Coal
-
O&M
Leading-Edge Conveyor Technologies Reduce Dust Emissions
Reducing dust from coal conveyors has moved from a housekeeping chore to a safety challenge, especially with Powder River Basin coals. Here’s what you need to know about the latest coal-handling system design.
-
O&M
High-Hazard Coal Ash Sites, and the TVA Spill Revisited
The EPA has identified 44 "high hazard" coal ash ponds around the U.S., and a recent Tennessee Valley Authority report indicates that the agency should have known its Kingston Plant pond would have been one of them.
-
Coal
Utility Business Customers to Feast on Free Allowances
An analysis by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities concluded that two-thirds of the value of carbon emission allowances described by the recent H.R. 2545 will benefit utility business customers and households in the top quartile of personal income. The middle quintile will see increased cost for electricity.
-
Coal
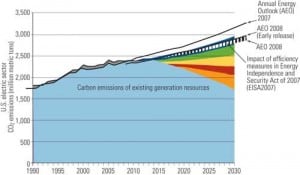
MIT Report Urges Faster Action on Carbon-Capture Retrofits
MIT researchers push for faster commercialization of carbon capture technologies for coal-fired power plants by reducing system costs.
-
O&M
PRB Coal Users’ Group Educates Industry on the Dangers of Combustible Dust
The annual meeting of the Powder River Basin Coal Users’ Group was held in association with the ELECTRIC POWER conference in early May in Chicago. Get a taste of the festivities, technical meetings, and the announcement of the group’s 2009 Large and Small Plant of the Year winners in this conference report.
-
Coal
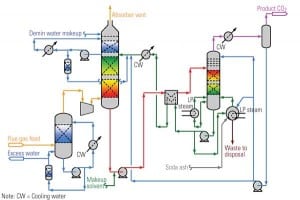
Commercially Available CO2 Capture Technology
While many CO2 removal technologies are being researched through laboratory and pilot-scale testing, an existing technology has a significant operating history at commercial-scale facilities, where it is collecting CO2 from multiple sources, including low-CO2 concentration flue gas (<3.1% by volume) with high oxygen concentrations (>13% by volume).
-
Coal
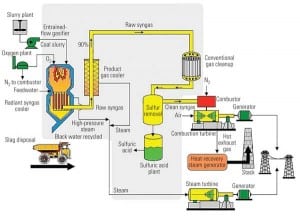
Revived FutureGen Faces Renewed Funding Obstacles
A little more than a year after the Bush administration abruptly withdrew its support for the FutureGen project, the Department of Energy has again announced it will back the proposed Illinois gasified coal power plant and carbon capture initiative. Though the 275-MW project may be different in technical aspects — it will be initially designed for 60% carbon capture, not 90%, and gasify only Illinois Basin Coal (Figure 2) — it is still riddled with many of same funding problems. Making matters worse, it may have been revived too late: Since the DOE withdrew its support, several major carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects and alliances have sprouted in the U.S., and these could give FutureGen a run for its money.
-
Coal
How Much Coal Does the U.S. Really Have?
The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), a federal mapping agency, has of late been propounding the difference between "resources" and "reserves." It says that although the two terms are used interchangeably, the distinction is simple: Reserves are a subset of resources. Coal resources, as an example, include those in-place tonnage estimates determined by summing the volumes for identified and undiscovered deposits of coal, whereas coal reserves are those resources considered "economically producible" at the time of classification, even though extraction facilities are not in place and operative.
-
Coal
Of Fracking, Earthquakes, and Carbon Sequestration
Hydraulic fracturing — the process of drilling and then pumping fluid deep into a formation to generate fractures or cracks, typically for extracting natural gas from shale formations — has been under fire lately, owing to concerns that it contaminates drinking water. But while Congress debates proposed legislation that would impose new restrictions on the technology, an entirely different concern related to fracturing — or "fracking" — is emerging: It may trigger earthquakes.
