Wind
-
Legal & Regulatory
Solving the Renewable Integration Puzzle
In November, California voters overwhelmingly rejected an initiative that would have put the brakes on AB 32, the state’s ambitious greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction law. Given the role that California has played in climate change policy, that such a vote took place only four years into the law’s implementation process and 10 years before the emissions reduction targets were to be met was a reality check on climate change policy for those on both sides of the issue.
-
Coal
The U.S. Power Industry 2011: The Sequel
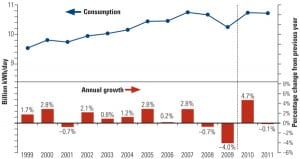
If Hollywood were scripting the power industry story for 2011, it would be a sequel to 2010—more of the same, but just not quite as good. Natural gas gets top billing and the accolades, wind power drops to a supporting role, and new nuclear answers the casting call but has yet to get a speaking part. Coal is like Mel Gibson—a talented Oscar winner unlikely to get another leading role. In this, our fifth annual industry forecast report, the story may be familiar, but the price of admission is going way up.
-
Wind
Wind Energy Soars Around the World
Denmark put into operation its 12th offshore wind farm this October. The €440 million Rødsand 2 wind farm, a 90-turbine installation with a nameplate capacity of 207 MW, was erected for owner E.ON by Siemens Energy—both German firms—over a mere 122 days. The wind farm joins Rødsand I, a 72-turbine installation that began operating nearby in the Baltic Sea in 2003.
-
Wind
Finding Fault: Improving Wind Farm Availability
Survey wind turbine manufacturers about how to calculate wind farm availability and you will get countless different definitions and exceptions to the rule.
-
Wind
Top Plant: Thanet Offshore Wind Farm, Isle of Thanet, UK
In September, the 300-MW Thanet Offshore Wind Farm, the world’s largest offshore wind energy facility, began operation off the southeastern coast of England. The wind farm has 100 3-MW turbines manufactured by Vestas. The facility will generate electricity equivalent to the annual consumption of more than 200,000 British households.
-
Solar
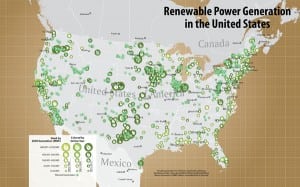
Map of Renewable Power Generation in the United States
For a full-size map, contact Platts. Courtesy: Platts Data source: POWERmap All rights reserved. No reproduction allowed.
-
Wind
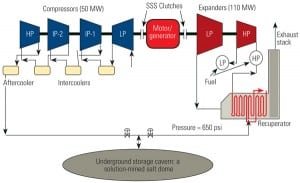
Could CAES Answer Wind Reliability Concerns?
As wind and solar energy capacity in the U.S. continues to grow, compressed air energy storage (CAES) and other bulk energy storage technologies will increasingly be used to help balance electrical supply and demand.
-
Wind
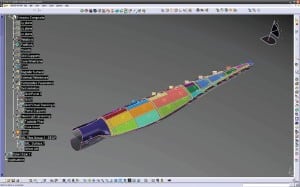
New Design Tool Improves Manufacture of Composite Wind Turbine Blades
Composite materials are ideal for producing wind turbine blades because of their strength, light weight, and ability to be tailored to provide the precise mechanical properties needed for any blade design. Now, best practices originally developed for rotorcraft blade manufacturing can be applied to designing and manufacturing wind turbine blades that are constructed from composites.
-
Hydro
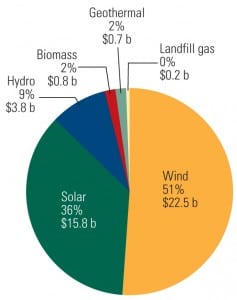
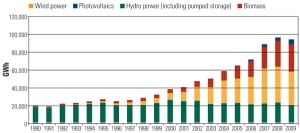
The Rush to Renewables
In 2010 investment in wind power continued to accelerate, particularly in California and Texas. California also entered several solar projects in the race for financing. The finish line that renewable power developers and their partners are racing to meet is a December 31 deadline to qualify for federal cash grants.
