Environmental
-
Coal
DOE Warns of Coal Plant Water Supply Shortages
With utilities already alarmed by looming federal regulations that could force construction of expensive cooling towers that would sharply increase water use, a report by the Energy Department’s Argonne National Laboratory warns that nearly 350 U.S. coal-fired power plants are vulnerable to potential water demand or supply conflicts over the next 20 years stemming from increased competition for dwindling water resources—particularly in the Southeast.
-
Coal
Peabody: China, India Leading Coal "Supercycle"
While U.S. coal production has been stagnant in 2010, demand for coal in China and India has sharply risen this year and could represent the early stages of a "long-term supercycle" for the global coal industry, according to Peabody Energy, the world’s largest private coal company.
-
Coal
EPA Regulations Accelerate Industry Shift from Wet to Dry Bottom Ash Solutions
Energy efficient and environmentally responsible dry bottom ash technologies will soon be required by regulation. Progressive companies will bring their plants into compliance early because it’s a good business strategy. Here are your compliance options.
-
Coal
Southern Co. Captures Carbon Dioxide at Plant Yates Pilot
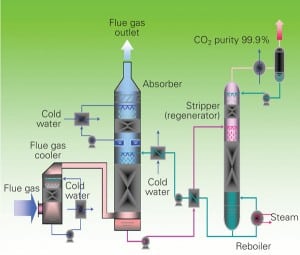
The pilot-scale project at Georgia Power’s Plant Yates near Newnan, Ga.—the first step in one of the industry’s largest demonstrations of a start-to-finish coal-fired power plant carbon capture and storage system—reached a significant milestone this September, capturing the greenhouse gas for the first time.
-
Coal
Frog-Inspired Artificial Foam Could Help Trap CO2
In August, researchers from the University of Cincinnati who are working on creating an artificial foam that could absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the flue gas at power plants and convert it into biofuel won the grand prize at the 2010 Earth Awards in London.
-
Nuclear
NRC Confident in Long-Term Dry Cask Storage
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) approved an updated “waste confidence” rule in mid-September that reflects the agency’s confidence that spent nuclear fuel (SNF) can be safely stored for at least 60 years beyond the closing date of any U.S. nuclear plant. Approval of this rule was required before the NRC can license any new reactors that will be required to store SNF on site indefinitely.
-
Legal & Regulatory
EPA’s Mercury Rule: Another Incarnation Coming
Much like the shape-shifting substance it regulates, the mercurial enforcement rule that governs mercury emissions from coal-fired power plants has changed unpredictably several times in recent years.
-
Gas
Smart Power Generation at UCSD
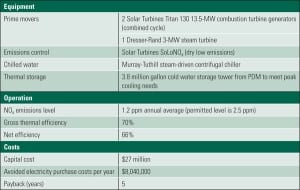
The University of California, San Diego has been accumulating awards for its savvy use of a constellation of power generation and energy-saving technologies. The campus already controls a fully functioning microgrid—including a cogeneration plant—and, as befits a research institution, is constantly looking for new ways to make its energy system smarter. This “living laboratory,” as campus leaders like to call it, demonstrates what it takes to build a smarter grid and why the effort is worth it.
-
Coal
EPA Air Regulations Shrinking Power Glut
Pending Environmental Protection Agency regulations to slash U.S. power plant emissions likely will lead to the closure of nearly 18% of the nation’s coal-fired generation capacity, trim demand for steam coal by 15% to 31% and boost demand for natural gas by 8% to 16%, a new Credit Suisse analysis concludes.
-
Coal
TVA Eyes Cleaner "Vision" with More Nukes, Less Coal
Responding to looming federal regulations to reduce power plant pollution, the Tennessee Valley Authority’s board signed off on a proposal to shut down 1,000 MW of older coal-fired generation and replace it with an equal amount of natural gas capacity while also pursuing 1,900 MW of demand response and energy efficiency programs and adding 1,140 MW of new nuclear generation by 2015.
-
Coal
EPA Boiler Regulations Will Strangle Construction of New Power Plants
An Environmental Protection Agency plan to tighten emission limits for new and existing industrial boilers has sparked alarmed protests from the biomass generation industry and electric utilities, who say the proposed regulations are so onerous they threaten to shut down existing biomass power plants and already are chilling deployment of new facilities.
