POWER
-
Distributed Energy
Aggregated backup generators help support San Diego grid
Last year, San Diego Gas & Electric tapped Boston-based EnerNOC Inc. to aggregate 25 MW of backup generators throughout SDG&E’s service area to relieve the grid when it’s stressed by peak demand for electricity. By combining stringent environmental controls with field-proven expertise managing distributed assets, EnerNOC has helped to improve grid stability in Southern California.
-
Commentary
What Congress can learn from Google
Chances are good that legislation to “cap and auction” greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions will become law as early as 2009. While many environmentalists, utilities, and energy companies agree that cap and auction is the right framework, huge differences remain. Environmentalists want an 80% reduction of GHG emissions by 2050, or sooner. Energy companies want more […]
-
Nuclear
U.S. a paper tiger in nuclear power
I was talking with a utility executive the other day about his recent vacation in India. It’s certainly not your usual holiday destination, but he’s the adventurous type, eager to mingle with different cultures and sample their cuisine. The exec did a lot more than tour the Taj Mahal and get a glimpse of endangered […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (February 2008)
FutureGen picks Mattoon, Ill./Duke applies for first greenfield COL/PPL to work with UniStar on another COL
/Areva seeks NRC certification of its reactor/Mitsubishi also in line at the NRC/PV project shines in Nevada/SunEdison commissions Colorado PV plant/Big concentrating solar plant proposed/Super Boiler celebrates first anniversary/Small fuel cell uses JP-8 jet fuel/POWER digest -
O&M
Focus on O&M (February 2008)
Survey captures industry’s carbon concerns; Sequestering coal plant emissions; Comparing mercury measurement methods
-
Legal & Regulatory
California constrains competition again
Given a chance to make a positive change in California’s wholesale generation market, the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) in December opted instead to maintain the state’s existing “hybrid” market model. That decision will further restrict meaningful opportunities for independent power producers (IPPs) and increase the likelihood that future generation will consist of utility ratebase […]
-
O&M
TVA’s Shawnee Fossil Plant Unit 6 sets new record for continuous operation
Shawnee’s new 1,093-day long-run record is a testament to the plant’s highly qualified and trained staff, excellent operations and maintenance processes, and the quality leadership required to keep all the moving parts pointed in the right direction. If running a power plant is a team sport, then the staff of Shawnee are in a league of their own.
-
O&M
Alliant Energy sweeps EUCG Best Performer awards
The Fossil Productivity Committee of the EUCG conducts an annual analysis of its member plants’ operating results and selects the Best Performer in the categories of small and large coal plants. For 2007, Alliant Energy’s Lansing and Edgewater Generating Stations took the top spots—the first time in recent history that a single utility claimed both awards.
-
Coal
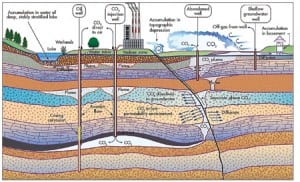
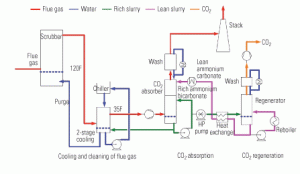
Alstom’s chilled ammonia CO2-capture process advances toward commercialization
Carbon dioxide emissions aren’t yet regulated by the EPA, but it’s likely they will be soon. There are many technically feasible, but as-yet-undemonstrated ways to reduce the considerable carbon footprint of any coal-fired plant, whether it uses conventional or unconventional technology. One promising approach to removing CO2 from a plant’s flue gas uses chilled ammonium bicarbonate to drive the separation process.
-
Coal
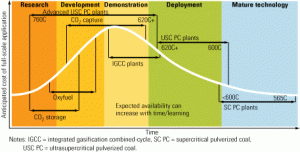
Accelerating the deployment of cleaner coal plants
The dearth of commercial operating experience for advanced coal-fired facilities is forcing their early adopters and builders to use long development cycles and pay high costs for unique engineering design studies. A broad-based industry collaborative effort fostered by EPRI to address this issue is beginning to show results.
-
O&M
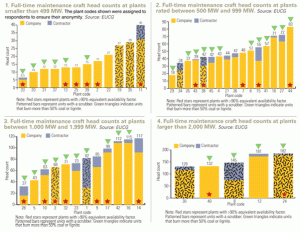
Who’s doing coal plant maintenance?
POWER has reported on several EUCG benchmarking studies over the past several years. This month we examine the maintenance staffing of 45 coal plants reported by 13 EUCG member utilities. If you benchmark your plants or fleet, as you should, some of the study’s results challenge what is considered conventional wisdom.
-
O&M
The case for cathodic protection
All fossil fuels carry some risk with their reward of an energy density that’s sufficient for producing electricity economically. For coal and natural gas, that threat is a fire or explosion. However, the risk of an explosion isn’t limited to gas-fired plants. Gas poses a threat to any plant that uses the fuel, even in small quantities for heating. Here’s an overview of what you should be doing to keep gas pipelines from corroding and exploding.
-
Nuclear
Renew Indian Point’s fission license
Early last month, Governor Eliot Spitzer and Attorney General Andrew M. Cuomo—both New York Democrats—asked the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) to reject Entergy Nuclear’s application to extend the operating licenses of Indian Point Units 2 and 3 for 20 years. The units, each rated at about 1,000 MW, are a major source of […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (January 2008)
Dominion applies for new Virginia reactor / ABB commissions world’s largest SVC / Google Earth adds air quality data / Alstom supplies integrated solar/CC project in Morocco / DOE updates coal plant database / Dam the Red Sea? / Complying with CWA Section 316
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (January 2008)
Single-window control of CHP plant’s energy converters / Safety stuffers entertain as they inform / Doubling up for a heavy load
-
Legal & Regulatory
One-size RPS does not fit all
The U.S. Congress continues to debate proposals that would mandate that a set amount of the nation’s electricity come from renewable energy sources such as wind, the sun, or biomass. These discussions about adopting a nationwide renewable portfolio standard (RPS) raise significant concerns for power providers and customers alike. Backers of a one-size-fits-all federal RPS […]
-
Coal
Regulatory risks paralyzing power industry while demand grows
In our second annual report on the state and future of the U.S. power generation industry, we combine the considerable experience of POWER’s editorial staff with the market savvy of Industrial Info Resources Inc. (see next story) to preview the industry’s direction in 2008. We anticipate that the specter of carbon control legislation will hobble coal and make renewables the hot ticket while nukes continue to inch forward in a generation market that is basically treading water.
