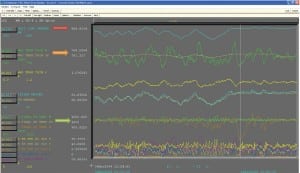
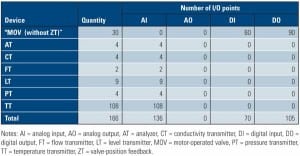
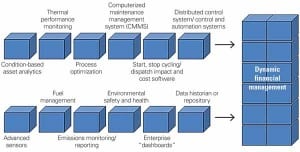
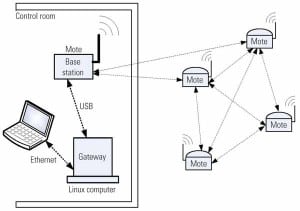
Instrumentation & Controls
-
O&M
Increasing Generation Ramp Rate at Morgantown Generating Station’s Coal-Fired Units
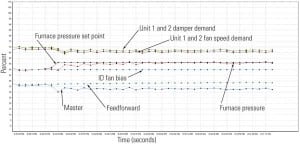
At Morgantown Generating Station, plant personnel used innovative methods to combine model predictive control with distributed control system–based process control algorithms to improve waterwall temperature control and main steam temperature control and to enhance unit ramp rate capability. The previous heat rate and NOx optimization performance gains were retained. Focusing beyond basic loops of feedwater, air, and O2, the project considered issues such as PID controller override configuration and limitations. The techniques used to overcome these challenges improved unit ramp rate capability beyond any previous unit performance.
-
Nuclear
I&C Update on Plant Vogtle Units 3 and 4
Development of Vogtle Electric Generating Station Units 3 and 4—the first new nuclear power plant units in the U.S. in decades—has generated considerable excitement. The next generation of nuclear plants, represented by these units, includes at least two major improvements: the use of passive safety systems and a reliance on digital control systems. The latter represents a gigantic leap in modernization and a fundamental change in control of the plant.
-
Coal
Luminant’s Oak Grove Power Plant Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
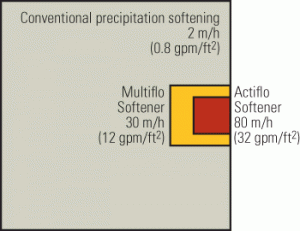
Luminant used remnants of the ill-fated Twin Oaks and Forest Grove plants (which were mothballed more than 30 years ago) to build the new two-unit 1,600-MW Oak Grove Plant. Though outfitted with equipment from those old plants, Oak Grove also sports an array of modern air quality control equipment and is the nation’s first 100% lignite-fired plant to adopt selective catalytic reduction for NOx control and activated carbon sorbent injection technology to remove mercury. For melding two different steam generators into a single project, adopting a unique and efficient “push-pull” fuel delivery system, assembling a tightly integrated team that completed the project on time and within budget, and for completing what was started almost four decades ago, Oak Grove Power Plant is awarded POWER magazine’s 2010 Plant of the Year award.
-
Nuclear
Concerns About Electromagnetic Interference in Nuclear Plants Related to Digital Upgrades
In order to operate aging nuclear power plant instrumentation and control systems for up to 60 more years or longer, there must be a smooth transition from existing analog technologies to advanced digital platforms. For this to occur, electromagnetic compatibility concerns related to both qualification testing and the electromagnetic environment must be addressed to ensure safe and reliable operation of these systems within the plant’s electromagnetic and radio frequency interference environment. By understanding the regulatory requirements and sharing implementation experience, digital system upgrades can be installed successfully.
-
Nuclear
The Advanced Digital Fieldbus Option for Nuclear Plants
Digital fieldbus technologies, including Foundation fieldbus and Profibus, are increasingly being used with success in the nuclear and fossil fuel power industries. This article compares a conventional control system with a Foundation fieldbus – based digital control system used in a typical circulating water system in a nuclear power plant. As shown in this example, using digital fieldbus technologies can result in significant savings in terms of installation and hardware costs.
-
Nuclear
The Value of a Knowledge-Based Culture Grows in Lean Times
Given delays and cancellations of new generating capacity, pushing the existing power generation fleet is more important than ever. At ELECTRIC POWER 2009, multiple presentations explored the premise that an active knowledge management strategy — requiring a blend of digital and human elements unique to each power plant — will help you extract the most productivity from your assets.