-
Coal
Overblown: Wind Power on the Firing Line, Part I
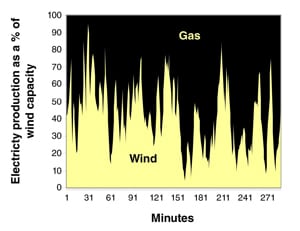
The conventional and oft-repeated truth is that wind generation directly reduces carbon emissions. Challenging the conventional wisdom has drawn much criticism from wind proponents, but the latest research has shown that wind has had, and will continue to have, negligible impact on the nation’s carbon emissions. The data are convincing and can no longer be ignored.
-
Coal
Overblown: Wind Power on the Firing Line, Part II
Wind electricity production must displace some existing generation. However, its relentless variability imposes daunting challenges for wind integration. Clever engineering schemes can mask the problem, but the data show that wind generation has and will continue to reduce carbon by negligible amounts, but at great expense.
-
Solar
What Utility Executives Think About the Smart Grid
This summary of results from a recent Platts/Capgemini survey of North American utility executives looks at what respondents had to say about all things related to the smart grid. Nearly half of respondents’ utilities have a smart grid strategy in place, while the other half said their utility has one in development.
-
Coal
AEP Blasts EPA Transport Rule; PSEG Supports It
An Environmental Protection Agency proposal to tighten sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides limits in 31 states and the District of Columbia to address transported air pollution fails to give utilities and state air regulators sufficient time to develop rules and install controls, according to American Electric Power Co. Officials from the EPA and New Jersey-based Public Service Enterprise Group said utilities already had begun making investments to cut emissions and they believed the agency’s compliance schedule could be met.
-
O&M
Wind Integration: Does It Reduce Pollution and Greenhouse Gas Emissions?
Many claim that wind generation is beneficial because it reduces pollution emissions and does not emit carbon dioxide. This isn’t necessarily the case. When wind is introduced into a generation system that uses carbon technologies to back up the wind, it actually reduces the energy efficiency of the carbon technologies.
-
Coal
Fourth Circuit Scuttles NC Air “Nuisance” Suit
Scuttling a high-profile “public nuisance” lawsuit, a federal appeals court has reversed a lower court ruling that required the Tennessee Valley Authority to accelerate plans to install pollution controls at four TVA coal-fired power plants to reduce the amount of pollution blowing into western North Carolina, saying the lower court decision could lead to other public nuisance suits that would wreak havoc on federal and state regulatory regimes for combating air pollution.
-
Coal
House Members Warn EPA on Coal Ash
Saying they have “grave concerns” about the agency’s two-option proposal to regulate coal combustion ash, 31 members of the House Energy and Commerce Committee have urged the Environmental Protection Agency to continue to regulate coal ash as a non-hazardous waste, saying an EPA proposal to designate it as a “special” hazardous waste eligible for reuse would lead to costly and unnecessary management and disposal requirements.
-
Coal
Advanced SCR Catalysts Tune Oxidized Mercury Removal
Catalysts used in selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems in utility boilers provide high NOx removal efficiencies that routinely exceed 90%. A major co-benefit of applying SCR to coal-fired power plants is that the SCR catalyst also oxidizes the vapor phase mercury from an elemental form to a soluble ionic form, which can be readily captured in a downstream flue gas desulfurization process. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and Cormetech have developed an advanced SCR catalyst technology with high mercury oxidation activity capable of achieving 95% oxidized mercury over a wide range of operating conditions.
-
Coal
Luminant’s Oak Grove Power Plant Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
Luminant used remnants of the ill-fated Twin Oaks and Forest Grove plants (which were mothballed more than 30 years ago) to build the new two-unit 1,600-MW Oak Grove Plant. Though outfitted with equipment from those old plants, Oak Grove also sports an array of modern air quality control equipment and is the nation’s first 100% lignite-fired plant to adopt selective catalytic reduction for NOx control and activated carbon sorbent injection technology to remove mercury. For melding two different steam generators into a single project, adopting a unique and efficient “push-pull” fuel delivery system, assembling a tightly integrated team that completed the project on time and within budget, and for completing what was started almost four decades ago, Oak Grove Power Plant is awarded POWER magazine’s 2010 Plant of the Year award.
-
Coal
Cleco’s Madison Unit 3 Uses CFB Technology to Burn Petcoke and Balance the Fleet’s Fuel Portfolio
With commercial operation of Madison Unit 3, Cleco Power now claims bragging rights for owning the largest 100% petroleum coke–fired circulating fluidized bed power plant in North America. For using readily available fuel in an environmentally attractive manner, adopting fuel-flexible combustion technology, balancing the utility’s generation portfolio, and adopting an innovative fuel-handling system design, Madison Unit 3 is the winner of POWER’s 2010 Marmaduke Award for excellence in operation and maintenance. The award is named for Marmaduke Surfaceblow, the fictional marine engineer and plant troubleshooter par excellence.
