Coal
-
Coal
Up in Smoke: Measuring Mercury in Stack Gases
Two types of mercury monitoring are required of coal-fired power plants: continuous emission monitoring and periodic Relative Accuracy Test Audit. One of the more attractive approaches for these analyses is provided by the Hydra-C Appendix K from Teledyne Leeman Labs.
-
Coal
California Climate Plan Touts New Renewables, Trading Allowance Schemes
In a sweeping climate change proposal that could serve as a model for the nation, two California agencies have proposed a comprehensive program for reducing the state’s greenhouse gas emissions that calls for aggressive improvements in energy efficiency, higher targets for renewable energy, and an innovative scheme for allocating emission allowances to electric utilities.
-
Coal
GAO: Lack of U.S. Greenhouse Strategy Slowing Carbon Capture
A Government Accountability Office (GAO) study released in late September concludes that technological, legal, and regulatory uncertainties—compounded by the absence of a national strategy for combating global warming—are blocking deployment of crucial technology to capture and sequester carbon dioxide from coal-fired power plants.
-
Coal
“Cap and Dividend” Proposal Targets Carbon Suppliers
As senior members of Congress lay the groundwork for a new legislative debate on climate change next year, a new proposal making the rounds of Capitol Hill offices would replace the cap-and-trade approach now in vogue with one in which all carbon permits are auctioned and all auction revenues are returned to consumers.
-
Coal
Debunking the Chinese coal monster myth
A detailed analysis of power plants in China by researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) debunks the widespread notion that outmoded energy technology or the utter absence of government regulation is to blame for that country’s notorious air-pollution problems. The real issue, the study found, involves complicated interactions among new market forces, new […]
-
Coal
Vattenfall inaugurates first CCS pilot plant
On Sept. 9, Sweden’s Vattenfall inaugurated the world’s first demonstration plant that connects carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology in a full-chain working system. The inauguration of the pilot plant at Schwarze Pumpe in Germany, which underwent 10 years of testing, was a milestone that marked its move from the laboratory to reality, Vattenfall said. […]
-
Coal
Under construction in South Africa
This summary of power generation projects is a web-only supplement to the November 2008 special report titled “Whistling in the dark: Inside South Africa’s power crisis.”
-
Coal
TS Power Plant, Eureka County, Nevada
Top Plant: Not all coal-fired power plants are constructed by investor-owned utilities or independent power producers selling to wholesale markets. When Newmont Mining Corp. recognized that local power supplies were inadequate and too expensive to meet long-term electricity needs for its major gold- and copper-mining operations in northern Nevada, it built its own generation. What’s more, Newmont’s privately owned 200-MW net coal-fired plant features power plant technologies that will surely become industry standards. Newmont’s investment in power and technology is also golden: The capital cost will be paid back in about eight years.
-
Coal
Rawhide Energy Station, Fort Collins, Colorado
Top Plant: The staff of the Rawhide Energy Station have been racking up operating stats and an environmental performance record that is the envy of other plant managers. In the past decade Rawhide has enjoyed an equivalent availability factor in the mid- to high 90s and an average capacity factor approaching 90%. Still not content with this performance, Rawhide invested in new technology and equipment upgrades to further optimize performance, reduce emissions, and keep cost competitive.
-
Coal
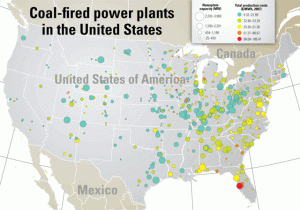
Map of Coal-fired Power Plants in the United States
Courtesy: Platts Data source: Platts Energy Advantage and POWERmap. All rights reserved.
-
Coal
Boryeong Thermal Power Complex, Boryeong-Si, Chungcheongnam-do Province, South Korea
Top Plant: From tall skyscrapers and flashing neon signs to Buddhist temples and pagodas, South Korea is a mixture of the new and old Asia. Doing its part to help modernize this country, the Boryeong Thermal Power Complex operates six coal-fired 500-MW units that provide electricity to power South Korea’s economic growth. One of the important reasons for this facility’s overall success is its operational reliability. An example of this is Boryeong Unit 3’s outstanding achievement of 3,000 days of trouble-free operation.