-
O&M
Low-Cost Wireless Sensors Can Improve Monitoring in Fossil-Fueled Power Plants
As equipment ages in fossil-fueled power plants, component wear leading to machinery failure increases as a result. Extending equipment life requires increased attention to maintenance, and one way to improve maintenance planning is to detect faults prior to failure so maintenance can be scheduled at the most cost-effective, opportune time. This type of strategy benefits from the use of additional sensors, and wireless ones can often be installed with the least time and cost.
-
O&M
How to Avoid Alarm Overload with Centralized Alarm Management
In 1999, the Engineering Equipment and Materials Users’ Association (EEMUA) released its general guide to the design, management, and procurement of alarm systems for industrial plants. The guidance document (EEMUA 191), however, is vague about applications to specific facilities, such as electric power plants. This article specifies EEMUA 191 standards and practices applicable to the electric power industry and spells out specific variations in alarming practices that are tailored for today’s power plants.
-
Nuclear
Nontechnical Issues Affecting Digital Upgrades at Nuclear Power Plants
Existing nuclear power plants are increasingly facing the conversion to digital instrumentation and controls technology. Meanwhile, new nuclear designs have digital technology integrated throughout the plant. Digital controls will soon be inevitable, so how do we make the transition as smooth as possible? Without losing focus on the technical solutions, organizations have to pay attention to the nontechnical issues as well.
-
Coal
Digital Plant Controls Provide an Essential Edge
It’s a digital world, and even aging power plants are experiencing the benefits of digital controls technologies. The following cover stories provide insight into the latest options and inspiration for your own plant controls projects.
-
O&M
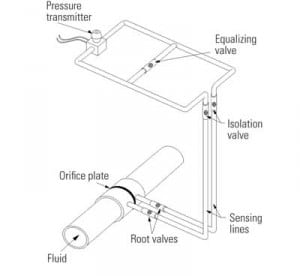
Pressure-Sensing Line Problems and Solutions
Improper pressure-sensing line design or installation is often found to be the cause of poor sensing system accuracy and response time. Here’s how to identify and solve those pesky pressure sensor problems in short order.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Digital Networks Prove Reliable, Reduce Costs
The debate over the benefits of using digital bus networks as the communications backbone of new power plants is all but settled. The technology is maturing, and the reliability of digital hardware is superior to that of hardwired systems. Newmont Gold Mining’s 200-MW TS Power Plant is perhaps the power industry’s best example of how a plantwide digital controls architecture can provide exceptional reliability and be significantly less costly to install.
-
O&M
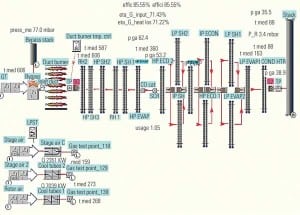
Computer Simulation of HRSGs Can Improve O&M
Obtaining accurate data about the performance of a plant’s heat-recovery steam generator is crucial to ensuring the smooth operation and maintenance of the equipment. Software designed to model and simulate HRSG operations can provide valuable information about corrosion and other operational problems.
-
O&M
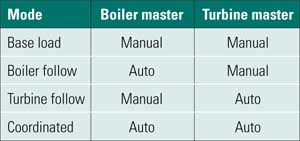
Boiler-Tuning Basics, Part II
Boilers have enormous thermal mass and are relatively slow to react. Turbines are nimble and quickly answer an operator’s command. Coordinating an entire plant requires an intimate knowledge of both systems and selecting the right logic tools to bring them together.
-
O&M
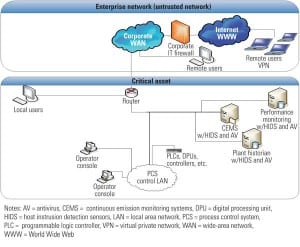
Helping Power Plant Control Systems Achieve NERC CIP Compliance
This guide offers suggestions from a control system engineering perspective for protecting power-generating units that are determined to be critical cyber assets
-
O&M
Reduce Costs with Wireless Instrumentation
New wireless technologies for power plant instrumentation offer significant cost savings when compared to traditional wired networks. The value of this cost savings is especially relevant in the highly competitive power industry, where aging facilities are common and upgrades are an expensive necessity. Modern wireless networks offer a reliable upgrade path that even provides some unexpected benefits when compared to traditional copper networks.
