In This Issue
-
News
Norway Inaugurates Osmotic Power Plant
One of the world’s first osmotic power plants started operation at Tofte on the Oslo fjord in Norway last November, producing 2 kW to 4 kW after more than a decade of collaborative research and development by the Norwegian University of Science and Technology and Norwegian state-owned utility Statkraft (Figure 1).
-
-
Nuclear
Concerns About Electromagnetic Interference in Nuclear Plants Related to Digital Upgrades
In order to operate aging nuclear power plant instrumentation and control systems for up to 60 more years or longer, there must be a smooth transition from existing analog technologies to advanced digital platforms. For this to occur, electromagnetic compatibility concerns related to both qualification testing and the electromagnetic environment must be addressed to ensure safe and reliable operation of these systems within the plant’s electromagnetic and radio frequency interference environment. By understanding the regulatory requirements and sharing implementation experience, digital system upgrades can be installed successfully.
-
News
California Releases Preliminary GHG Cap- and-Trade Rules
California’s Air Resources Board (ARB) in late November issued the nation’s first blueprint for a broad-based cap-and-trade program to control greenhouse gases (GHG). If they take effect in 2012 as proposed, the regulations in ARB’s preliminary draft will apply to 605 of the state’s largest stationary GHG emitters, including power plants and industries, as well as electricity imports. Starting in 2015, the regulations will also apply to fuel suppliers and smaller stationary GHG emitters such as homes and commercial businesses.
-
Nuclear
The Advanced Digital Fieldbus Option for Nuclear Plants
Digital fieldbus technologies, including Foundation fieldbus and Profibus, are increasingly being used with success in the nuclear and fossil fuel power industries. This article compares a conventional control system with a Foundation fieldbus – based digital control system used in a typical circulating water system in a nuclear power plant. As shown in this example, using digital fieldbus technologies can result in significant savings in terms of installation and hardware costs.
-
News
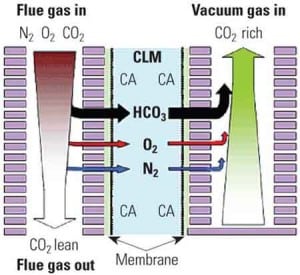
Carbon Capture Technology Based on a Blood Enzyme
The way our lungs separate and capture carbon dioxide from blood could be key to isolating emissions of the greenhouse gas in order to store them safely underground.
-
O&M
Can Your Boiler Feed Pump Handle a Deaerator Pressure Transient?
In a typical steam power plant, the boiler feedwater (BFW) pump takes suction from the deaerator (DA) and discharges high-pressure water to the boiler through the feedwater heaters. During normal operation, the DA is supplied with steam turbine extraction steam to mix with and heat the feedwater.
-
News
New Polymers Could Mop Up Radioactive Isotopes
Scientists from Germany and India say they have developed a new polymer that reduces the amount of radioactive waste produced during routine operation of nuclear reactors. The approach uses small beads of the material to "fish" out radioactivity from water pumped through the reactor’s core.
-
Commentary
How Myths Distort Energy Policy
Congress and various states are considering a fundamental restructuring and regulation of our energy policy. Any such effort should be based on facts, but legislators, unfortunately, incline to myths, such as the notion that most of our energy comes from oil.
-
News
Job Site Material Recycler
The new EZ Grout Hog Crusher Job Site Material Recycler from Multiquip is easily attached to a skid steer loader or forklift and can recycle most materials — brick, block, stone, rock, asphalt, non-reinforced concrete, and more — on the job site. The Hog Crusher is able to scoop up and pulverize recyclable material in […]
-
Nuclear
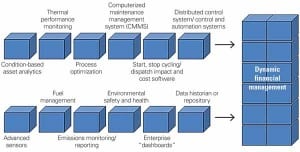
The Value of a Knowledge-Based Culture Grows in Lean Times
Given delays and cancellations of new generating capacity, pushing the existing power generation fleet is more important than ever. At ELECTRIC POWER 2009, multiple presentations explored the premise that an active knowledge management strategy — requiring a blend of digital and human elements unique to each power plant — will help you extract the most productivity from your assets.