-
Coal
Dubuque Generating Station, Dubuque, Iowa
Top Plant: Alliant Energy’s Dubuque Generating Station is a fine example of why small doesn’t mean insignificant in the power generation industry. This winner of the EUCG Best Performer award in the small plant category shows that its operating excellence towers over that of many larger and much newer coal-fired power plants.
-
Coal
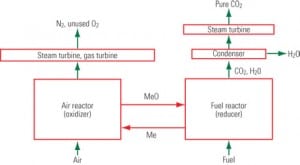
Chemical looping and coal
What does human metabolism have in common with coal combustion? Quite a bit, it turns out, say researchers at the National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL) who are studying chemical looping combustion (CLC) involving coal gasification, an emerging technology for clean energy production from fossil and renewable fuels.
-
Coal
Computer simulation as a NOx reduction design tool
A utility evaluated various methods of obtaining a NOx reduction of at least 30%, as required by upcoming regulations for its boiler, which originally produced 0.54 lb of NOx/million Btu at 410 MW full load. Nalco Mobotec engineers performed a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation of the boiler to first understand the boiler’s combustion process and then determine the most economical method to achieve the required NOx reduction.
-
Coal
J.K. Spruce Power Plant, Unit 1, San Antonio, Texas
Top Plant: CPS Energy’s J.K. Spruce Power Plant, Unit 1 was recently recognized by the EUCG Fossil Productivity Committee as the best performer in the large coal plant category over the 2002-2006 evaluation period. The competition was tough, with more than 80 plants in the running, but Unit 1 emerged as the clear winner by earning top points for high plant reliability and very low nonfuel O&M costs.
-
Coal
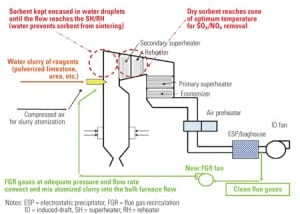
Bringing down the cost of SO2 and NOx removal
A twist on an old technique, flue gas recirculation, helps prevent slagging in the upper furnace and convective pass, according to pilot testing recently completed by APTECH CST and the Southern Research Institute. The technology—along with a companion technology for furnace sorbent and urea injection for SO2 and NOx control—could help owner/operators of smaller, older coal-fired plants meet emissions limits at a reasonable cost.
-
Coal
Finessing fuel fineness
Most of today’s operating coal plants began service at least a generation ago and were designed to burn eastern bituminous coal. A switch to Powder River Basin coal can stress those plants’ boiler systems, especially the pulverizers, beyond their design limits and cause no end of operational and maintenance problems. Many of those problems are caused by failing to maintain good fuel fineness when increasing fuel throughput.
-
O&M
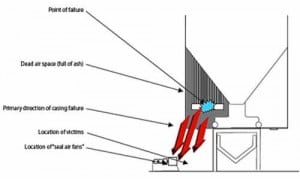
Anatomy of a Boiler Failure—A Different Perspective
The power industry’s operating and maintenance practices were held up to intense regulator and public scrutiny when on November 6, 2007, a Massachusetts power plant’s steam-generating boiler exploded and three men died.
-
O&M
The Low-Down on Low-Alloy Filler Metals
Chromium-molybdenum (chrome-moly) pipe has become a standard in the power generation industry, not only because of its corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength, but also for its cost-effectiveness. In many applications, it is a viable alternative to a more costly stainless steel pipe.
-
Coal
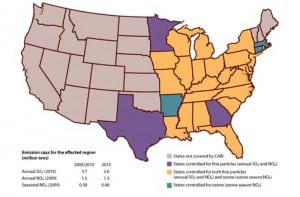
Who Cares about CAIR?
In a bid to preserve some of the health and air quality benefits of a defunct regulation, House Democrats have floated a legislative proposal to codify the near-term emission reductions required under the Bush administration’s Clean Air Interstate Rule, a regional cap-and-trade program for utility emissions that was thrown out in July by a federal appeals court.
