Environmental
-
Legal & Regulatory
Fracking: With the Gas, a Flow of Litigation
The rapid growth of gas extraction by hydraulic fracturing has drawn increasing allegations of property damage and health risks. In many cases, these allegations are being followed by a wave of lawsuits.
-
Coal
One Step Forward, Two Steps Back for CCS Projects
Last December, as Spain’s national carbon capture and storage (CCS) research laboratory Fundación Ciudad de la Energía (CIUDEN) began a much-watched testing phase of oxycombustion in its 30-MWth circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boiler in Cubillos del Sil, Vattenfall scrapped the €1.5 billion ($2 billion) Jänschwalde CCS demonstration project that it had planned to build and begin operating by 2015 in the German federal state of Brandenburg.
-
Coal
Colstrip’s Cure for Mercury
In January 2012 a new mercury control system at the Colstrip power plant in Montana reached its first major milestone: two years of operation with mercury emissions below the state regulatory limit. The plant uses Alstom’s unique Mer-Cure technology to capture up to 90% of the mercury leaving the stack.
-
Coal
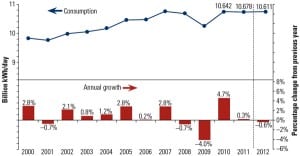
EIA: Policy and $3 Gas Could Prompt Accelerated Decline of Coal Power, Renewables
The U.S. power sector will see heightened electricity consumption over the next two years, a spurt in natural gas–fueled power generation that is expected to offset a slight decline in coal power, and a significant decline in hydropower generation that could mark a decline in overall renewable generation, the Energy Information Administration (EIA) says in its latest short-term outlook.
-
Coal
EPA Finalizes Air Toxics Rule
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Dec. 21 issued its final Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS), which will require about 40% of all coal-fired power plants in the U.S. to deploy pollution control technologies to curb emissions of mercury and other air pollutants such as arsenic and cyanide within three years.
-
Coal
EPA Releases, Federal Court Blocks CSAPR
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit temporarily blocked the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) just two days before it was set to go into effect. The federal court ordered the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to continue administering the previously promulgated Clean Air Interstate Rule (CAIR) until a final decision can be made on the merits of the rule, likely this summer or fall.
-
Coal
Editors Select Top Five Stories of 2011
The POWER editorial staff’s picks for the most significant stories of 2011.
-
Coal
THE BIG PICTURE: Gas Taxes
After years of political wrangling, coal-rich Australia in November passed legislation that will require the nation’s top 500 polluters, starting in July 2012, to pay a tax at a fixed price of A$23 (US$23.50) per ton of carbon. The tax increases 2.5% annually until 2015, when an emissions trading program will begin. With the Kyoto […]
-
Coal
Australia Levies Landmark Carbon Tax
After more than a decade debating whether to pass a carbon-limiting law, Australia’s Senate in November voted in a landmark bill that will impose a price on carbon emissions. The country, which accounts for just 1.5% of global carbon emissions, but which is the world’s highest emitter per capita because 80% of its power comes […]
-
O&M
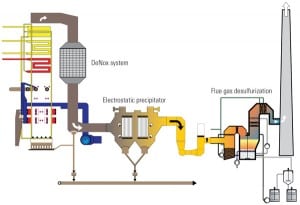
Level Switches Keep Electrostatic Precipitators Online
Measuring the level of dust and fly ash collected in electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) is a very difficult technical problem. At one utility, level switches were so unreliable that operators could not trust their readings because failures were so frequent. When a switch did fail, the precipitator would often clog up, costing the utility up to $100,000 in downtime and repair costs.
-
Coal
U.S. Confronts Pipeline Gaps While Europe Juggles Renewables and Debt
U.S. optimism has been restored by reports of abundant, reasonably priced natural gas to fuel most new generation; however, huge gaps in the fuel delivery system (thousands of miles of pipelines are needed) will soon challenge gas plant development. Meanwhile, the cloud of sovereign debt hangs over all major capital projects in Europe, where the UK moves ahead with new nuclear projects while many of its neighbors shut the door on nuclear and struggle to finance their commitment to renewables.
-
O&M
EPRI Bridges Industry R&D Gaps
The technologies used to generate and distribute electricity will be radically transformed during the coming decade. Amid that change, the power industry must continue to meet customer reliability, safety, and cost-of-service expectations. Achieving the right balance among these often-conflicting goals is the primary focus of every utility. The Electric Power Research Institute is helping utilities achieve that balance with R&D programs for many new and emerging technologies.
-
Coal
China’s 12th Five-Year Plan Pushes Power Industry in New Directions
The Five-Year Plan is the expression of the centralized planning goals for China’s economy. The 12th Five-Year Plan, approved by the Chinese Government on March 14, 2011, established many social and economic goals, including significant expansion of the country’s power generation industry in many new directions.
-
Coal
Gas Taxes: Carbon Taxes Around The World
A supplement to “The Big Picture: Gas Taxes” in our January 2012 issue.
-
Coal
UK Pulls Funding for Flagship Longannet CCS Demonstration
Ditching the only project remaining in its £1 billion ($1.60 billion) carbon capture and storage (CCS) competition, the UK government declined to back the much-watched CCS project at the Longannet power station in Fife, Scotland, in October. The decision balances the UK’s low-carbon ambition with the need to ensure that taxpayer money is invested in “the most effective way,” the nation’s Department of Energy and Climate Change said. The funds are now expected be used to “pursue other projects” in both Scotland and England.
