O&M
-
O&M
Advanced Coatings Protect Plant FGD Systems
Now that many flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems are reaching middle age, corrosion repairs of structural and process vessels are becoming more common. Corrosion is caused by condensates of acids formed during the FGD process, which accelerate pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly in scrubbers where high sulfate solutions are present. Scrubbers lined with 2205 duplex stainless steel are among the most vulnerable to pit or crevice corrosion, from both chlorides and fluorides.
-
O&M
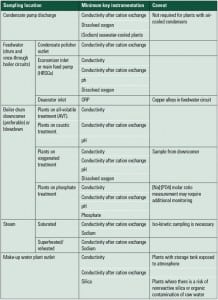
The New Water Lab
Recent advances in water laboratory instrumentation—from improved sample conditioning to advanced online instruments—have reached the market. Here’s a look at the equipment you’ll find in the best-equipped power plant laboratory this year.
-
O&M
BIG PICTURE: Lights Out (Web Supplement)
A web supplement to the September issue with details of global power shortages.
-
O&M
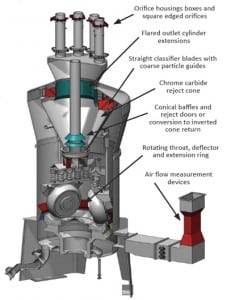
Pulverizers 101: Part I
Pulverizers prepare raw fuel by grinding it to a desired fineness and mixing it with the just the right amount of air before sending the mixture to boiler burners for combustion. In Part I of three parts, we’ll examine the essentials of pulverizer capacity, what should be done after a coal pulverizer fire or other incident, and how to tune up pulverizer performance. In future articles we’ll discuss measuring pulverizer performance and performance optimization.
-
O&M
Fighting Pipe Abrasion
Steel piping systems used to convey coarse materials, often over long distances, are under constant attack from abrasion. In power plants, the materials are usually coal and limestone slurry. The common industry solution has been to install abrasion resistant (AR) pipe that is much harder on the Brinnell Scale than standard steel pipe. The harder the inner wall, studies have shown, the better it resists the gouging or plowing action of abrasive sliding particle flow.
-
O&M
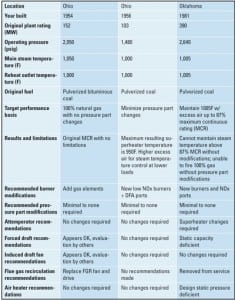
Natural Gas Conversions of Existing Coal-Fired Boilers
Why should utilities consider converting existing coal-fired plants to burn gas? We explore the rationale for fuel switching, some of the options available for the conversion of coal-fired units, technical considerations related to conversion, and some of the financial considerations that will impact the final decision.
-
O&M
Marmaduke Award: CFE Extends CTG Universidad Unit 2’s Life with Conversion to Synchronous Condenser
CTG Universidad is a two-unit combustion turbine plant commissioned in late 1970 by the Comisión Federal de Electricidad (CFE) on the north side of Monterrey, Mexico’s third-largest city and an important industrial center. By the 1990s, the two 14-MW turbines were obsolete, used sparingly, and slated for demolition in 2010. However, by 2002, portions of Monterrey began experiencing power restrictions caused by a lack of sufficient reactive power production, and that situation presented an opportunity for the plant. By repurposing an old combustion turbine for use as a synchronous condenser to provide local reactive power, CFE significantly reduced local power supply limitations. For that savvy plant repurposing, CFE’s CTG Universidad Unit 2 is the winner of POWER’s 2011 Marmaduke Award for excellence in power plant problem-solving. The award is named for Marmaduke Surfaceblow, the fictional marine engineer and plant troubleshooter par excellence.
-
O&M
Make Your Plant Ready for Cycling Operations
Cycling your steam power plant is inevitable, so now is the time to learn how to minimize equipment damage and assess the true costs of cycling. Whether cycling is required by the grid operator because of renewable integration or other factors, you must be proactive about updating operating processes and upgrade equipment so the transition to cycling operation goes smoothly.
