In This Issue
-
News
The Big Two
In this column last month I quoted Indian Environmental Minister Jairam Ramesh to represent India’s intention to not agree to any legally binding emissions targets at the Copenhagen Climate Change Conference in December. That conference will start formal negotiations of a follow-on agreement to the Kyoto Protocol. A number of readers wrote to say that they believe India and China, despite their protestations to the contrary, will cave to international pressure and at the end of the day agree to some binding carbon emissions limits. I disagree.
-
Commentary
Climate Change Litigation: Ripe for Growth?
For some time, the U.S. energy industry has feared the prospect of large-scale climate change litigation (CCL) that seeks to link emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG) to global warming. Thus far though, only a handful of such suits have been filed, and none has yielded any judgments against the energy industry. This begs the question of whether the energy industry can now stop worrying about CCL.
-
-
Environmental
PNNL Pioneers New Sulfur and Carbon Dioxide Scrubbing Liquid
A reusable organic liquid developed by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) or sulfur dioxide (SO2) from power plant emissions could one day replace current scrubbing methods and allow power plants to capture the gases in a cost-efficient way that uses no water and less energy.
-
O&M
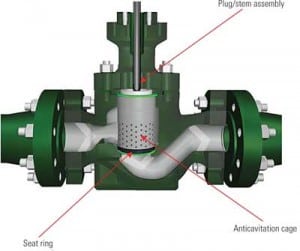
Ensure Your Valve Replacement Parts Meet OEM Specs
When high-temperature boiler feedwater passes through a control valve, the pressure drop can exceed several thousand pounds per square inch, placing extreme stress on the valve body and internal parts. If those parts are not engineered and manufactured to the highest industry standards, there is a very real possibility of the severe conditions damaging or destroying the valve.
-
Nuclear
Using the Sterling Engine for Solar and Lunar Power
Since Robert Stirling invented the Stirling engine in 1816, it has been used in an array of specialized applications. That trend continues today. Its compatibility with clean energy sources is becoming apparent: It is an external combustion engine that can utilize almost any heat source, it encloses a fixed amount of a gaseous working fluid, and it doesn’t require any water — unlike a steam engine.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Feds Must Deliver on Climate Change Legislation
For several years there has been widespread doubt about Washington’s ability to move forward with a national program to address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. At various times during the Bush administration, it appeared that legislation might be possible, but it always collapsed under the weight of partisan politics and competing special […]
-
Coal
Enel’s Fusina Hydrogen-Fueled Plant Goes Online
Italy’s Enel said in August that it has successfully begun operating a power plant in Fusina, near Venice, in the Veneto region of Italy, that is fueled 100% by hydrogen. The industrial-sized plant’s building site was officially opened in April 2008, after which infrastructure and technology work was carried out on schedule. Initial testing of the turbine using methane gas was conducted in the spring of 2009, and now — after completion of the special pipeline — the plant has switched to 100% hydrogen fueling, Italy’s largest energy company said.
-
Coal
Top Plants: Bull Run Fossil Plant, Clinton, Tennessee
When TVA’s Bull Run Fossil Plant was erected in the mid-1960s, it could boast of having the largest boiler in the U.S., and the plant has enjoyed a long, enviable efficiency track record. Today the public judges coal plants by their emissions. Now that it’s been outfitted with the most advanced air quality control systems, including the latest flue gas desulfurization system design, Bull Run scores a perfect "10" in both categories.
-
Nuclear
Africa Looks to Nuclear for Future Generation
Africa is emerging as a prominent voice in calling for a global nuclear renaissance. Driven by chronic shortages from population explosions, decades of drought, and dependence on hydropower — and spurred by discoveries of significant uranium reserves on the continent — several countries are considering nuclear power as a viable option.
-
Coal
Top Plants: Hirakud Power, Sambalpur, Orissa, India
Hirakud Power uses environmentally friendly circulating fluidized bed (CFB) combustion technology to produce electricity for one of the world’s oldest aluminum-smelting operations. This "captive power plant" has engineered a number of technical fixes to its original boiler designs to improve plant reliability and reduce outages and boiler repair costs. It also has made strategic investments in upgraded machinery to reduce auxiliary power consumption. In addition to an excellent environmental track record, as evidenced by being Asia’s first ISO 14001 (BS 7750) – certified power plant, Hirakud Power has solidified its position as an industry leader in CFB boiler operating experience and efficient power production.
-
Solar
DLR to Commercialize Technology from Solar Tower Demonstration
A solar thermal demonstration power plant in Jülich, Germany, that was developed by the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR), was formally handed over to its future operator, the Jülich Department of Works this August.
-
Coal
Top Plants: Hutsonville Power Station, Crawford County, Illinois
This plant’s staff proves that a can-do attitude and high productivity can be compatible with a safer workplace. The proactive approaches they used at the 162-MW Hutsonville plant ranged from improving boiler efficiency to better managing risks to workers.
-
O&M
Proper Valve Selection Reduces Downtime, Increases Process Efficiency
Many customer quotation requests provide only the line size, pressure class rating, and valve type. A typical request might read: size 4, Class 900 globe valve. Though this may be enough information to produce a valve quote, it rarely is enough information to size the best valve from both a performance and cost perspective.
-
Coal
Top Plants: Nebraska City Station Unit 2, Nebraska City, Nebraska
Omaha Public Power District commissioned Unit 2 at its Nebraska City Station in May of this year. The new 682-MW unit joins Unit 1, which went commercial 30 years ago in the same month. The project is outfitted with all the requisite air quality control systems and sports a very good thermal efficiency. More importantly, the plant will provide reasonably priced power for customers of eight municipal utilities that share ownership of the plant’s electrical output. Those utilities paid for their portion of the construction cost and now receive a like portion of the electrical output from Unit 2 under a unique participation power agreement.
