O&M
-
O&M
Partners in Reliability: Gas and Electricity
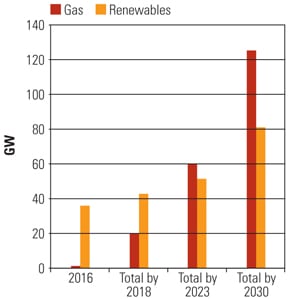
The natural gas and electricity industries have entered into an increasingly codependent relationship as coal-fired electricity gives way to natural gas–fired generation. Both industries are firmly committed to providing reliable service, although each goes about its business in different ways. Utilities, regulators, and stakeholders are searching for ways to align interests and expectations.
-
O&M
O&M and Human Stresses Caused by Low Gas Prices
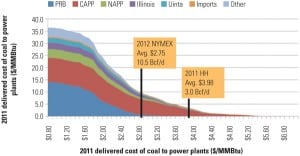
Plentiful supplies of low-cost natural gas have changed unit dispatch orders across the U.S., led to thermal stress–induced maintenance issues at cycling coal plants, and resulted in management challenges at coal and gas units alike. This scenario is unlikely to change so long as gas holds its competitive edge over coal.
-
O&M
Self-Regulating Condensate Pumps Power Austrian CHP
When Verbund Thermal Power needed reliable and flexible condensate pumps for its new combined heat and power plant in Mellach, Austria, it used a new type of self-regulating centrifugal unit.
-
O&M
Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Maintenance
Nobody can schedule unplanned events that will affect power generation. And no one wants to start a day expecting an emergency to occur. But when critical systems fail in the power supply system, it’s time to respond. That’s a given of power plant maintenance.
-
O&M
Plant of the Year: AES Gener’s Angamos Power Plant Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
AES Gener recently completed construction of twin coal-fired, 260-MW units in the electricity-starved desert of northern Chile that may serve as models for future hybrid-fossil plant designs. For meeting an aggressive construction schedule, integrating a 20-MW battery energy storage system, embracing desalination, using the first-of-its-kind seawater cooling tower in South America, and employing innovative financing methods, the AES Gener Angamos plant has earned POWER’s 2012 Plant of the Year Award.
-
O&M
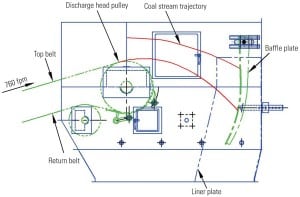
Flow Control Chutes Reduce Fugitive Coal Dust
Moving thousands of tons of coal per hour at high speeds through a complex handling system is a main cause of airborne coal dust in a coal-fired plant. Depending upon the coal’s characteristics, that dust can become explosive when its concentration reaches 80 g/m3 and, hence, a threat to life and property. The best option is to stop the dust from becoming airborne in the first place.
-
O&M
Why Coal Plants Retire: Power Market Fundamentals as of 2012
Announcements about coal plant retirements have become commonplace. Are new EPA rules completely to blame, or are there other power market pressures at play?
-
O&M
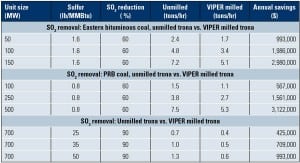
In-Line Sorbent Milling Improves Dry Sorbent Injection Performance
Complying with air emissions rules doesn’t always require construction of a scrubber or SCR. Finely ground trona has proven to be very successful at economically removing SO3, SO2, and HCl from stack gases.
-
O&M
Coal Could Regain Ground from Gas as Summer Demand Ramps Up
Natural gas-fired generation enjoyed a competitive advantage through this past winter and spring as historically low prices for the commodity combined with mild weather and relatively light demand to turn the dispatch stack on its head and favor gas over coal. That advantage is narrowing as summer demand approaches. A senior market analyst with Bentek Energy expects coal-fired generation to be advantaged at least until the fall shoulder season.
-
O&M
Improving Slurry Knife Gate Valves in FGD Applications
The primary considerations in slurry valve selection are reliability in function and design, abrasion resistance, and ease of maintenance. In addition, valves with a straight-through, unobstructed flow minimize the effect of abrasion and therefore reduce the need for maintenance.
-
O&M
Dusty Trail: The Movie
The season’s blockbuster includes white-hatted heroes, good-natured regulatory sidekicks, bar fights, and a lurking menace named Fugitive Dust.
-
O&M
Making the Switch: Converting a Simple-Cycle Plant to Combined Cycle
A lot goes into the decision to upgrade a simple-cycle plant to combined cycle. Careful planning and analysis can make the difference between a profitable, successful switch and an expensive hassle.
-
O&M
Startup Purge Credit Benefits Combined Cycle Operations
Combined cycle power plants use fuels and other materials that can cause fires or explosions in the combustion turbine, ducting, or heat recovery steam generator. Purging that equipment with ambient air to displace residual combustible gases before starting is a normal safety practice. But when plants are cycled, the disadvantages of purging often outweigh the advantages.
-
O&M
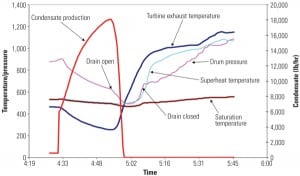
Improve Condenser Performance Through Better Instrumentation
Most power plants use some form of condenser performance-monitoring protocol. Some of those protocols are deficient because the proper instrumentation is not installed to collect the necessary data. Three case studies illustrate how collecting good condenser performance data enabled plant staff to troubleshoot problems and make good plant performance improvement decisions.
-
O&M
Combustible Dust Management Training: Rely on Best Practices, Not Shifting Regulatory Winds
None of you reading this magazine needs an article—or new governmental regulations—to tell you that flash fires and explosions involving coal dust can cause catastrophic incidents, fatalities, facility damage, and financial consequences.