-
O&M
Mitigating the Effects of Flexible Operation on Coal-Fired Power Plants
As coal-fired power plants increasingly operate in cycling modes, many plants are confronting the potential for higher levels of component damage and degraded performance of environmental control equipment. Generators and EPRI are working together to find ways to mitigate the effects of cycling operation and to manage the transition of formerly baseload plants to flexible operation.
-
O&M
Systems Integration, Flexible Control Reduce Makeup Water Cost
Longview Power, a 695-MW coal-fired power plant now under construction in Maidsville, W.Va., is scheduled to begin commercial operation later this year. The $2 billion project reached 580 MW in early June, just a month after completing the “first fire on coal” schedule milestone. Testing and tuning of the controls and various systems continue.
-
O&M
Improving the Efficiency of Toronto’s District Heating Plant
Enwave Energy Corp.’s district heating plants in downtown Toronto will be operating cleaner and more efficiently before the fall 2011 heating season begins when boiler upgrades now under way are completed. Enwave hired Benz Air Engineering (BAE) to design and install upgrades to all eight boilers inside Enwave’s Pearl Street Station. When the $20 million project is completed, the retrofits will produce energy savings exceeding $5 million per year. In addition, the company will receive incentives of $100,000 per boiler from Enbridge, its natural gas provider.
-
O&M
Texas Competitive Model Spreads to Pennsylvania and Illinois
A record 400 attendees participated in KEMA’s 22nd annual Executive Forum in San Antonio, Texas, in late April to debate and discuss the “retail resurgence” of competitive electricity sweeping America.
-
O&M
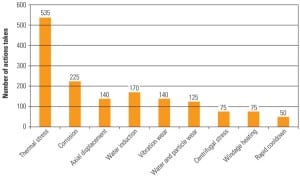
Predictive Maintenance That Works
This installment of the series continues our review of different conditioning-monitoring techniques commonly in use at power plants using any generation technology. In the May issue we began exploring specific PdM techniques with an examination of electrical surge comparison and motor-current signature analysis.
-
O&M
Defeating Concrete Reinforcing Steel Corrosion
Four concrete cooling towers at a coal-fired electrical generation plant exhibited reinforcing steel corrosion that was causing concrete deterioration. This case study follows the repairs to those towers—how the corrosion control solution was selected, how repairs were made, and how follow-up tests found the repairs to be effective three years later.
-
O&M
Titanium Tubing Still Going Strong After 40 Years
Since 1972, titanium-tubed power plant surface condensers have been providing corrosion-free service. Recent process advances are making the material suitable for even more applications.
-
O&M
Solid Fuels: Moving Material and Managing Emissions
In today’s solid-fueled power plant, managing emissions and moving materials more defines the task than the traditional work of making megawatts. That’s the message that emerged from the coal and solid fuels track at this year’s ELECTRIC POWER.
-
O&M
Air Preheater Uses New Adaptive Brush-Sealing Design
Radial, axial, and circumferential metallic seals installed on rotary, regenerative air preheaters have evolved little from the original metal strip designs that date back to the original Ljungström preheaters developed nearly a century ago. Unfortunately, metallic strip seals degrade soon after installation, allowing excessive air-to-gas leakage, which translates into increased fuel consumption and fan power.
-
O&M
Artificial Intelligence Boosts Plant IQ
Neural networks have already found practical application in many plants, and recent advancements in artificial intelligence promise to shape the design of the next generation of power plant supervisory controls. Will future plant operators be fashioned from silicon?
-
O&M
Applying CFD to Optimize Furnaces Cofiring Biomass, and the Impact of Cofiring on SCR
The international policy framework regulating the emissions of greenhouse gases from industrial and utility boilers is in flux. Meanwhile, most boiler owners are evaluating potential strategies for when, not if, more stringent emissions reduction regulations are put in place. One of the most attractive compliance options is the cofiring of biomass in existing coal-fired boilers.
