-
Environmental
Power Industry Needs to Do a Better Job of Educating and Messaging
At the opening ELECTRIC POWER 2009 plenary session, both the keynote speaker and the Power Industry Executive Roundtable participants kept circling back to the problems created by a public and lawmakers who seem to be promoting policies without an adequate understanding of energy realities. Most of the speakers acknowledged that the industry itself is partly to blame, but nobody offered a way forward.
-
Nuclear
Sweden Selects Site of First Permanent Spent Nuclear Fuel Repository
In early June, as U.S. Energy Secretary Steven Chu confirmed to a House Subcommittee that Yucca Mountain repository was, without doubt, "off the table" and that a blue ribbon panel would further advise the government on what it should do with its high-level nuclear waste, Sweden announced the site of what could be the world’s first permanent spent fuel repository.
-
News
Ontario Suspends Multibillion Dollar Nuclear Projects Amid AECL Uncertainties
The Ontario government has suspended a 10-year multibillion dollar nuclear upgrade project to replace two reactors at the Darlington site, citing pricing and uncertainty regarding the future of Atomic Energy of Canada Ltd. (AECL), Canada’s sole bidder.
-
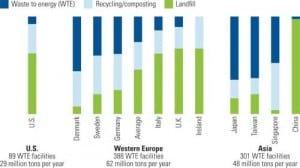
Waste to Energy
The Growing Role of Waste-to-Energy in the U.S.
Using nonhazardous waste for power generation is a trend that’s gaining steam for several reasons. Though there are several environmental reasons, another is the reliability of the fuel supply.
-
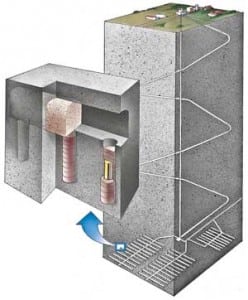
Hydro
Ethiopia Completes Construction of Africa’s Tallest Dam
Ethiopia, the landlocked nation in East Africa from which key tributaries to the Nile River originate, completed construction of the continent’s highest dam, the 188-meter Tekezé Arch Dam (Figure 3) in February.
-
News
Exelon Suspends Victoria Nukes on Economic Uncertainties, Loan Guarantees
Exelon, the largest nuclear power generator in the U.S., has suspended plans to build a proposed two-unit nuclear plant in Victoria, Texas, because of uncertainties in the domestic economy and limited federal loan guarantees.
-
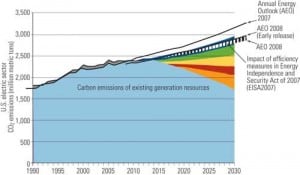
Coal
Carbon Control: The Long Road Ahead
The industry is preparing for carbon legislation by exploring options for dealing with CO2. But even if the technical issues are resolved, actually sequestering CO2 poses a number of other daunting challenges.
-
Gas
Qatar Starts Construction on Middle East’s Largest Power and Water Plant
The gas-rich Persian Gulf state of Qatar in May commenced construction of the region’s largest power and water plant, a massive project comprising eight gas turbine generators, eight heat-recovery steam generators, four steam turbine generators, and 10 desalination units.
-
News
Report: Combination of “Rarely Found” Factors Led to TVA Coal Ash Spill
The breach of a 50-year-old coal ash storage pond and subsequent ash spill at the Tennessee Valley Authority’s (TVA’s) Kingston Fossil Plant in Roane County, Tenn., last December was caused by a rare and complex combination of conditions, a six-month independent engineering study has found. These included the existence of an unusual bottom layer of ash and silt, the high water content of the wet ash, the increasing height of ash, and the construction of sloping dikes over the wet ash.
-
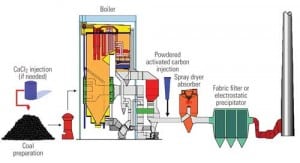
Coal
Technology Could Deliver 90% Hg Reduction from Coal
Reducing mercury emissions at coal-fired power plants by 90% has been considered the holy grail of mercury control. A new technique promises to get us there — at a price.
-
Wind
"Smart Turbine Blades" to Improve Wind Power
Engineers at Purdue University and Sandia National Laboratories have developed a technique that uses sensors and computational software to constantly monitor forces exerted on wind turbine blades. Their achievement could one day improve the efficiency of wind turbines by providing the blades’ "smart" structure with necessary data to adjust to rapidly changing wind conditions.
-
News
Interior Department to Fast-Track Solar Development on Public Lands
Federal agencies will work with western leaders to designate tracts of U.S. public lands in the West as prime zones for utility-scale solar energy development, fund environmental studies, open new solar energy permitting offices, and speed reviews of industry proposals, Secretary of the Interior Ken Salazar said on Monday.
-
O&M
Improved Filler Metal Enables Higher-Temperature Dissimilar Metal Welds
The welding of dissimilar metal joints in new and retrofit power plant boiler tubing has long proved challenging. New plants designed to operate at higher temperatures and pressures require advanced alloys and a filler metal that produces reliable welds. EPRI recently developed and sponsored the commercialization of a new filler metal. Its first application is the fabrication of boiler tubes for American Electric Power’s ultrasupercritical John J. Turk, Jr. Power Plant.