-
Coal
Major Scottish Coal Plant Starts CCS Pilot Program
Energy provider ScottishPower on May 29 flicked on the switch of a carbon capture and storage (CCS) pilot program at its 2,304-MW coal-fired Longannet power plant, in Fife, Scotland, marking the beginning of a seven-month test — and the first time a UK coal-fired power plant has reportedly attempted to capture its carbon emissions.
-
Coal
City of Springfield’s CWLP Dallman 4 Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
City Water, Light & Power (CWLP), the municipal utilities agency of the City of Springfield, Ill., determined that coal-fired generation was its best alternative for providing long-term reliable and economic electricity to the city’s residents. For negotiating an unprecedented agreement with the Sierra Club that allowed the project to move forward, for choosing the latest in coal-fired technology and air quality control systems as the foundation for the city’s comprehensive energy policy, and for assembling a tightly integrated team that completed the project well before the contractual deadline and under budget, CWLP’s Dallman 4 is awarded POWER magazine’s 2009 Plant of the Year award.
-
Coal
IGCC Update: Are We There Yet?
If a number of technical, financial, and regulatory hurdles can be overcome, power generated by integrated gasification combined-cycle technology could become an important source for U.S. utilities. Our overview presents diverse perspectives from three industry experts about what it will take to move this technology off the design table and into the field.
-
Coal
Designing an Ultrasupercritical Steam Turbine
Carbon emissions produced by the combustion of coal may be collected and stored in the future, but a better approach (in the near term at least) is to reduce the carbon produced through efficient combustion technologies. Increasing the efficiency of new plants using ultrasupercritical technology will net less carbon released per megawatt-hour using the world’s abundant coal reserves while producing electricity at the lowest possible cost.
-
Coal
Carbon Control: The Long Road Ahead
The industry is preparing for carbon legislation by exploring options for dealing with CO2. But even if the technical issues are resolved, actually sequestering CO2 poses a number of other daunting challenges.
-
Coal
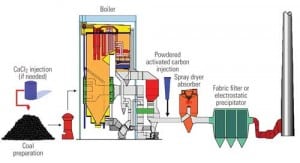
Technology Could Deliver 90% Hg Reduction from Coal
Reducing mercury emissions at coal-fired power plants by 90% has been considered the holy grail of mercury control. A new technique promises to get us there — at a price.
-
Coal
Biomass Cofiring: Another Way to Clean Your Coal
Demand for renewable power is burgeoning as state governments (and maybe soon the U.S. federal government) impose increasingly rigorous environmental and procurement standards on the energy industry. Surprisingly, biomass cofiring has yet to attract much attention, even though it could help many utilities meet their renewable portfolio requirements, reduce carbon emissions, and solve other regional environmental problems. U.S. developers, investors, and regulators should consider including cofiring as part of the energy mix going forward.
-
Coal
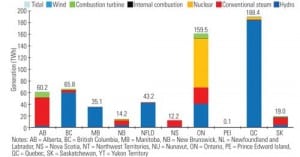
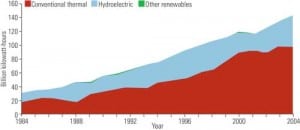
Canada Moves to Rebalance Its Energy Portfolio
Though Canada is rich in fossil fuels, nuclear power may fuel a significant portion of the nation’s future electrical generation needs, especially in provinces that have traditionally relied on hydropower and fossil fuels.
-
O&M
Turkey Opens Electricity Markets as Demand Grows
Turkey’s growing power market has attracted investors and project developers for over a decade, yet their plans have been dashed by unexpected political or financial crises or, worse, obstructed by a lengthy bureaucratic approval process. Now, with a more transparent retail electricity market, government regulators and investors are bullish on Turkey. Is Turkey ready to turn the power on?
-
Coal
CHP: Helping to Promote Sustainable Energy
Because combined heat and power (CHP) plants optimize energy use, they cut fuel costs and pollution. Even though U.S. power plants have been using CHP for decades, today’s energy experts have a newfound appreciation for its ability to promote sustainable energy use.
-
Coal
Capturing CO2: Gas Compression vs. Liquefaction
Carbon capture and sequestration is very likely to be a key element of any future greenhouse gas legislation. Integrated gasification combined-cycle plants now under design have provisions to separate the CO2 at elevated pressures. Coal-fired plants have a far more difficult and expensive task — separating and compressing CO2 from pressures just above atmospheric conditions.