-
Coal
EPA Moves Forward with GHG Regulations for Power Plants
The EPA’s proposed rules on limiting greenhouse gas emissions from new, modified, and existing power plants has taken another step forward.
-
Coal
California Adopts Final Cap-and-Trade Regulation
After three years of development, dozens of public workshops, and hundreds of meetings with stakeholders, the California Air Resources Board (ARB) on Oct. 20 adopted a final rule to cap California’s greenhouse gas emissions and put a price on carbon. The cap-and-trade program starts in 2013 for electric utilities and large industrial facilities.
-
Coal
Consultancy Group Downgrades Coal Plant Retirement Projections
ICF International, a consultancy group that earlier this year had predicted 68 GW of coal-fired power plants could retire by 2030 as a result of finalized and proposed regulations from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), downgraded its retirement projections to 50 GW this fall.
-
O&M
Enhanced Capture of Mercury Using Unique Baghouse Filter Media
Several states have already instituted mercury emission limits in expectation of tightening mercury emission rules that will require reductions of up to 91%. Coal-fired plants searching for an economical way to meet the new limits may need to look no further than replacing their baghouse filter elements.
-
Coal
Luminant, AEP to Mothball Coal Units, Implement Derates on CSAPR Compliance Concerns
Dallas-based Luminant, Texas’ largest power generator, on September 9 filed a legal challenge against the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) Cross State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) but said the newly finalized rule that will require generators to dramatically reduce sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions from power plants had forced it to idle two coal-fired units and reduce capacity at three other units. This decision follows a similar decision made by American Electric Power to shutter 6GW of coal-fired plants in June.
-
Commentary
Is Coal a Fuel of the Future?
Few reasonable people can dispute that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is conducting a war against coal. If you doubt that conclusion, just look at the large number of new regulations affecting coal-fired power plants that have been proposed in rapid-fire succession by the EPA.
-
Coal
EPA Indefinitely Delays Power Plant Greenhouse Gas Rules
Just two weeks after the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) withdrew its smog rule, the agency confirmed it would not meet a Sept. 30, 2011, deadline for issuing proposed New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) to limit greenhouse gas emissions from new, modified, and existing power plants. The agency did not specify a new deadline for proposing the rule.
-
Coal
Obama Shelves Smog Rule on Concerns About Regulatory Burdens, Uncertainty
President Obama has scuttled the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) smog rule, saying that he had underscored the importance of reducing regulatory burdens and uncertainty. The decision has dealt a blow to environmental groups—which are contemplating legal action—and won the Democratic president praise from Republicans and industry groups.
-
O&M
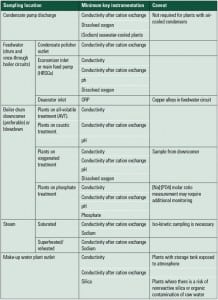
The New Water Lab
Recent advances in water laboratory instrumentation—from improved sample conditioning to advanced online instruments—have reached the market. Here’s a look at the equipment you’ll find in the best-equipped power plant laboratory this year.
-
Hydro
Chart a New Course
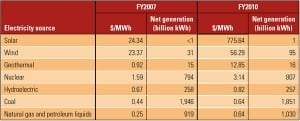
I examined the magnitude of electricity subsidies for renewables compared with conventional generation technologies in my May 2011 editorial, based on data from a 2008 report prepared by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). An updated EIA report released in July determined that federal government subsidies have risen substantially during the past three years. In fact, overall renewable energy subsidies have almost tripled, increasing from $5.1 billion to $14.7 billion. In my opinion, we aren’t getting value for the money spent.
-
Coal
THE BIG PICTURE: Lights Out
Heat waves, droughts, and other weather and climate phenomena; economic woes; aging or inadequate infrastructure; fuel shortages. These are some of the most obvious causes that have led to record peaks in power demand or sudden drops in available capacity. The results have been sometimes debilitating load-shedding, brownouts, and blackouts around the globe this summer (and, in some cases, for much longer). Here’s an overview of which countries are affected by which difficulties. For a more detailed look at the extent of shortages and what’s causing them, visit Web Exclusives at https://www.powermag.com
-
Legal & Regulatory
Critics Get Crossways with New Cross-State Air Rule
From the East Coast to the Lone Star State, a number of elected officials and power industry representatives are bashing the new aggressive regulation aimed at controlling specific power plant emissions. Complying with a federal court mandate, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) finalized the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) on July 6. The new […]
-
Coal
House GOP Moves to Block EPA from Regulating Coal Ash as Toxic Waste
Continuing the House Republicans’ aggressive attack on Obama administration environmental proposals, a House subcommittee approved legislation in June to prevent the Environmental Protection Agency from regulating coal ash as a hazardous waste—one of two options the EPA is considering for tightening coal ash management regulations in response to a disastrous leak from a Tennessee Valley Authority ash impoundment in 2008.
-
Coal
Dominion to Convert Three Coal Plants to Biomass
Dominion Virginia Power has asked the Virginia Corporation Commission for approval to convert three aging and relatively small coal-fired plants to biomass, saying the move would provide substantial long-term savings to customers while cutting air emissions and creating hundreds of forest-related and trucking jobs in the state.
-
Commentary
Water Issues, Carbon, and Price of Power Top Utility Concerns
In a clear sign of growing industry unease about the availability of water for power plant operations, utility officials recently surveyed by Black & Veatch on a host of policy and business issues ranked water supply as their second-highest environmental concern and identified water management as the business issue that could have the greatest impact on the utility industry in the near future.