Coal
-
Coal
Court Kicks CAIR Rules to the Curb
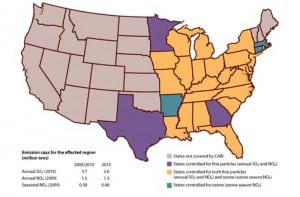
A federal appeals court has struck down a key Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) program for reducing fine particulate and smog-causing emissions in the eastern half of the nation, saying the rules were riddled with “several fatal flaws,” including the agency’s failure to properly focus pollution cuts to prevent movement of air pollution from one state from worsening air quality in a downwind state.
-
Coal
EEI Leaders Say Promise of Carbon Capture and Storage “Overblown”
In a sobering assessment of a key technology that’s expected to help keep the coal industry viable in the face of likely greenhouse gas caps, several electric utility executives have expressed deep concern that the promise of carbon capture and storage for coal-fired power plants has been “overblown” and “oversold.”
-
Coal
Woods and power company CEOs agree: “The state of the industry is cautious”
It is rare indeed to witness, at an otherwise staid industry forum, the public rebuke of the country’s most prominent supplier to the electric power industry. But at the Keynote session and Power Industry CEO Roundtable of the 2008 ELECTRIC POWER Conference & Exhibition in Baltimore this May, Milton Lee, general manager and CEO of […]
-
Coal
Carbon Constraint Conference: Dealing with the climate change conundrum
“Once it’s enacted, the impact of climate change legislation on the electric power industry will be ten times bigger than that of the Clean Air Act,” said Dan Adamson, an attorney with the law firm of Davis Wright Tremaine and chair of the opening session at the 2nd Annual Carbon Constraint Conference (Figure 1). 1. […]
-
Coal
PRB Coal Users’ Group enjoys growing interest in its concerns
The 2008 Powder River Basin Coal Users’ Group (PRBCUG) set new records for attendance again this year with more than 400 registered members for the three-and-a-half-day event, 268 of whom were from operating companies. The meeting’s Grand Sponsor was Benetech and its Plant Professionals group. The meeting began with the Power Plant Awards Banquet on […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (July 2008)
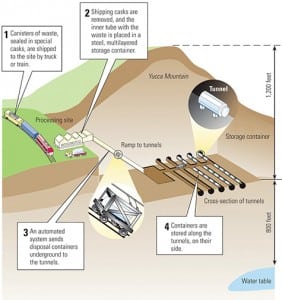
Yucca Mountain plan sent to NRC/ CPV cells get cooling chips from IBM/ StatoilHydro to pilot test first offshore floating wind turbine/ U.S. rivers next massive power source?/ Siemens delivers 500-MW gasifiers/ Algae: A green solution/ POWER digest
-
Coal
Luminant’s Big Brown Plant wins for continuous improvement and safety programs
Staff from Luminant’s Big Brown Plant accepted the PRB Coal Users’ Group’s top honor for innovative improvements to coal-handling systems and a sterling safety record. The numbers reveal their accomplishments: an average EFOR less than 4%, an availability factor averaging 90% for a plant that burns a lignite/PRB mix, and staff who worked more than 2.6 million man-hours since March 2000 without a lost-time injury.
-
Coal
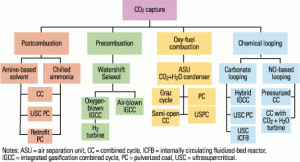
Options for reducing a coal-fired plant’s carbon footprint, Part II
A conventional coal plant’s CO2 emissions can be reduced either after combustion (see Part I of this article in POWER, June 2008) or before. In the latter case, typified by integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) plants, the fuel used is synthesis gas (syngas), which contains mostly hydrogen (H2) and CO. A water-shift reactor converts the CO […]
-
Coal
From Plan to Plant: The Struggle to Make “Clean Coal” a Reality
In early June, New York Gov. David Paterson proclaimed that his state would commit $6 million to buttress a carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) viability study for the development of a new 50-MW clean coal plant in Jamestown, in western New York. The circulating fluidized-bed (CFB) project, which would use pure oxygen to combust coal and subsequently capture and sequester 90% of emitted carbon dioxide (CO2), would be “the first of its kind in the world” and could potentially enable New York firms to launch exports of the technology worldwide, Paterson promised.
-
Coal
New Source Review Update
The mere mention of the words "New Source Review" (NSR) will immediately capture the full attention of any utility executive and might cause the cancellation of even the best power plant "upgrade" project. The effects of those three words have nothing to do with project economics or whether a project increases or decreases emissions. It’s all about the lawsuits.