-
O&M
Optimizing Your Coal Ash Recovery Operation
Coal combustion products often can be recycled into a variety of construction and building materials. However, first you must be able to retrieve the wet ash from a holding pond before the ash can be dried and sold.
-
O&M
What Are the Safety Rules for Anyway?
Following safety rules is the foundation to eliminating injuries. Commonly, a safety presenter will say that safety rules are “written in blood.” At one time, such dramatic statements were a way to get attention and illustrated the seriousness of following safety rules. Today, more highly educated workers demand less drama and more facts.
-
O&M
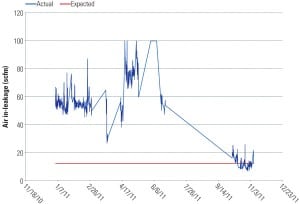
Predictive Maintenance That Works
This is the fifth in a series of predictive maintenance (PdM) articles that began in the April 2011 “Focus on O&M” in which the essentials of PdM were introduced. In the May and June 2011 issues, we explored specific PdM techniques, such as motor-current signature analysis and oil analysis. In the November 2011 issue, we introduced the value of thermographic analysis and its routine use. This installment focuses on ultrasonic and vibration analysis.
-
O&M
Managing the Catalysts of a Combustion Turbine Fleet
Natural gas–fired fleets comprising diverse turbine unit types are operating their units more these days because of the historic low price of natural gas. With increased operating hours, fleet owners are challenged to find the best ways to manage their SCR catalyst systems.
-
O&M
Safe Work Practices in Confined Spaces at Power Plants
Confined space work is often considered to be one of the most dangerous types of work performed in power generation settings. Confined spaces may contain hazardous atmospheres, they can trap entrants, and they generally can increase the hazards associated with otherwise common tasks. When the risks are not recognized, workers all too often regard incidents as surprises, but the hazards of working in confined space can be predicted, monitored, and mitigated. These “accidents” are caused by unsafe conditions, unsafe acts, or both; all accidents are preventable.
-
O&M
Preventing Downtime by Picking the Best Switch Technology
Common fuel-handling problems in the power industry often result in production downtime, costing the owner perhaps up to $200,000 per hour. There are many areas within a coal-fired power plant where mishaps can cause stoppage of material flow. Here we discuss how to select the best switch technology to reduce the possibility of coal flow stoppages.
-
O&M
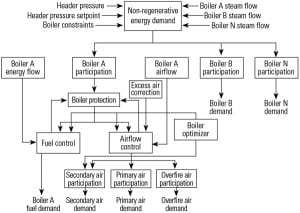
Intelligent Control of FBC Boilers
Optimizing combustion control is critical to reducing emissions and increasing plant operating efficiency, particularly for fluidized bed combustion (FBC) boiler plants burning biomass fuel that has unpredictable moisture content. The secret: measuring actual energy flow.
-
O&M
NERC: Loss of Reactive Power, Voltage Instability Likely Outcome from Geomagnetic Disturbance Effects
A new report released in early March by the North American Electric Reliability Corp. (NERC) found that loss of reactive power was the most likely outcome from a severe solar storm that was centered over North America. Significant losses of reactive power could lead to voltage instability, and, if not identified and managed appropriately, power system voltage collapse could occur, the report concludes.
-
O&M
Preventing and Mitigating Oil Fires in Power Plants
It has been said that a picture is worth a thousand words. However, photos of the conflagrations that have resulted from ignition of minor lube oil leaks on a typical steam turbine room floor will leave you speechless. Full-scale physical simulations of oil fires by the insurance company FM Global leave no doubt that power plant fire prevention and mitigation is a judicious blend of art and science.
-
O&M
Using Explosives for Boiler Deslagging
This unconventional technique for removing slag from solid fuel-fired boilers, used for more than two decades, has exploded in popularity. But the risks are very real, and not all blasters are created equal.
-
O&M
7EA Conversion Saves Time and Money
ProEnergy Services (PES) was recently contracted to install six Frame 7 DLN1.0 dual-fuel assemblies in Venezuela. The problem: The lead time to purchase the conversion hardware from the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) would not meet the customer’s schedule. The only option was for PES to convert the fuel nozzles removed from a gas-only unit to a dual-fuel configuration, a process that had never before been attempted.
-
O&M
Inlet Fogging Boosts Power in High-Humidity Environments
Turbine inlet fogging has been in use now for 20 years in combustion turbine plants. It is an obvious choice for boosting power in hot, dry areas such as Nevada or Arizona, where plants have long used fogging, but it has also proven effective in many other climates.
-
O&M
User Group Profile: Philippine Coal Plant Users’ Group
The Philippine Coal Plant Users’ Group (PCPUG), the leading nonprofit organization involved in generating electricity in the Philippines, recently held a conference introducing its mission and vision.
-
O&M
Regional Service Organization Provides Supplemental Maintenance Support
American Electric Power’s Field Services Regional Service Organization augments resident power plant maintenance teams to provide outage support and non-outage balance-of-plant support. The augmentation approach adds significant value to the maintenance process, with the greatest benefits coming in the areas of expertise, cost, productivity, and ownership.
-
O&M
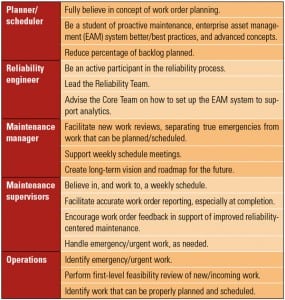
Achieving Sustainable Performance Improvement
Well-organized operations and maintenance (O&M) and outage efforts enable power plants to reduce overall operating costs, improve equipment reliability, and increase long-term productivity. Experienced contractors can help plant staff maximize the success of their outages and O&M endeavors.