-
O&M
Preventing Copper Deposition in Steam Turbines
Many large utility-scale units with copper alloy condensers and feedwater heaters lose generating capacity when copper and copper oxide deposits develop on high-pressure (HP) steam turbine blading. It is not unusual for a 400-MW unit to lose 10% of its generating capacity over a six-month period when water treatment processes aren’t properly tuned to prevent copper transport in the steam and condensate systems. In fact, one utility reported that it lost 20 MW of capacity in one month because of such deposits. The financial implications of such deposits, particularly in power markets where plants are pushed to their generating limits, are tremendous.
-
O&M
Predictive Maintenance That Works
This series of articles focuses on the nuts and bolts of predictive maintenance (PdM), also known as condition-based maintenance. A well-defined and well-executed PdM program saves time and money by reducing unneeded time-based maintenance tasks and by identifying and fixing problems before they cause equipment failure or plant shutdown. In this article, we begin introducing condition-monitoring techniques commonly in use at power plants.
-
O&M
Predictive Maintenance That Works, Part I
This year’s series will focus on predictive maintenance (PdM), also known as condition-based maintenance.
-
O&M
Plan for the Worst: Insurance Insights
Imagine this scenario: Two separate power plants experience a bowing problem greater than 18 mils with a steam-turbine rotor. The turbines are from the same manufacturer and several repair options are reviewed. Management at both plants selects an innovative approach involving removal of a substantial amount of material, which is replaced with weld overlay and then machined to correct diameters and centerline of the balance piston area. One plant’s insurance company covers the repair, the other plant’s doesn’t. Why?
-
O&M
Fire Protection Options for Air-Cooled Hydroelectric Generators
Fire protection systems for air-cooled hydroelectric generators have several special requirements due to these generators’ unique geometries. This survey of options will help plant owners and operators make the best equipment selections for their plants and thereby avoid unexpected surprises.
-
O&M
Condenser Performance Improvement Through Innovative Cleaning and Leak Detection Technologies
One of the largest returns on investment a plant can achieve is the improved condenser performance that results from an effective condenser tube cleaning. Perhaps it is time to reevaluate your choice of cleaning technologies, establish an optimal cleaning schedule, and add routine air and water in-leakage surveys to your plant’s maintenance schedule.
-
O&M
Respect Your Refractory
Because refractory is out of sight inside the gas flow path of a steam generator and its auxiliaries, it’s also often out of mind. That is, until the refractory fails and causes a forced outage.
-
O&M
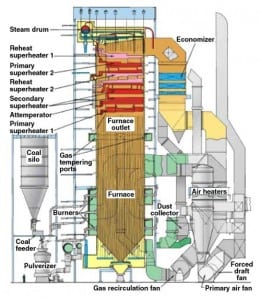
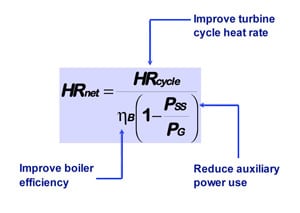
Power 101: Improving the Performance of Boiler Auxiliaries, Part III
Efficient boiler operation requires boiler auxiliary equipment to operate in harmony. In this third and last installment of our Power 101 series, we examine ways to decrease the auxiliary power requirements of boiler auxiliaries.
-
O&M
TECO’s San José Plant Models Safe and Sustainable Practices
In operation since 2000, TECO Energy Inc.’s 132-MW San José Power Station was the first coal-fired power plant built in Central America and is still the largest one. Used as a baseload plant, the facility successfully combines high availability with a business model that promotes sustainable environmental practices and a safe workplace.
-
O&M
Proper Sizing of Steam Header Drains Prevents Water Induction
Steam turbines convert the thermal energy in motive steam to rotating mechanical energy, and the generator converts that energy into electrical power. One important requirement for safe and reliable operation is preventing water induction in the steam turbine and avoiding water hammer in the steam piping system. ASME standards present the design guidelines for removing moisture from steam lines; this article explains a practical design process.
-
O&M
The Heat Is On at Arctic Air Base
Thule (“Two Lee”) Air Base is a 254–square mile base located in a coastal valley in the northwestern corner of Greenland, within the Arctic Circle. The base, the U.S.’s northernmost military installation, is nestled between mountains and surrounded by icebergs and glaciers as far as the eye can see.