-
Commentary
Wind Energy Blown Away by Natural Gas
The environmental push for renewables and mandates to force them into existence are rightly facing some serious headwinds. The American Renewable Energy Production Tax Credit Extension Act of 2011 foundered in Congress, and more states are experiencing significant power rate increases to cover renewable energy production costs. While renewables are generally not ready for prime time in large quantity on today’s power grid, that doesn’t mean environment concerns ought to be trashed, especially when a more effective off-the-shelf solution is available.
-
Coal
Tactical Advantage
A three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit on June 26 unanimously rejected all pending legal challenges against the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) interpretation of the Clean Air Act (CAA) that allows the agency to regulate greenhouse gases (GHGs). What is the EPA’s future strategy in its war on coal?
-
Legal & Regulatory
Proposed Cooling Water Rule’s Ripple Effects
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has a long history of making waves with the electric power industry because of its efforts to regulate the way thermal power plants construct and operate their cooling water intake structures (CWIS). These structures divert billions of gallons of water into power plants’ cooling systems and can injure or kill billions of aquatic organisms.
-
-
O&M
Plant of the Year: AES Gener’s Angamos Power Plant Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
AES Gener recently completed construction of twin coal-fired, 260-MW units in the electricity-starved desert of northern Chile that may serve as models for future hybrid-fossil plant designs. For meeting an aggressive construction schedule, integrating a 20-MW battery energy storage system, embracing desalination, using the first-of-its-kind seawater cooling tower in South America, and employing innovative financing methods, the AES Gener Angamos plant has earned POWER’s 2012 Plant of the Year Award.
-
Hydro
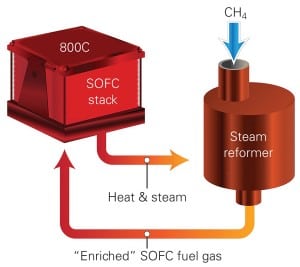
Major Developments for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), which oxidize a fuel to produce electricity, have received much attention of late for the technology’s myriad benefits, including high efficiency, long-term stability, fuel flexibility, and low carbon emissions—all at a relatively low cost.
-
Waste to Energy
Marmaduke Award: Combined Solar Technologies’ Hybrid Plant: Using Wastewater and Olive Pits to Produce Clean Water and Clean Energy
Combined Solar Technologies (CST) has designed, built, owns, and operates a water purification system located at the Musco Family Olive Co. facility in Tracy, Calif., that burns olive pits to purify highly saline wastewater through a distillation process while also producing electric power. For its pioneering approach, CST is the winner of POWER’s 2012 Marmaduke Award for excellence in plant problem-solving. The award is named for Marmaduke Surfaceblow, the fictional marine engineer and plant troubleshooter par excellence, whose exploits were chronicled in POWER beginning in 1948.
-
Wind
The Age of the Mammoth Wind Turbine Blade
Siemens Energy in June announced it had produced the first batch of its new B75 Quantum wind turbine rotor blades, fiberglass components 75 meters (m) in length that were cast in one piece (Figure 3). The blades were manufactured to be installed this fall on Siemens’ second prototype of the German firm’s SWT-6.0 6-MW offshore […]
-
Solar
Smart Grid Award: Customers Motivate San Diego Gas & Electric’s All-Inclusive Smart Grid Vision
“If you build it, they will come” has proven a risky strategy for some smart grid projects. One of California’s largest investor-owned utilities faced the opposite challenge—customers whose behaviors necessitated a smarter grid. Customer involvement in and support for smart grid plans is a major reason SDG&E’s smart grid efforts continue to garner accolades, including the 2012 POWER Smart Grid Award.
-
Hydro
Tubular Turbine Hydropower Plant Comes Online
Albania this June inaugurated its first major hydropower project since the early 1980s, bringing online Ashta I, the first of two run-of-river plants with a combined capacity of 53 MW. At the inauguration ceremony, Albania’s Prime Minister Sali Berisha called the plant “a novelty” because it is the largest in the world to use advanced tubular turbines technology.