-
Coal
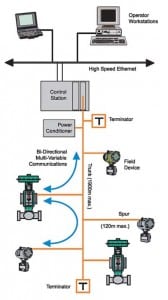
A Fieldbus Primer
Many automation engineers are coming face to face with real fieldbus applications for the first time. Fieldbus (the use of digital communications networks for distributed instrumentation and control) is a wonderful technology with many benefits, but fieldbus installation requires some additional considerations over and above normal 4-20 mA projects. In this article, I present some of those issues and show you how to deal with them.
-
Coal
Debate on the Cost of Carbon Control Begins
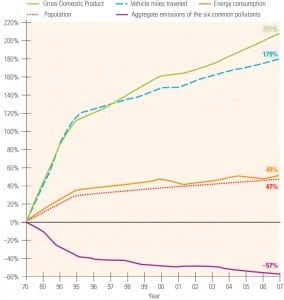
Senate legislation to cap U.S. greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions beginning in 2012 would have generally modest cost impacts on the national economy, leading to reductions in gross domestic product (GDP) by 2030 that range from 0.2%, or $444 billion, to 0.6%, or $1.3 trillion, according to an Energy Information Administration analysis.
But the analysis, which concluded that the costs of the legislation would depend largely on the availability of advanced nuclear and coal-fired generation technologies, drew criticism from Republicans for its projection of a massive buildup of nuclear generation.
-
Coal
Designing Material-Handling Systems for FGD Projects
Reducing NOx, SO2, and other air pollutants continues to be a challenge for the power generation industry. The technologies are well-understood, but the devil is always in the details, especially when a complex treatment system is retrofitted to an existing plant.
The most common method for reducing SO2 from plant emissions is the conventional lime- and limestone-based flue gas desulfurization (FGD) system. Material-handling systems for limestone and gypsum present specific challenges and opportunities that differ from those of coal-handling systems. This article looks at factors to consider before and during the design of a new material-handling system. The choices you make about these many variables will determine the cost and longevity of your system.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (June 2008)
Artificial photosynthesis for solar power? / Poultry litter to fuel 55-MW N.C. plan / First fuel cell-powered plane takes flight / First HTS transmission cable energized / PTC powers wind power industry / Renewing Greensburg / GAO deems coal-to-gas switch impractical / Assessing the Congo River’s power potential / POWER digest / Corrections
-
Legal & Regulatory
The green trade-off
By Steven F. Greenwald and Jeffrey P. Gray These should be good times for environmentalists who focus on “green” energy policy. More than half the U.S. states have adopted renewable portfolio standards (RPS) that require utilities to meet specific renewable generation targets, and many are considering additional actions to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Such […]
-
Coal
Options for reducing a coal-fired plant’s carbon footprint: Part I
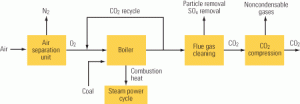
Caps on greenhouse gas emissions are imminent in the U.S., and they will change how we design tomorrow’s coal-fired power plants. Efforts are already under way to develop alternative capture and sequestration technologies, mainly for CO2. Unfortunately, the proposed processes all consume lots of energy, reducing plants’ net output and efficiency. In Part I of our look at these technologies, we list and quantify the negative impacts of postcombustion removal of CO2 from a coal plant’s flue gas. Next month, in Part II, we’ll do the same for four other CO2 reduction techniques: oxyfuel combustion, using higher-temperature and higher-pressure boilers, cofiring biomass, and replacing some coal-fired capacity with renewable capacity.
-
O&M
Boiler optimization increases fuel flexibility
Burning spot market fuels can reduce plant fuel costs, but it can also introduce unexpected operational problems throughout the boiler island. Orlando Utilities Commission’s Stanton Energy Center optimized its Unit 2 combustion system and improved O&M practices as part of a project to increase the unit’s fuel flexibility without degrading reliability or heat rate. OUC’s attitude: If you can measure it, you can manage it.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (May 2008)
National Grid divested of Ravenswood/ GE to sell Baglan Bay plant; From prairie grass to power/Renewables experience 40% growth/ The sustainable city/Solar recharger for developing countries/ Seeking CCS solutions/ Hoover Dam could stop generating/ Japan turns to fossil fuels/U.S. reactors produce record power/ POWER digest
-
Coal
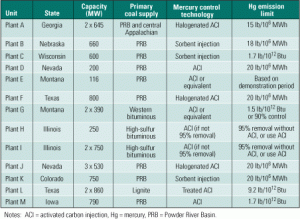
Future of national mercury rule now uncertain