-
News
Power Source for Quality Gas Welds
ESAB Welding & Cutting Products’ newly introduced CaddyTig 2200i AC/DC power source is designed to produce quality gas tungsten arc (TIG) and shielded metal arc (stick) welds in a variety of materials. With a light, compact design, the CaddyTig 2200i offers control panels that present all welding parameters in an easy-to-understand layout. ESAB’s two-program function […]
-
Coal
Top Plants: Rockport Power Plant, Rockport, Indiana
Hard work was required at the 2,600-MW Rockport Plant to make improvements to equipment, materials, and processes. But that hard work has paid off: The plant’s units operate much better, employee safety has improved, the facility is setting generation records with both of its 1,300-MW units, and it earned the PRB Coal Users’ Group Large Plant of the Year honors.
-
News
Water-Saving Liquid Ring Vacuum Pump
The design of Nash’s new ECO-FLO builds on the company’s previous liquid ring vacuum pump models. While it offers the same reliability, performance, and operating costs, the ECO-FLO reduces water usage by up to 50%. The inlet and discharge piping are unchanged, and the upgraded model uses an existing base, motor, and drive. ECO-FLO is […]
-
Coal
Top Plants: Seminole Generating Station, Palatka, Florida
Complying with a corporate environmental policy requires much more than just writing a check for equipment upgrades. It takes a dedicated and knowledgeable staff that’s willing to invest years of work to permanently reduce a plant’s environmental footprint. The staff of Seminole Generating Station have completed multiple, incremental plant improvements over the past decade that have significantly reduced air emissions and minimized solid waste disposal.
-
News
Small-Diameter Split Frame
E.H. Wach’s newly launched Small Diameter Split Frame (SDSF) is an externally mounted machine tool for cutting, beveling, and counterboring pipe from 0.84 inch to 4.5 inch diameter. Featuring a self-squaring clamping system for precise cutting results that are typically available only with fixed machine tools, the SDSF is also capable of performing socket weld […]
-
News
Wind Power Converters
Independent designer, manufacturer, and service provider of energy control and optimization solutions Woodward Governor Co. recently started production of its CONCYCLE wind power converters in the U.S. The electric power convertor units are designed for use with wind turbines with a power range of 1 MW to 10 MW for onshore and offshore applications. Woodward […]
-
Environmental
Techniques for Determining Limestone Composition and Reactivity
Limestone composition and reactivity are critical factors that determine the performance of limestone-based wet flue gas desulfurization systems. Limestone quality affects sulfur dioxide (SO2) removal, reaction tank sizing, limestone consumption rate, and composition of the gypsum product and waste streams. Reactivity is a direct measure of how readily a limestone will provide alkalinity to neutralize the acid resulting from SO2 dissolution in water. In this article we review your limestone analytic measurement options and discuss their relative accuracy and limitations.
-
News
CWP Grounding Clamps
ERICO has developed a range of CWP grounding clamps that are ideal for use in applications including lightning protection, fault current ground, signal reference grid, and static ground. The clamps help minimize the possibility of damage from a lightening strike or other transient voltage by reducing the electrical potential between metallic objects and building systems. […]
-
O&M
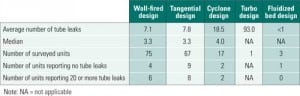
Update: Benchmarking Boiler Tube Failures
Boiler tube failures continue to be the leading cause of downtime for steam power plants. Is your boiler tube failure reduction program showing improvement when compared to programs at peer plants? The EUCG’s recent update of its boiler tube failure study can help you answer that question. The full study is available only to members, but this POWER exclusive presents many of the key results, which could help you improve the operation of your plant.
-
Coal
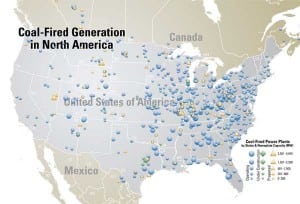
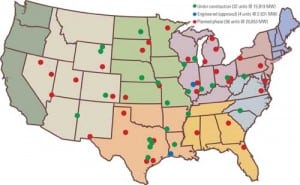
Coal-Fired Generators Worried About Getting Burned
The expected renaissance for U.S. coal-fired generation has been more evolutionary than revolutionary: Less than half of the announced plants will likely progress to construction. However, the percentages for coal-fired plants aren’t significantly different from those for combined-cycle plants a decade ago, when dozens were ultimately canceled, leaving developers with warehouses full of unused gas turbines. The difference this time: The threat of carbon control legislation has moved many projects to the “wait and see” category.
-
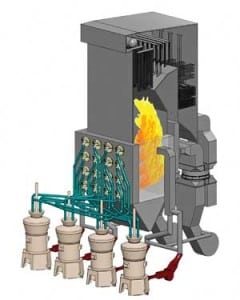
O&M
Measuring Coal Pipe Flow
Once pulverized coal flows have been measured, they can be balanced and optimized. Until then, tuning is simply guesswork. The right way to balance furnace fuel flows is to establish solid baseline performance by proper measurement of fuel flow, fineness, and velocity. Only then can all the coal pipes be accurately balanced and followed by a tune-up of the boiler controls.
-
News
Rugged Belt Cleaner
Martin Engineering’s Performance Duty QC#1 Belt Cleaner (PDQC#1) is the latest addition to the company’s line of "Quick Change" belt cleaners. The PDQC #1 Cleaner features a more rugged steel mainframe, a low-maintenance spring tensioner, and a high-volume urethane blade that extends life while maintaining cleaning performance. It also uses a one-piece urethane blade featuring […]