-
O&M
Hill Backing New FERC Powers on Grid Cyber Attacks
Spurred on by a recent audit showing widespread utility noncompliance with voluntary recommendations meant to protect the grid from cyber attacks, key lawmakers have unveiled plans to give the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) broad powers to enact new mandatory measures to close vulnerabilities in the U.S. bulk power system to potentially devastating computer-launched assaults.
-
Coal
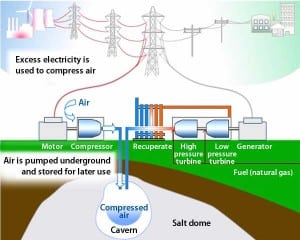
Revived Energy Storage Technology Offers Major Grid Benefits
In a move that could boost the value of wind and nuclear generation, relieve stress on the nation’s transmission grid, and reduce utility carbon emissions, PSEG Global LLC and energy storage pioneer Michael Nakhamkin have announced that they have formed a joint venture to market and deploy “second generation” compressed air energy storage technology.
-
Coal
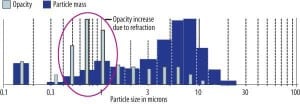
The Problem of Fine Particles
No matter what its size, fine particulate matter is a serious matter for coal-burning power plants. A process that charges those particles shows promise for mitigating the problem.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (September 2008)
Cost hikes for all things nuclear in the U.S. and UK / North Americans plan liquid makeover for coal / California balloon bill deflates in legislative process / The Lego skyscraper / Of manure and methane / U.S. small wind turbine market moving slowly / Israeli desert center tests solar thermal tech for California desert / POWER digest / Correction
-
Coal
Wisconsin Public Service Corp.’s Weston 4 earns POWER’s highest honor
Wisconsin Public Service Corp. placed its world-class Weston 4 into commercial service on June 30 and is now enjoying the benefits of coal-fired supercritical technology’s inherently higher efficiency, operating flexibility, and lower CO2 emissions. For its unequalled environmental protection credentials, well-integrated project team, and employing without a doubt the most advanced coal-fired steam generation technology in the U.S. today, Weston 4 is awarded POWER magazine’s 2008 Plant of the Year award.
-
Coal
Lamar Repowering Project’s creative melding of old and new wins Marmaduke Award
Lamar Light and Power is a municipal utility that has been generating the southeastern Colorado city’s electricity since 1920. Rising natural gas and oil costs pushed LL&P to retire its steam plant five years ago and begin hunting for more economic power sources. The answer: repower the existing plant with a state-of-the-art coal-fired circulating fluidized-bed combustor and cross-connect old and new steam turbines. The $120 million project will stabilize the region’s electricity rates for many years to come and is the winner of POWER’s 2008 Marmaduke Award for excellence in O&M—named for Marmaduke Surfaceblow, the fictional marine engineer/plant troubleshooter par excellence.
-
Coal
Oh Canada! B.C. ratifies North America’s first carbon tax
British Columbia began collecting increased tax revenue on fossil fuels on July 1 with a promise to rebate those taxes through reduced income and business tax rates. This "revenue recycling" plan makes little progress toward the province’s goal to reduce CO2 emissions 33% by 2020, yet it is hailed by proponents as a legislative milestone. Others believe B.C. residents are victims of another governmental "bait and switch" program. Does it matter to the rest of the world?
-
O&M
How to Measure Flyash Levels
Measuring the level of flyash in your silos is not an easy task, in part because the flyash collected at one plant can be remarkably different from that collected at another plant, even if both fire the same coal. Such variability means that selecting the right instrument for your application is important.
-
Coal
Court Kicks CAIR Rules to the Curb
A federal appeals court has struck down a key Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) program for reducing fine particulate and smog-causing emissions in the eastern half of the nation, saying the rules were riddled with “several fatal flaws,” including the agency’s failure to properly focus pollution cuts to prevent movement of air pollution from one state from worsening air quality in a downwind state.
-
Coal
EEI Leaders Say Promise of Carbon Capture and Storage “Overblown”
In a sobering assessment of a key technology that’s expected to help keep the coal industry viable in the face of likely greenhouse gas caps, several electric utility executives have expressed deep concern that the promise of carbon capture and storage for coal-fired power plants has been “overblown” and “oversold.”