Gas
-
Gas
Arcos de la Frontera Grupo III Combined-Cycle Plant, Cádiz, Spain
Iberdrola is rapidly making a name for itself on the world stage for building large, very efficient combined-cycle plants and for being the largest owner and operator of wind power plants. The utility’s most recent achievement was the successful commissioning of the Arcos de la Frontera Group III project, which marks the commercial debut of General Electric’s Frame 9FB gas turbine.
-
Coal
Bethlehem Energy Center, Glenmont, New York
A great location, a fish-friendly cooling system, and the extent of environmental remediation needed to permit it distinguish this repowering project on the Hudson River just south of the New York State capital.
-
Gas
Brooklyn Navy Yard Cogeneration Facility, Brooklyn, New York
The Brooklyn Navy Yard Cogeneration facility supplies critical electricity and steam to New York City. Situated on an historic site, the plant has earned a series of awards and was the first cogeneration plant to be accepted into both the U.S. EPA National Environmental Performance Track and OSHA’s Voluntary Protection Program in 2005. Through Delta Power’s unique asset management approach that brings added value to projects, BNYC has reinvented itself from a struggling, prematurely aging facility into one of the nation’s leading plants.
-
Coal
Currant Creek Power Plant, Mona, Utah
Commercial operation of PacifiCorp’s first new power plant in more than 20 years coincided with the company’s acquisition by MidAmerican Energy Holdings Company this past March. Currant Creek treads lightly on the environment, provides needed power to PacifiCorp’s eastern control area, and has demonstrated its commitment to be a good corporate citizen of the local community. By any account, Currant Creek is a model for how to develop a power project.
-
Gas
Linden Generating Station, Linden, New Jersey
It would be easy to dismiss Linden—which is powered by now-ubiquitous GE 7FA gas turbines and D11 steam turbines—as just another cookie-cutter combined-cycle plant. But its size (1,240 MW), key location near New York City, and use of reclaimed water for all cooling water needs makes Linden deserving of recognition as one of POWER’s Top Plants of 2006. Perhaps its most interesting story is how the project survived more than five years from groundbreaking to commissioning.
-
Gas
Mountainview Power Plant, Redlands, California
Southern California Edison and Bechtel resurrected the 1,054-MW Mountainview power project after a two-year hiatus while meeting aggressive budget and schedule constraints. Edison exercised its option to purchase the project after regulatory approvals were received at light speed, and construction resumed the very day approval was granted. Residents of California’s Inland Empire will enjoy their air conditioners this summer because Mountainview was transformed from a wasteland into a productive plant.
-
Gas
NYPA Astoria Project, Astoria, New York
New York City has an insatiable appetite for power, but supplying that power from plants inside the city’s five boroughs (where 80% of its peak demand must come from) is tough. So it’s nothing short of miraculous that a 500-MW combined-cycle plant in Astoria, Queens, began commercial operation at the end of 2005. What did it take to bring this plant on-line? The largest state-owned power organization in the U.S.—The New York Power Authority.
-
Gas
Global Monitor (May 2006)
Nuclear hot streak continues/Who’s winning in U.S. wind power?/ Canadian wind picking up too/ Brazilian port powers itself/ Biomass meets CHP in Sweden/ Power surfing from Scotland to Germany
-
Gas
Cheng Cycle flirts with 2 ppm NOx— and CO
Three years ago, an article in POWER described how Cheng Power Systems, by modifying the combustors of several popular gas turbines, had used steam injection to lower the units’ NOx output to about 5 ppm—but some models had substantial CO levels without combustor modifications. Since then, the company has developed new combustor nozzles that recently […]
-
Gas
Designing duct burners for variable GT loads
Duct burners use supplementary firing to increase the heat energy of a gas turbine’s exhaust, making it possible to increase the output of a downstream heat-recovery steam generator (HRSG). Early systems of the 1960s took a conventional approach to burner design. The exhaust of the turbine was directed into a windbox and then into a […]
-
Gas
Giant GE GT goes global
In late February, the largest gas turbine ever manufactured by GE Energy at its Belfort plant in France began a 30-day journey by land and sea that will take it to a new power plant in Spain. The Frame 9FB gas turbine—which is also the first built completely in Belfort—was loaded onto a special, wide-load […]
-
-
Gas
Designing HRSGs for cycling
With U.S. combined-cycle plants increasingly being cycled—rather than being run continuously, as they were designed to do—owner/operators worry that units expected to last two or three decades may survive only a few years without an expensive overhaul. Cycling takes as much of a toll on heat-recovery steam generators as it does on gas turbines. Whether you’re procuring a new HRSG or adapting an existing one for cycling service, robust design features should be what you’re looking for.