-
News
Laser Pulley Alignment Tool
Seiffert Industrial’s new laser pulley alignment tool, Pulley PRO, uses a green laser beam for maximum angular resolution and for reliable and accurate readings. The lightweight and compact units magnetically attach to the inside or outside face of any pulley or sprocket and have no small parts or targets that can get lost. A laser […]
-
Coal
Plant Efficiency: Begin with the Right Definitions
The race is on to claim the title of "most efficient coal-fired power plant" on the planet. However, it’s tricky identifying finalists because of the widespread misuse of the term "efficiency" and all those nagging assumptions. Let’s first establish clear definitions and then identify the title contenders.
-
News
Mildew-Resistant Epoxy
Sherwin-Williams introduced the Tile-Clad High Solids Mildew Resistant epoxy, an industrial coating that protects against mildew growth on exterior surfaces where dampness and humidity are of concern. The epoxy is well-suited for areas where mildew growth must be guarded against in order to maintain operations, such as water tank exteriors, structural and support steel, power […]
-
O&M
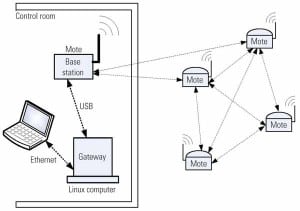
Low-Cost Wireless Sensors Can Improve Monitoring in Fossil-Fueled Power Plants
As equipment ages in fossil-fueled power plants, component wear leading to machinery failure increases as a result. Extending equipment life requires increased attention to maintenance, and one way to improve maintenance planning is to detect faults prior to failure so maintenance can be scheduled at the most cost-effective, opportune time. This type of strategy benefits from the use of additional sensors, and wireless ones can often be installed with the least time and cost.
-
News
Compact Centrifugal Pump
Acknowledging that ANSI centrifugal pumps often need to be installed in areas where space is at a premium, Griswold Pump Co. has developed the 811CC (Close Coupled) ANSI centrifugal pump. This pump offers the features and flexibility of standard Griswold 811 ANSI pumps but with a smaller electrical motor encased in a compact package. Despite […]
-
O&M
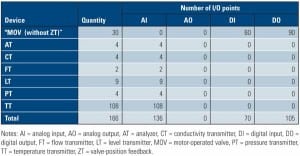
How to Avoid Alarm Overload with Centralized Alarm Management
In 1999, the Engineering Equipment and Materials Users’ Association (EEMUA) released its general guide to the design, management, and procurement of alarm systems for industrial plants. The guidance document (EEMUA 191), however, is vague about applications to specific facilities, such as electric power plants. This article specifies EEMUA 191 standards and practices applicable to the electric power industry and spells out specific variations in alarming practices that are tailored for today’s power plants.
-
News
Digital Surface Chloride Testing Device
CHLOR*RID International launched the Chlor*Ion Meter, a handheld digital testing device that electronically measures chloride on surfaces with an internal ion-specific electrode. Most surface chloride testing devices offer an external electrode on a cord, but these could be damaged in the field, CHLOR*RID says. Because it digitally measures chloride on surfaces, the Chlor*Ion Meter’s ion […]
-
Nuclear
Nontechnical Issues Affecting Digital Upgrades at Nuclear Power Plants
Existing nuclear power plants are increasingly facing the conversion to digital instrumentation and controls technology. Meanwhile, new nuclear designs have digital technology integrated throughout the plant. Digital controls will soon be inevitable, so how do we make the transition as smooth as possible? Without losing focus on the technical solutions, organizations have to pay attention to the nontechnical issues as well.
-
News
Water-Cooled MIG Guns and Consumables
Bernard’s new customizable W-series water-cooled MIG guns and water-cooled Centerfire consumables are designed to meet the wide-ranging needs of high-amperage, water-cooled metal inert gas (MIG) applications. The W-Guns (shown here) are durable and may be customized. Users can choose neck styles, cable lengths, handle styles, consumables, and direct plugs. The W-Guns are rated to 600 […]
-
Coal
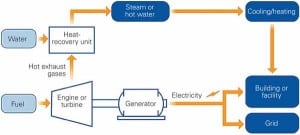
Digital Plant Controls Provide an Essential Edge
It’s a digital world, and even aging power plants are experiencing the benefits of digital controls technologies. The following cover stories provide insight into the latest options and inspiration for your own plant controls projects.