-
O&M
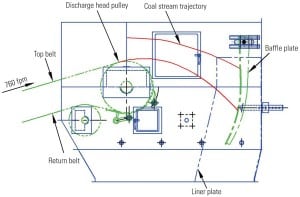
Flow Control Chutes Reduce Fugitive Coal Dust
Moving thousands of tons of coal per hour at high speeds through a complex handling system is a main cause of airborne coal dust in a coal-fired plant. Depending upon the coal’s characteristics, that dust can become explosive when its concentration reaches 80 g/m3 and, hence, a threat to life and property. The best option is to stop the dust from becoming airborne in the first place.
-
Gas
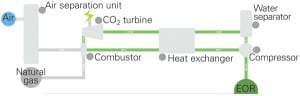
New Gas-Fired Technology Gains Backers
A new gas-fired power generation technology that uses an oxyfuel, high-pressure, supercritical carbon dioxide cycle and produces pipeline-ready carbon dioxide for sequestration or use in enhanced oil recovery (EOR), without reducing plant efficiency, garnered the interest of three new partners in June.
-
Coal
New Environmental Rules Keep Pressure on Coal-Fired Generation
New U.S. Environmental Protection Agency regulations affecting the nation’s coal power plants are routinely in the national news. The latest proposed rule focuses on the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. With a substantial amount of coal generation expected to be shut down (up to 40 GW to 50 GW in the coming years by some accounts), the new regulations are increasing the likelihood that this lost capacity will not be replaced by new coal generation.
-
Business
POWER Digest (August 2012)
FP&L to Increase Output at Turkey Point. Florida Power & Light (FP&L) on June 19 received approval from the Nuclear Regulatory Commission to increase the power generating capacity of Turkey Point Nuclear Generating Units 3 and 4 by 15%. The power uprate for the pressurized water reactors will increase each unit’s capacity from approximately 700 […]
-
Nuclear
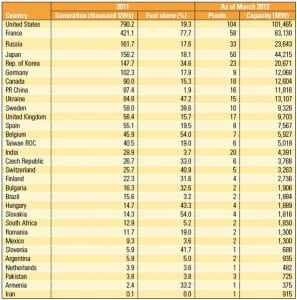
2011 Nuclear Industry Scorecard
The world nuclear industry experienced few substantial changes in performance metrics for 2011—beyond Japan, that is. In the aftermath of Fukushima, the once–world leading Japanese nuclear industry fell to the bottom of the rankings, perhaps for good.
-
Nuclear
Too Dumb to Meter, Part 3
As the book title Too Dumb to Meter: Follies, Fiascoes, Dead Ends, and Duds on the U.S. Road to Atomic Energy implies, nuclear power has traveled a rough road. In this POWER exclusive, we present the third chapter, “Micro-Mismanagement by Committee.” During the frenzy to manage atomic power after World War II, Congress created an executive branch agency that threatened to be too independent, too powerful, and too isolated from the rest of government. Compounding their errors, perhaps in recognition of what they had created, the solons also developed a way to insert their own power into the action. This proved to be a major mistake—blurring the lines between executive and legislative authority—causing no end of problems for the nation’s nascent atomic energy venture.
-
General
Too Soon to Make Sense of the India Blackouts
By Kennedy Maize (@kennedymaize) Washington, D.C., 31 July 2012 – What to make of the two successive, horrendous electric power failures in India? The smart money avoids conclusory leaps. When the first cascading blackout hit on Monday, there was much media chatter about generating capacity. The implication was that the outage was demand-driven. But there […]
-
Coal
WPL to Retire Three Coal Units, Tamp Down Pollution Emissions with New Controls
Wisconsin Power and Light (WPL) Co. plans to retire three of its oldest and smallest coal-fired generating units and invest $1.4 billion into the company’s generating fleet over the next five years to ensure it will be able to manage "current and emerging environmental regulations," the Alliant Energy Corp. subsidiary announced on Friday.
-
Coal
Consent Decree Could Force Closure of FirstEnergy Coal Ash Impoundment Facility in Penn.
A lawsuit filed in federal court on Friday by Pennsylvania’s Department of Environment Protection (PDEP) alleges that FirstEnergy’s Little Blue Run Dam coal ash impoundment pond in Beaver County, a facility that stores coal ash from the generator’s 2,470-MW Bruce Mansfield coal-fired power plant in Shippingport, Pa., has leached heavy metals in drinking water supplies and surface water. A proposed consent decree could force the generator to shut down the impoundment facility.