-
Wind
World’s Largest Offshore Wind Farm Opens in the UK
Swedish company Vattenfall in late September officially opened the 300-MW Thanet Offshore Wind Farm in southeast England. Covering an area of 35 square kilometers, the installation comprising 100 Vestas V90 turbines, each 115 meters (m) high, is the largest offshore wind farm in the world to date.
-
Solar
The Global Smart Grid Scene
Presenters at the inaugural GridWise Global Forum in Washington, D.C., September 21 to 23 had a lot to say about the prospects for smarter grids. This synopsis of facts and opinions shared at the event, which attracted several smart grid A-listers, looks at the major challenges ahead, especially for the U.S.
-
Wind
Offshore Devices Get Bigger and Lighter
UK firms unveiled two innovative offshore turbines in July and August—one to reap the wind’s energy and the other, tidal power. Wind Power Ltd. made public the latest embodiment of its Aerogenerator project, a lighter 10-MW design, while Atlantis Resources Corp. unveiled and then deployed its mammoth AK1000 tidal turbine, which it says is the […]
-
Wind
The Art of Power Generation
Much opposition to large-scale renewable projects concerns aesthetics. U.S. federal regulators, for example, ordered the developer of the $1 billion Cape Wind project—a 468-MW offshore wind farm proposed to be built in a 25-square-mile section of Nantucket Sound off the Massachusetts coast—to change the design and configuration of the project to reduce “visual impacts.” Among […]
-
Solar
What Utility Executives Think About the Smart Grid
This summary of results from a recent Platts/Capgemini survey of North American utility executives looks at what respondents had to say about all things related to the smart grid. Nearly half of respondents’ utilities have a smart grid strategy in place, while the other half said their utility has one in development.
-
Wind
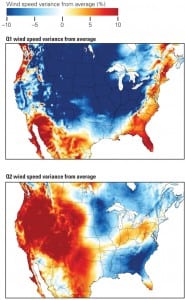
U.S. Wind Speeds Bluster on Climate Phenomena
Renewable energy information services provider 3TIER in July confirmed with its publication of wind performance maps what U.S. wind developers with poor generation numbers had been suggesting earlier this year: A long-lasting El Niño event paired with a North Atlantic Oscillation event caused wind speeds to slump abnormally from the fall of 2009 through spring 2010.
-
Solar
The Feed-in Tariff Factor
Most countries are trying to increase the percentage of their electricity supply that comes from renewable sources. But because capital costs for renewable generation still, in most cases, are higher per kilowatt-hour than for fossil-fueled power, governments are looking at all options for encouraging the development of greater renewable capacity. Feed-in tariffs (FITs) are one policy tool that has been used, most notably in Europe. Now North America is testing FITs as well.
-
Solar
Bulk Storage Could Optimize Renewable Energy
A defining challenge for the U.S. electricity industry is to economically integrate renewable energy facilities into grid operations without sacrificing reliability. Bulk energy storage options are commercially proven technologies that enable that integration most expediently. Existing and emerging national and state policy frameworks are supporting their application in projects under development throughout the country.
-
Solar
Feed-in-Tariffs Around the World
Feed-in-tariffs (FITs)—above-retail rates paid for renewable power that producers "feed" into the grid—are gaining momentum all over the world as a means of driving project growth. Here are some of those established and proposed FITs.
-
Hydro
Integrating Wave and Wind Power
While Europe’s offshore wind sector has taken off, interest is resurging in marine energy. The UK’s Crown Estate took the major step this March, for example, of awarding leasing rights to 10 wave power projects to develop generation in Scotland’s Pentland Firth and Orkney waters of the North Sea.
-
History
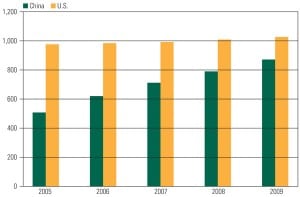
China: A World Powerhouse
It’s no surprise that China leads the world in recent power capacity additions. What may surprise you is the precise mix of options this vast country is relying upon to meet its ever-growing demand for electricity. As a result, this ancient civilization is fast becoming the test bed and factory for the newest generation and transmission technologies.