-
Coal
Stressed merchant industry hopes for better days
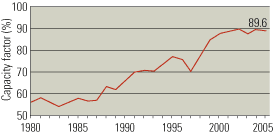
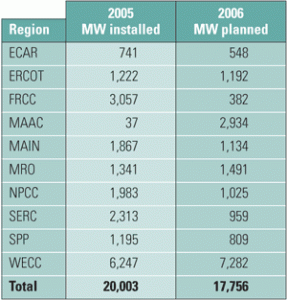
The U.S. power generation industry is changing at warp speed, via regulatory changes, consolidation, mergers, and sales of assets at yard-sale prices. New players have entered the market and become major players overnight, while several mainstays have gone bankrupt. Though many of the latter blamed high gas prices for their woes, well-diversified merchants enjoyed a record year. Whatever changes are in store for the business of combined-cycle generation, you can be sure that innovations in plant design and O&M such as those described in this special section will keep pace with them.
-
Coal
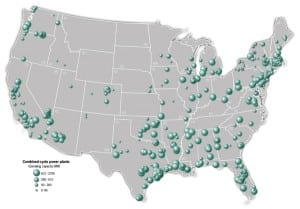
Map: Combined-cycle plants constitute about 20% of U.S. generating capacity
Copyright 2006 Platts, a Division of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. 800-PLATTS-8. Data Source: Platts Energy Advantage www.maps.platts.com
-
Coal
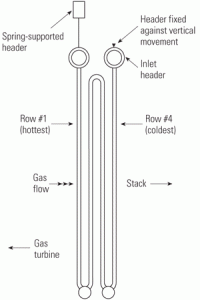
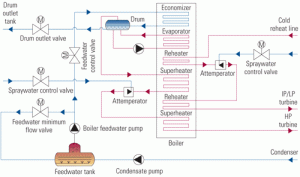
Designing HRSG desuperheaters for performance and reliability
Increased cycling of combined-cycle plants has made precise control of attemperator spray water within heat-recovery steam generators more important if damage to their hardware and piping is to be avoided. Complicating the issue is the industry’s still-limited experience with cycling and the fact that demands on the attemperator and turbine bypass of cycled plants are more stringent than those on baseloaded units.
-
Gas
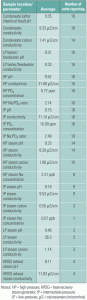
Fleetwide standardization of steam cycle chemistry
Nearly five years ago, a major IPP began standardizing steam cycle chemistry feed, control, and monitoring across its combined-cycle fleet. This article discusses the steps taken, the costs incurred, and the technical and financial benefits achieved. Although the project focused on non-cogeneration plants, the findings detailed below are broadly applicable to other kinds of plants. However, the specific implementations (especially of the chemistry standards) described may have to be modified slightly for application to cogen plants.
-
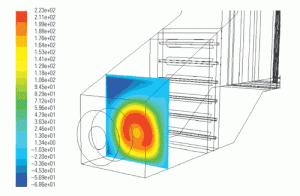
Gas
Fluid dynamics of the HRSG gas side
Designers of heat-recovery steam generators are using computational fluid dynamics software as one tool to reveal the invisible forces affecting the flow over, under, around, and through structures such as inlet ducts, distribution grids, and guide vanes.
-
Coal
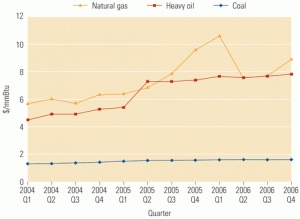
Gas turbine "refueling" via IGCC
The jury is still out on the economic and technical feasibility of burning gasified coal to generate electricity. Gasification technology has yet to be proven on a utility scale, especially with Powder River Basin coal as the feedstock. And on the generation side, there are more questions than answers about the capital cost and availability of integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) plants. But with natural gas prices high and rising, it’s definitely worth examining whether it would be economically and technically feasible to convert the existing U.S. fleet of gas-fired combined-cycle plants to burn gasified coal.
-
O&M
O&M staff keep their cool at Alaskan plant
Operating a combined-cycle power plant profitably is no walk in the park, even under ideal conditions. But the extreme conditions at the Beluga Power Plant—from isolation to volcanoes—challenge its staff every day in ways that operators in the lower 48 can only imagine.
-
Gas
Frame 6C debuts in Turkey
GE Energy’s latest "first" is in Turkey, where the Frame 6C gas turbine-generator—a younger cousin of the popular Frame 6B—has made its commercial debut. The turnkey 130-MW combined-cycle plant, called the GE206C, comprises two 40-MW Frame 6Cs, one GE steam turbine-generator, two heat-recovery steam generators, and a distributed control system. The gas-fired plant (Figure 1), […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Gas storage investment stymied
The U.S. needs to add 600 to 800 billion cubic feet (Bcf) of natural gas storage capacity ASAP. Independent storage providers (ISPs) are the entities best equipped to build this needed infrastructure, but they continue to be restrained by anachronistic regulatory policies. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s (FERC’s) December 2005 rule-making to modify its […]
-
Gas
Rockin’ the casbah
Munich-based Siemens Power Generation (PG) recently finished building the 384-MW combined-cycle Tahaddart Power Plant in the city of the same name in Morocco (Figure 2). The turnkey project, which is about 20 miles south of Tangier, was completed in 25 months. The plant’s natural gas fuel comes through a new, 8-mile-long spur that connects to […]