-
Coal
Greater fuel diversity needed to meet growing U.S. electricity demand
Industrial Info Resources’ strengths are tracking capital projects and cost projections and providing intelligence about the power generation market, among others. IIR has used its large industry databases and numerous industry contacts to develop its outlook for 2008. Here’s what you should expect and plan for this year.
-
Water
Costlier, scarcer supplies dictate making thermal plants less thirsty
The Energy Information Administration estimates that U.S. thermoelectric generating capacity will grow from 709 GW in 2005 to 862 GW in 2030 to help meet annual demand increases of 2%. The makeup and cooling water needed by plants generating that increased capacity certainly won’t be available from withdrawal sources, so plant developers and owners will have to apply water-stingy technologies plantwide. As is usually the case, conservation saves money as well as the environment. Here’s a thumbnail economic analysis of some solutions to the water problem.
-
O&M
Eliminating oil whip–induced vibration after a steam turbine retrofit
Nobody expected driveline vibration to occur after a flawless retrofit of a 200-MW steam turbine. But when it did, Mitsubishi Power Systems and Exelon vibration specialists identified the symptoms and rapidly narrowed the list of possible causes. Confounding factors made the root cause difficult to identify, but the experts pinpointed the problem, made necessary hardware modifications, and placed the turbine back in service in a week.
-
O&M
Protecting plant equipment from voltage sags
Immunity from voltage sags is vital for reliable operation of our ever-more-sophisticated electronic controls and equipment. Every electrical product should be able to ride through typical voltage sags, but in many cases the first sag test occurs after equipment is installed and in operation. Select the appropriate sag immunity specification and equipment compliance testing, and you’ll be glad you did.
-
Business
Workforce analysis: Replacing management by fad with management certainty
The biggest problem facing industrial managers is ensuring that they’ll continue to have a skilled workforce. With so many people nearing retirement, organizational skills are at risk, which poses a direct threat to operations. Many companies are making big investments to capture the unique knowledge and experience of graybeards before they move on. But that is just one aspect of a far more complex issue.
-
Commentary
U.S. nuclear power’s time has come—again
In the U.S. today, there are continual discussions about energy independence, energy security, and ways to slow climate change. But meeting the nation’s projected 40% increase in electricity demand by 2030, while reducing overall power plant CO2 emissions, will require much more than talk. During the 1990s, American utilities increased their gas-fired generating capacity because […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Rigid COD deadlines do more harm than good
A utility executive responsible for procuring renewable power recently lamented that, at the time of contract execution, renewable “projects” are typically at a very preliminary stage of development, offering scant information about project specifics. Regulatory or other objectives often cause the utility to require that the power purchase agreement be executed before critical permits have […]
-
Wind
Burbo Bank Offshore Wind Farm, Liverpool Bay, UK
POWER congratulates DONG Energy and Siemens Power Generation on the October 18 inauguration of their 90-MW Burbo Bank Offshore Wind Farm. This project was the first commercial application of Siemens’ new 3.6-MW wind turbine and exemplifies how the right developer and supplier team can quickly add much-needed offshore wind power to a country’s generation mix.
-
Waste to Energy
Central Vermont Public Service, Cow Power Program
Central Vermont Public Service developed the nation’s first farm-to-consumer renewable energy choice by using cow manure to generate electricity. CVPS gave beleaguered farms new economic hope; developed a generation system that provides clean, renewable energy; and helped solve numerous manure management environmental challenges. CVPS and Cow Power’s four member dairies are recognized as a 2007 Top Plant for generating renewable energy one cow at a time.
-
Solar
Nevada Solar One, Boulder City, Nevada
Concentrating solar thermal projects fell out of favor more than 15 years ago, when the last SEGS plant was commissioned. But advances in reflective mirror, thermal receiver, and tracking system technologies have significantly improved the systems’ energy conversion efficiency at a much lower capital cost. POWER recognizes Nevada Solar One as a 2007 Top Plant for pushing the limits of solar thermal technology and for being the first of a new generation of concentrating solar projects now being developed around the world.
-
Geothermal
Raft River Geothermal Project, Malta, Idaho
Geothermal power is a unique renewable energy because it has the best potential capacity factor and is perhaps the only option for baseload power generation. U.S. Geothermal has constructed the first geothermal plant in Idaho in a generation by restoring an abandoned DOE demonstration project site that may possess a development potential of over 100 MW using proven power generation technology. The success of Raft River may well determine the future of geothermal energy production in Idaho.
-
Wind
Steel Winds Project, Lackawanna, New York
This year, for the first time, the U.S. wind power industry is poised to push past the 3,000 MW installed per year milestone. At 20 MW, Steel Winds may seem like a footnote, but its importance is measured in more meaningful terms than just size. Steel Winds is the first commercial deployment of the Clipper Windpower 2.5-MW Liberty turbine, the first installation on a former Superfund site, and is said to be the largest wind farm in the U.S. developed in an urban setting. In addition, the project anchors Lackawanna’s redevelopment of a former industrial site along Lake Erie for public use.