-
Too soon to make sense of the India blackouts
Washington, D.C., 31 July 2012 – What to make of the two successive, horrendous electric power failures in India? The smart money avoids conclusory leaps. When the first cascading blackout hit on Monday, there was much media chatter about generating capacity. The implication was that the outage was demand-driven. But there was nothing particularly unusual […]
-
Coal
Eight Oxy-Combustion Projects Get DOE Awards to Advance CCUS
The Department of Energy (DOE) on Thursday announced it would award $7 million to eight projects to advance the development of transformational oxy-combustion technologies capable of high-efficiency, low-cost carbon dioxide capture from coal-fired power plants. Leveraged with recipient cost-sharing to support about $9.4 million in total projects, the awards are expected to support the development and deployment of “carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS)” by focusing on further improving the efficiency and reducing the costs associated with carbon capture.
-
Commentary
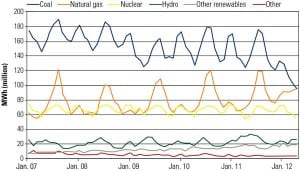
Changing of the Guard
Preliminary data published by the Energy Information Administration shows that the amounts of power generated by coal and natural gas in April were virtually equal. Was this a one-time event or an indicator of a future trend?
-
Commentary
Stopping the EPA: The Long Game
The D.C. Court of Appeals recently declined to examine the science behind the EPA’s Endangerment Finding that is the foundation beneath the its greenhouse gas rules. The next step is to challenge the EPA’s science.
-
Commentary
Green Jobs Count: Fewer Than Before, Sillier Than Ever
The Bureau of Labor Statistics has released another report on green jobs. According to the BLS, an oil industry lobbyist could be considered as having a green job. The report’s definitions still lack common sense.
-
O&M
Why Coal Plants Retire: Power Market Fundamentals as of 2012
Announcements about coal plant retirements have become commonplace. Are new EPA rules completely to blame, or are there other power market pressures at play?
-
Coal
Design Features of Advanced Ultrasupercritical Plants, Part III
Advanced ultrasupercritical (A-USC) is a term used to designate a coal-fired power plant design with the inlet steam temperature to the turbine at 700C to 760C. In the first two parts of this three-part report, we introduced the A-USC boiler and the metallurgical advancements required for the A-USC boiler to operate at such high temperatures. This final report explores the A-USC boiler’s unique design challenges.
-
O&M
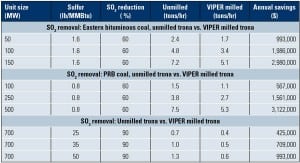
In-Line Sorbent Milling Improves Dry Sorbent Injection Performance
Complying with air emissions rules doesn’t always require construction of a scrubber or SCR. Finely ground trona has proven to be very successful at economically removing SO3, SO2, and HCl from stack gases.
-
Coal
Federal Court Rejects Challenges to EPA Industrial, Automotive GHG Rules
A three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit on June 26 ruled that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was "unambiguously correct" in its interpretation of the Clean Air Act (CAA) to regulate carbon dioxide emissions. The federal agency’s endangerment finding that greenhouse gases (GHG), including carbon dioxide, are a threat to public health and welfare, and its decision to set limits for industrial and automotive emissions of GHGs, was "neither arbitrary nor capricious," the court ruled. The court, however, found that it lacked jurisdiction to review the timing and scope of the GHG rules that affect larger stationary sources, including new coal-fired power plants.
-
Coal
EPA Proposes Clean Air Standards for PM2.5
In response to a court order, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) proposed updates on June 15 to its national air quality standards for harmful fine particle pollution, including soot (known as PM2.5). The agency says that 99% of U.S. counties are projected to meet proposed standards without any additional actions.
-
O&M
Coal Could Regain Ground from Gas as Summer Demand Ramps Up
Natural gas-fired generation enjoyed a competitive advantage through this past winter and spring as historically low prices for the commodity combined with mild weather and relatively light demand to turn the dispatch stack on its head and favor gas over coal. That advantage is narrowing as summer demand approaches. A senior market analyst with Bentek Energy expects coal-fired generation to be advantaged at least until the fall shoulder season.
Search