-
O&M
Boiler-Tuning Basics, Part I
Tuning power plant controls takes nerves of steel and an intimate knowledge of plant systems gained only by experience. Tuning controls also requires equal parts art and science, which probably is why there are so few tuning experts in the power industry. In Part I of a two-part series, we explore a mix of the theoretical and practical aspects of tuning boiler controls.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
ISA POWID: Where Power Computing Professionals Meet
Which new and emerging technologies will be essential to your power plant’s success? Our special cover story series gives you a glimpse into the future of advanced distributed controls, wireless applications, and automation technologies.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Distributed Control Technology: From Progress to Possibilities
The past decade has seen an explosion of technology that has significantly altered the process control industry. The adoption of commercially available technology driven by desktop computing has allowed suppliers to focus on applications to enhance the process and deliver ever-greater value to the user.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Optimize Your Plant Using the Latest Distributed Control System Technology
Distributed control systems are powerful assets for new and modernized power plants. Thanks to three product generations of technology innovations, these systems now provide new benefits — including improved O&M efficiency, greater plant design flexibility, and improved process control and asset reliability — that help competitive plants advance in the game.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Power Plant Automation: Where We Are and Where We’re Headed
Over the past decade, power plant control systems have evolved from DCS-centered platforms with proprietary software, to open systems using industry standard hardware and software, and then to totally integrated plant automation systems with almost unlimited connectivity and the ability to interrogate field instruments from many different manufacturers. What’s next?
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Enhancing Plant Asset Management with Wireless Retrofits
Wireless technology is a mostly untapped resource in the power generation industry that can have a significant impact on the way business is done. It enables a greater degree of connectivity among devices for enhanced monitoring and asset utilization and has led to the development of new applications that improve productivity, uptime, and overall business performance.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Wireless Technology Unlocks Possibilities
Modern wireless systems improve productivity, monitoring activities, and safety at power plants by enabling the right people to be at the right place at the right time. Wireless technology can put hard-to-access process and asset information at your fingertips, wherever you are, to enable more accurate and timely decisions.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Upgraded Control System Adds to Merchant Plant’s Bottom Line
If the rotating equipment and boiler are a plant’s brawn, then a control system that efficiently integrates myriad plant functions is its brains. Luckily, in a power plant, we can perform a brain transplant when the control system becomes unreliable or too costly to maintain. But first, you have to justify that surgery.
-
O&M
JCP&L’s SCADA-controlled adaptive relay scheme saves 25 SAIDI impact minutes
In 2005, Jersey Central Power & Light (JCP&L), a subsidiary of Akron, Ohio – based FirstEnergy Corp., initiated a project to identify protection system improvements that could be made to proactively combat wind- and lightning-related weather events that create sustained power outages (Figure 2). JCP&L determined that these changes had the potential to improve the […]
-
O&M
Entergy’s “big catch”
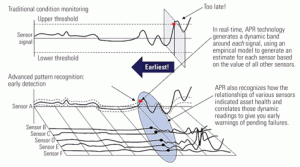
Entergy christened its Performance Monitoring and Diagnostic Center several years ago to leverage the expertise of its most senior operators and technicians across the company’s entire fleet of plants. The center also makes use of advanced software tools that increase plant availability and reliability by identifying faults before they become major, unplanned outages. The center paid for itself for years to come with a single “big catch” last year.
-
O&M
Focus on O&M (September 2008)
Tackling substandard water sources / Control abrasive wear in scrubber piping / Sensors and final control elements
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Digital technology spawns need for configuration management
Documenting changes to the distributed control system and other digital plant applications should be considered a critical element of managing risk—and of safe, efficient daily operations and maintenance. Coming up with a practical configuration management approach, though, isn’t easy.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Assessing and addressing cyber threats to control systems
Control systems used by utilities and other operators of America’s industrial infrastructure increasingly rely on an Internet connection that makes them as vulnerable to hackers as any computer or network. One reason many utility control systems are vulnerable is that, unlike your ISP’s systems, they don’t record an audit trail that reveals the source of the attack.
-
O&M
Boiler optimization increases fuel flexibility
Burning spot market fuels can reduce plant fuel costs, but it can also introduce unexpected operational problems throughout the boiler island. Orlando Utilities Commission’s Stanton Energy Center optimized its Unit 2 combustion system and improved O&M practices as part of a project to increase the unit’s fuel flexibility without degrading reliability or heat rate. OUC’s attitude: If you can measure it, you can manage it.