting the coming resurgence of natural gas – fired generation. Yes, a few more coal plants will be completed this year, but don’t expect any new plant announcements. A couple of nuclear plants may actually break ground, but don’t hold your breath. Many more wind turbines will dot the landscape as renewable portfolio standards dictate resource planning, but their peak generation contribution will be small. The dash for gas in the U.S. has begun, again.
-
Coal
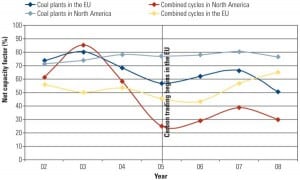
The Impact of Carbon Trading on Performance: What Europe’s Experience Can Teach North American Generators
The European carbon trading system experience suggests that North American generators should expect severely altered coal-fired power plant operating profiles if cap-and-trade legislation becomes law. In a groundbreaking study, Solomon Associates predicts the reduction in mean run time that North American generators should expect. The trends outlined in this study provide an overview of some of the broad challenges facing generators in moving to a carbon-constrained market environment.
-
Coal
Brazil: Latin America’s Beacon
With the eighth-largest economy in the world, Brazil has a clear need for power, but balancing supply and demand has proven tricky in recent decades. Even in a country where over 80% of generation capacity comes from renewables, planning for future capacity additions isn’t straightforward or easy.
-
Gas
New-Generation Gas Turbines Steam Ahead
This September, as Siemens Energy wrapped up testing of its H-class SGT5-8000H gas turbine at E.ON’s Irsching 4 gas power plant in Bavaria, Germany, the company raved about what it is calling "the world’s most powerful gas turbine."
-
O&M
Top Plants: Royal Pride Holland Commercial Greenhouse Cogeneration Plant, Middenmeer, North Holland Province, Netherlands
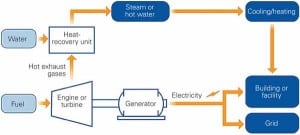
At Royal Pride Holland’s commercial tomato greenhouse, green thumbs and green energy go hand in hand. With a total energy utilization of 95% in this application, GE’s new Jenbacher J624 natural gas – fired engines offer the innovative greenhouse an economical supply of on-site electrical and thermal power, as well as CO2 fertilization, to support its operations.
-
Coal
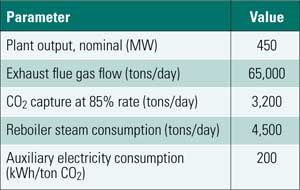
Combined-Cycle Carbon Capture: Options and Costs, Part I
Uncertainty about CO2 emissions legislation is prompting power plant owners to consider the possibility of accommodating "add-on" CO2 capture and sequestration solutions for coal-fired plants in the future. Those same plant owners may be overlooking the possibility that future natural gas – fired combined cycles will also be subject to CO2 capture requirements. This month we examine the capture options. In a future issue, Part II will present the installation and operating costs of different carbon capture technologies.
-
Gas
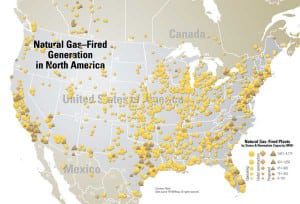
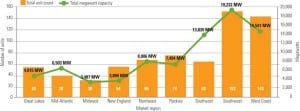
New Natural Gas–Fired Projects on an Upswing
Over the past decade, the development of new natural gas – fired generating assets has been similar to an amusement park roller coaster ride — very high peaks and the lowest of lows, with fast and stomach-churning movement between. Expect the ride to continue into the near future.
-
O&M
Accurate Online Silica Analyzers Ensure Boiler Performance, Add Boiler Life
One key area at the 800-MW Michoud power station where O&M excellence is evident is in maintaining plant water quality.