-
Coal
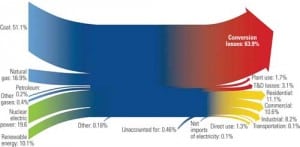
Recession Reduces Demand for Electricity
When roving Contributing Editor Mark Axford attended several recent energy conferences, he found the same questions asked at each one about new U.S. generation sources and consumption patterns. Unfortunately, the experts had few good answers to those questions.
-
Coal
Australia Faces Imminent Power Supply Issues, Groups Say
Australia, the world’s second-largest exporter of thermal coal and uranium, and a significant exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG), faces inevitable electricity rationing and the threat of blackouts unless the government acts urgently to ensure large-scale investments are made in new power-generating capacity, experts from five nations said in April. The Australian Academy for Technology […]
-
-
Coal
Energy R&D: The Missing Link to a Sustainable Energy Future
Q: What do you get when you gather roughly two dozen top researchers from academia, government, and industry to speak on interdisciplinary energy-related issues for a week?
A: A lot of informative but crowded slides, high-octane brain power, fact-based analysis of where we are and we’re headed globally, informed questions, and surprisingly practical answers. -
Coal
EPA Preparing Regulations for Coal Plant Ash
New coal-fired power plant ash management regulations appear to be inevitable, perhaps as soon as year-end. The Tennessee Valley Authority and Edison Electric Institute are on board with new regulations, as long as the ash is regulated as a nonhazardous waste under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act.
-
Coal
UK Sets Binding Carbon Cuts; Requires CCS at Coal Plants
The UK has all but doomed new coal-fired capacity by simultaneously setting binding carbon reduction goals and by requiring carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) of carbon emissions from new mid-size coal-fired power plants. Existing plants will also be required to retrofit their plants when CCS technology is demonstrated, now estimated to happen by 2020.
-
Coal
FirstEnergy Retools Coal Plant to Burn Biomass
FirstEnergy has announced plans to repower two coal-fired units at the R.E. Burger plant to burn biomass. Conversion of the two units, expected to be completed by 2012, gets the utility off the hot seat with the EPA for alleged Clean Air Act violations.
-
O&M
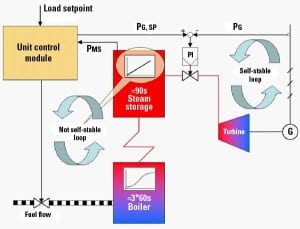
A New Era in Power Plant Control Performance
Recent improvements in the performance of steam power plants have been achieved with advanced computerized controls. These new control schemes not only reduce fuel consumption and make the plant much more responsive, but they also can significantly decrease start-up commissioning time and cost.
-
Coal
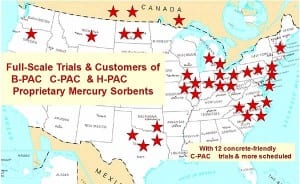
Commercial Experience with Concrete-Friendly Mercury Sorbents
Commonly, 20% of the cement (by weight) in a concrete mix is replaced by fly ash. Fly ash enhances the workability, durability, and ultimate strength of concrete at a lower cost than cement. However, mercury sorbents can change the ash properties to make it unsuitable as a concrete additive. New “concrete-friendly” sorbents can keep the revenues from ash sales flowing.
-
O&M
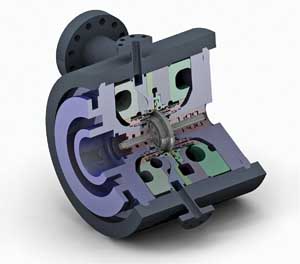
Better Combustion Airflow Monitoring at the Hunan Yiyang Power Plant
Measuring combustion airflow in a coal-fired power plant can be problematic when using annubar instruments that feature small holes that can easily plug with coal dust. Sierra Instruments eliminates this big maintenance headache with its more-accurate, nonplugging thermal mass flow meter design.