-
News
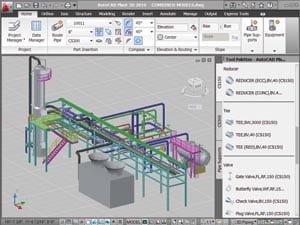
New 3-D Plant Design Software
Building and engineering software designer Autodesk Inc. announced the availability of AutoCAD Plant 3D 2010, a product that it says brings the benefits of model-based design to mainstream plant design projects. The vast majority of plant design and engineering projects support the operation, maintenance, and expansion of existing facilities. These projects are typically executed by […]
-
Legal & Regulatory
Renewable Realities
"It’s anti-renewables" is becoming a familiar refrain voiced before public utility commissions, air quality management districts, and other public agencies with jurisdiction over the siting and operation of new fossil-fueled electric generation projects. The survival — and, in some cases, expansion — of legislatively mandated renewable energy requirements, tax incentives, and outright subsidies through the recent economic downturn has further encouraged opponents of new fossil-fueled generation to cloak themselves in the environmental flag, irrespective of their underlying motives and goals.
-
News
Laser Alignment of Steam and Gas Turbines
LUDECA’s new CENTRALIGN ULTRA was specifically developed for the alignment of steam and gas turbines. The system precisely aligns internal elements with upper halves for distances up to 133 feet. Accurate bore measurements can be acquired and wirelessly transmitted without interrupting other processes, saving time over traditional methods like piano wires, micrometers, and optical instruments. […]
-
News
Level the Playing Field for Open-Loop Biomass
Congress snubbed the biomass power industry in 2004 when open-loop biomass power plants were given only half the production tax credits (PTCs) received by other renewable sources, such as wind, solar, and geothermal. It further dissed open-loop biomass plants by authorizing the credit for only five years (it expired December 31, 2009) rather than the 10 years given to other renewables. Why is the biomass power industry not getting the policy respect and equity with other renewable technologies that it deserves?
-
News
AC Power Sources for Submerged Arc Welding
ESAB Welding & Cutting Products launched the TAF 801/1251 square wave AC power sources for submerged arc welding. The power sources, designed to be used with the fully digital PEK controller, convert the secondary voltage from a sinus wave — via a thyristor-controlled rectifier bridge — to a square wave arc voltage with excellent arc […]
-
News
AREVA Makes Debut in Renewables with German Offshore Turbines
The first six of a dozen high-capacity turbines were commissioned in mid-December at the 60-MW Alpha Ventus project in the North Sea, Germany’s first offshore wind park. All 12 turbines of the €250 million project are already standing, put up in just seven months by a consortium of EWE, E.ON, and Vattenfall — formally known as Deutsche Offshore Testfeld und Infrastruktur (DOTI).
-
O&M
Widespread Voltage Collapse Demonstrates the Importance of Generator Acceptance Testing
A September 2005 power outage that affected two million people in the California Southland was initiated when workers cut live electrical wires after consulting erroneous design drawings, but it was exacerbated by a number of extant problems with local generation and protection configurations.
-
News
Of Floating Power Barges and Ships
More than 60 floating power stations are in operation around the world, deploying some 4 GW at continental shores where electricity is most needed. Though these feature a variety of power sources (including nuclear, gas, and heavy fuels), most are power barges — they do not have their own propulsion systems and would have to be towed to desired locations.
-
News
The Age of the 800-kV HVDC
High-voltage direct current transmission (HVDC) has come a long way since 1882 when the first of its type carried power from Miesbach in Bavaria to an electricity exhibition in Munich, 57 kilometers (km) away, at a mere 1,400 V. Last December, just before the world ushered in the new decade, Siemens Energy and grid operator China Southern Power Grid put into operation the first pole of a transmission link between the southern Chinese provinces of Yunnan and Guangdong, a 1,418-km ultra-high-voltage direct current (UHVDC) system. That line has a transmission capacity of 5 GW, and it operates at a voltage of 800 kilovolts (kV) — a world record.