This February, a federal appeals court tossed out the Clean Air Mercury Rule and its cap-and-trade program and ordered that mercury be regulated more stringently as a hazardous air pollutant. Adding insult to injury, the court made its ruling effective one month later. While the EPA regroups, state energy and environmental regulators will have an opportunity to look closely at recent power plant permits for guidance. This article reviews the technology options and regulatory approach for mercury control used on recently permitted and currently operating coal-fired plants.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (April 2008)
Tenaska proposes first new coal-fired plant with carbon capture/ Concerns raised over growth of China’s CO2 emissions/ Sandia, Stirling Energy Systems set new world record/ Indonesia orders first Wärtsilä Gas Cubes/ First wind turbines on Galapagos Islands cut oil imports/ Harnessing waste heat for electricity/ POWER digest/ Correction
-
Coal
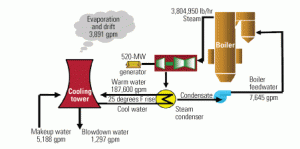
New coal plant technologies will demand more water
Population shifts, growing electricity demand, and greater competition for water resources have heightened interest in the link between energy and water. The U.S. Energy Information Administration projects a 22% increase in U.S. installed generating capacity by 2030. Of the 259 GW of new capacity expected to have come on-line by then, more than 192 GW will be thermoelectric and thus require some water for cooling. Our challenge will become balancing people’s needs for power and for water.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (March 2008)
DOE scraps FutureGen / U.S. nuclear plants have record year / Westinghouse wins TVA contract / UniStar Nuclear to file for COL / AEP ranks second in U.S. construction / China moving to the driver’s seat / New solar cycle poses risks / Dutch favor power from natural gas / POWER digest / Corrections
-
Coal
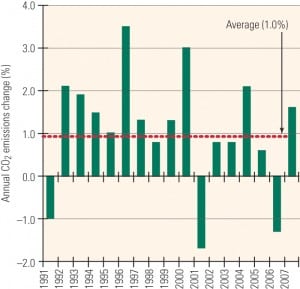
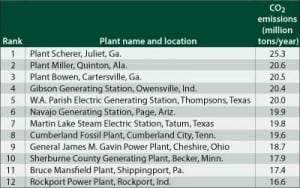
The Coal Patrol: Ranking the CO2 Emissions of the World’s Power Plants
The Environmental Integrity Project, a Washington-based advocacy group, announced in March that CO 2 emissions from U.S. power plants increased 2.9% last year over 2006 levels. The group used 2006 and 2007 CO 2 emissions data from the U.S. EPA and the DOE’s Energy Information Administration. It’s hard to normalize CO 2 numbers — and […]
-
Coal
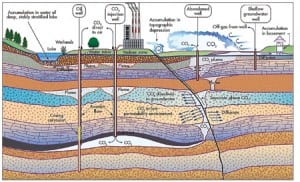
The Future of Coal Power: Modeling Geological Sequestration of CO2
Everyone in the power generation business knows that coal will continue to be a necessary fuel source for the foreseeable future. Many of those same people are beginning to understand that, politics aside, coal plant operations in the foreseeable future won’t look like the operations of yesterday or today. But what exactly will the future […]
-
Coal
The Future of Coal Power: Development and Siting Obstacles for New Coal Plants
In recent years, Sargent & Lundy has evaluated many potential sites for new coal-fueled generation. Some of the sites studied were lands adjacent to existing power plants (brownfield sites); others were undeveloped greenfield sites. The numerous technical, environmental, economic, and regulatory issues that bear on power plant siting generally apply to both brownfield and greenfield […]
-
Coal
Emissions: Unintended Consequences of Problem-Solving
Most folks probably don’t think that power plants burning coal and ethanol — the latter touted as a having a smaller carbon footprint — have much in common. But at least one ethanol plant — Blue Flint Ethanol in Underwood, N.D. — is co-located with a coal-fired power plant in order to use its excess […]
-
Coal
Plant Design: Trends in Coal Pile Design
An optimal coal pile design takes into account the site-specific (and often conflicting) needs of a new power plant early in its design — rather than using whatever land is available after the plant layout has been finalized. Determining site requirements necessitates a detailed analysis of all potential coal-fueling options. A coal pile designer should […]
-
Coal
Speaking of Coal Power: The True Costs of Going Green
Three of the best-kept secrets in the U.S. today have nothing to do with national security in the traditional sense. They all involve costs: the cost of fulfilling campaign promises, a valid estimate of the cost of carbon control legislation (S. 2191) expected to reach the Senate floor in a few months, and the real […]
-
Coal
Global Monitor (February 2008)
FutureGen picks Mattoon, Ill./Duke applies for first greenfield COL/PPL to work with UniStar on another COL
/Areva seeks NRC certification of its reactor/Mitsubishi also in line at the NRC/PV project shines in Nevada/SunEdison commissions Colorado PV plant/Big concentrating solar plant proposed/Super Boiler celebrates first anniversary/Small fuel cell uses JP-8 jet fuel/POWER digest -
O&M
Focus on O&M (February 2008)
Survey captures industry’s carbon concerns; Sequestering coal plant emissions; Comparing mercury measurement methods