-
Coal
Industry Pivots on Natural Gas, Hails Cap and Trade
At the opening ELECTRIC POWER 2010 plenary session, both the keynote speaker’s address and discussion among the Power Industry Executive Roundtable participants pointed to the renewed appeal of natural gas and proposed cap-and-trade legislation as being potential game-changers for the U.S. power industry.
-
Hydro
Utility Perspectives on Using Renewable Power
As U.S. utilities increase the percentage of renewable energy in their generation portfolio, they must deal with a number of key issues related to selecting specific technologies. Additionally, they must figure out what it will take to make renewables emerge as a mainstream generating option in the future.
-
Wind
Offshore Wind Takes Off Around the World
After more than a decade of debate, in April, U.S. Interior Secretary Ken Salazar approved Cape Wind, a proposed 130-turbine offshore wind farm for Nantucket Sound in Massachusetts. It would be the first wind facility in U.S. waters. Despite remaining hurdles, the approval marks a shift in political winds for the nation’s fledgling industry, and it could spur further development of projects proposed for relatively shallow waters along the East Coast and in the Great Lakes.
-
Wind
Competition for Offshore Turbine Market Heats Up
One indication that the world’s offshore wind sector is poised to soar is the escalating competition between turbine makers. This April, General Electric (GE)—the world’s second-largest manufacturer of wind turbines—announced it would introduce a 4-MW gearless wind turbine (a design requiring no gearbox between turbine and generator) in 2012. The move directly challenges market leader Siemens Energy, of Germany, and its head-to-head competitor, Denmark’s Vestas Wind Systems.
-
Hydro
Power in Mexico: Renewables Remain More Desired than Real
Mexico has already developed substantial large hydro and geothermal resources. However, without policy changes and government-sponsored financial incentives, unconventional renewable sources are taking the equivalent of baby steps.
-
Wind
Wind Destroyed and Now Powers Greensburg, Kansas
Greensburg was destroyed by an EF5 tornado on May 4, 2007. Instead of abandoning the Kansas town, the community quickly embraced the task of rebuilding it from the ground up, maximizing the use of renewable energy sources and energy efficient building techniques. Rebuilding continues, but the future of Greensburg has never been stronger.
-
Solar
A New Foundation for Future Growth
As the economy begins to grow again, the banking industry continues to stabilize, and lawmakers work on finalizing climate change legislation, the decisions made in 2010 will lay the foundation for the power industry for decades to come.
-
Coal
Brazil: Latin America’s Beacon
With the eighth-largest economy in the world, Brazil has a clear need for power, but balancing supply and demand has proven tricky in recent decades. Even in a country where over 80% of generation capacity comes from renewables, planning for future capacity additions isn’t straightforward or easy.
-
Solar
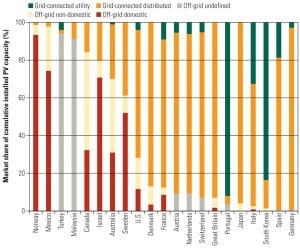
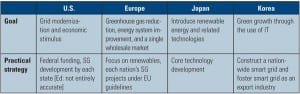
Which Country’s Grid Is the Smartest?
The U.S. isn’t the only country evaluating and implementing elements of smart grid technology. In fact, it could be argued that other nations are much farther along the path to a comprehensive, technically advanced system for integrating renewables, managing load, and creating a more flexible power grid.
-
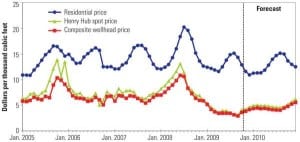
O&M
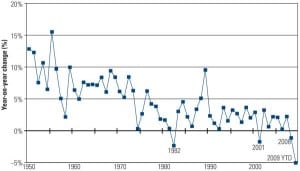
The U.S. Gas Rebound
"It’s déjà vu all over again," said Yogi Berra. The Hall of Fame catcher could easily have been predicting the coming resurgence of natural gas – fired generation. Yes, a few more coal plants will be completed this year, but don’t expect any new plant announcements. A couple of nuclear plants may actually break ground, but don’t hold your breath. Many more wind turbines will dot the landscape as renewable portfolio standards dictate resource planning, but their peak generation contribution will be small. The dash for gas in the U.S. has begun, again.