-
O&M
New Process Transforms Waste into Product for Controlling Emissions
In April, Solvay Chemicals Inc. commissioned a new facility that uses an innovative process to recover and transform sodium carbonate waste streams into a market-grade sodium bicarbonate used in air emissions control.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Climate Change: Avoid Political Thickets
A federal judge recently dismissed a lawsuit in which the plaintiffs alleged that defendants’ production of chemicals and electricity had “added to the ferocity of Hurricane Katrina.” The judge’s reasoning reveals the inherent limitations of courts unilaterally initiating policies to address climate change issues.
-
History
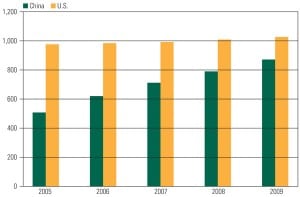
China: A World Powerhouse
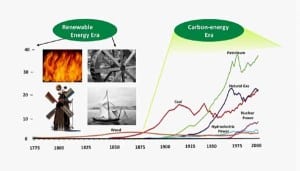
It’s no surprise that China leads the world in recent power capacity additions. What may surprise you is the precise mix of options this vast country is relying upon to meet its ever-growing demand for electricity. As a result, this ancient civilization is fast becoming the test bed and factory for the newest generation and transmission technologies.
-
Water
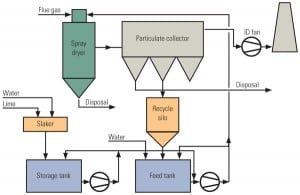
ReACT Reduces Emissions and Water Use
Regenerative activated coke technology (ReACT) is an integrated multipollutant control approach that removes SOx, NOx, and Hg from coal-fired plants by adsorption with activated coke to attain emissions levels found at natural gas–fired plants. One big advantage of this technology is that it uses only a fraction of the water used by conventional wet flue gas desulfurization. A recent license agreement brings this technology to the U.S.
-
Water
Circulating Fluid Bed Scrubbers Bridge the Gap Between Dry and Wet Scrubbers
Circulating fluid bed (CFB) dry scrubbing technologies provide distinct advantages over conventional spray dryer absorber scrubbers for removing SO2 from flue gases. The CFB also competes well against wet limestone flue gas desulfurization processes typically favored for large boilers firing high-sulfur coals. With high SO2 removal rates in a dry treatment process, the CFB scrubber appears to be the best of both technologies: a water-stingy scrubber with high SO2 removal rates.
-
Coal
Drax Offers Model for Cofiring Biomass
When it is completed, later this summer, the UK’s Drax Power Station biomass facility will become the largest dedicated cofiring project of its kind in the world. As U.S. coal-fired generators come under increasing pressure to cut emissions and take advantage of incentives to promote power generation from renewables, Drax offers an example of what is possible.
-
Environmental
Regulations and Economics Drive Wet FGD Upgrades
Today’s coal-fired power plants face the twin challenges of improving their wet flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems’ emission control capabilities in order to comply with environmental regulations while at the same time cutting their operational and maintenance costs. Smart strategies for retrofitting existing FGD systems can help plant personnel meet both of these objectives.
-
Coal
Industry Pivots on Natural Gas, Hails Cap and Trade
At the opening ELECTRIC POWER 2010 plenary session, both the keynote speaker’s address and discussion among the Power Industry Executive Roundtable participants pointed to the renewed appeal of natural gas and proposed cap-and-trade legislation as being potential game-changers for the U.S. power industry.
-
Environmental
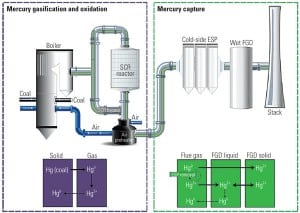
Determining AQCS Mercury Removal Co-Benefits
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is expected to propose an emissions standard for mercury and other hazardous air pollutants emitted by coal- and oil-fired electric generating units in March of 2011. The anticipated rule would require emission control to meet the various standards using maximum achievable control technology, as determined by the prescriptive requirements of the Clean Air Act. In response to the expected rule-making, utilities will be required to make technology decisions in order to ensure compliance. One cost-effective approach to compliance may be the use of “co-benefits” from air quality control systems (AQCSs) already in service that are designed to remove other pollutants.