-
Business
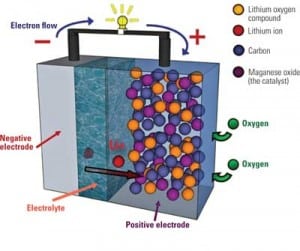
Energy Storage Efforts Making Progress
The intensifying spotlight on renewable energy seems to be casting a brighter light on the energy storage problem, with lawmakers, researchers, and investors scrambling to seek out the most feasible solution to bridge the intermittent nature of renewable power sources.
-
News
GE Energy and MHI to Co-Develop “Next Generation” Steam Turbine
GE Energy and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) last week agreed to co-develop a “next generation” steam turbine for use in gas turbine combined-cycle power plants. If successful, the parties will separately manufacture and sell the co-developed steam turbine.
-
Solar
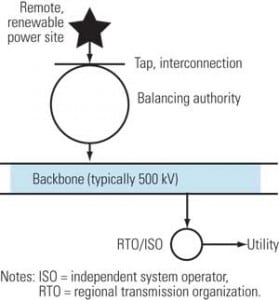
The Odd Couple: Renewables and Transmission
The tension between the growing number of renewable energy projects and limited transmission capacity is reflected in Washington’s legislative agenda of establishing a national renewable portfolio standard and new transmission lines dedicated to moving renewable energy coast-to-coast. Even if those ideas become law, hurdles to the happy marriage of renewables and transmission remain.
-
Solar
PG&E Makes a Deal for Space-Based Power
Just as reports emerged earlier this year that NASA had abandoned, for lack of financial resources, its research into space-based solar power that would be harnessed via orbiting solar arrays beaming microwaves to earthly receivers, California’s Pacific Gas & Electric Co. (PG&E) wrote the California Public Utilities Commission (PUC) requesting its approval of a power purchase agreement from a similar technology.
-
HR
TREND — Power Companies Push Hiring Military Vets
Many U.S. power companies are focusing their hiring efforts on military veterans. According to human resources HR experts, it makes a lot sense—beyond pure patriotism. Vets are motivated, experienced, often well-trained, and instilled with team-work. Plus, there is a great need to replace the retiring “baby boomers” generation who have populated many key industry jobs. In some cases, there’s even a financial incentive for hiring vets.
-
Legal & Regulatory
White House Announces Cyber Security Plan
The Obama administration has unveiled its long-awaited policy on cyber security of government and private-sector communication and distribution systems. Is it less than meets the eye, as some critics argue?
-
Smart Grid
Electrical Manufacturers Warn Against “Aggressive” Smart Grid Strategy
Clashes between industry and the Department of Commerce on backward compatibility of standards could stifle and delay the development of a “smart” electric transmission and distribution grid.
-
Legal & Regulatory
New Administration’s Energy Priorities: Hydrogen Is Out, Coal Is In
The Obama administration has pulled the plug on the Department of Energy’s attempts to develop hydrogen-powered fuel cell cars. (The Bush administration had been touting H-powered cars for many years, with nothing to show for the effort other than large expenditures and a General Motors concept car that cost in the millions to build.) At about the same time, the Obama administration announced it would resurrect the billion-dollar FutureGen coal-fired generating project, aimed for Mattoon, Ill.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Obama Names Jaczko to Head NRC
As expected, President Obama has named Nuclear Regulatory Commissioner Gregory Jaczko, an ally of Sen. Harry Reid (D-Nev.), as chairman of the NRC, almost certainly dooming the Yucca Mountain, Nev., site for disposal of spent nuclear fuel.
-
Supply Chains
Is Unconventional Gas the New Energy Super Supply?
Gas found in shale deposits and recently discovered natural gas hydrates may be game-changers when it comes to supplying natural gas to the United States.
-
Commentary
Learning from Past, Failed Energy Laws
It’s not easy writing energy legislation, as the experience of the past demonstrates. Nor are the results always in the public interest.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Cap-and-Trade or a Carbon Tax for Greenhouse Reductions?
What makes more sense to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from power plants—a cap-and-trade regime or a carbon tax? It’s a contentious issue among those who generate power and among academic economists and policy makers.
-
Commentary
Why I Am a Climate Realist
I was one of the scientists counted as supporting the United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 1996 report. It turns out that effort was bogus and intellectually dishonest.
-
Commentary
Regulatory Effectiveness: Is It Measurable?
A [state utility regulatory] commissioner asked recently, “By what metrics can I assess my commission’s performance?” That’s a tough question.
-
Commentary
America’s Many Energy Policies
It’s not that the U.S. doesn’t have any energy policy, says this veteran of energy politics and head of a major Washington energy and environmental think tank. It’s that we have too many, and they aren’t coordinated and coherent.
-
News
U.S. Senate Energy Committee Clears Wide-Ranging Energy Bill
The Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee last week cleared by a 15–8 vote a broad energy bill that, among other things, would impose a federal renewable energy standard, reaffirm the government’s commitment to nuclear waste disposal, and implement grid cybersecurity measures.
-
News
MIT Report: Technology Options for Existing Coal-Fired Plants Are Crucial
There is no credible pathway toward prudent greenhouse gas stabilization targets without carbon dioxide emissions reductions from existing coal power plants, but the U.S. urgently needs technology options for these plants and policies that incentivize implementation, a new study from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) finds.
Search