Environmental
-
Coal
Settlement Allows Mississippi Power to Request Higher Rates for Kemper Coal Plant
Mississippi regulators last week approved a settlement with Mississippi Power that will allow the Southern Co. subsidiary to seek higher customer rates for rising costs associated with its 582-MW Kemper integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) plant under construction in Kemper County. On the day following that ruling, the utility asked the state for permission to recover $172 million for the 2013 regulatory year.
-
Coal
MidAmerican Energy to Switch 674-MW of Coal Capacity to Nat. Gas, Other Fuels
A settlement agreement reached with environmental group the Sierra Club last week may mean that Iowa’s largest utility, MidAmerican Energy Co., will switch 674 MW of coal-fired capacity to natural gas or other fuels by April 2016.
-
Nuclear
German Court Deems Nuclear Fuel Tax “Unconstitutional”
A German tax court on Tuesday ruled that the country’s excise tax on nuclear fuel levied since January 2011 is unconstitutional and lacks legal competence. The matter now proceeds to the Federal Constitutional Court, which alone has the jurisdiction to rule on the invalidity of the law.
-
O&M
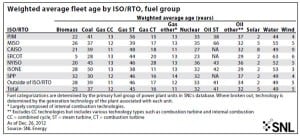
America’s Aging Generation Fleet
Proposed U.S. Environmental Protection Agency rules and a greater reliance on newer generation technologies have put the nation’s aging fossil-fueled generation units at risk of retirement. The numbers demonstrate that the U.S. power generating fleet is older than you may believe.
-
Coal
EPA Tightens Fine Particulate Matter NAAQS
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued a final rule in December that strengthens its National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS) for fine particulate matter (PM2.5) to 12.0 micrograms per cubic meter (μg/m3) but declared it would not finalize a proposal to update separate secondary PM2.5 standards. The final rule’s issuance was lauded by environmental and public health groups, though industry groups opposed it, citing concerns that nonattainment areas would suffer economic setbacks.
-
Coal
EPA Finalizes Standards for Industrial Boilers, Certain Incinerators
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Dec. 20 finalized changes to a specific set of adjustments to the Clean Air Act that apply to coal, oil, natural gas, and biomass boilers and certain solid waste incinerators.
-
O&M
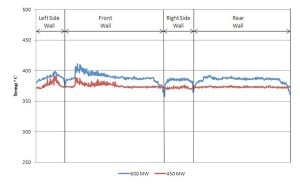
Jinzhushan 3: The World’s First PC-Fired Low Mass Flux Vertical Tube Supercritical Boiler, Part 3
The world’s first supercritical pulverized coal–fired low mass flux vertical tube Benson boiler is Jinzhushan 3, located in the Hunan Province of the People’s Republic of China. The 600-MW Babcock & Wilcox Power Generation Group Inc. once-through boiler burns Chinese anthracite using downshot pulverized coal (PC) technology. Part 1 of this three-part article presented a summary of the project design features. Part 2 discussed the boiler technology. This third and final part reviews the plant’s performance test results.
-
Coal
Climate Change on Obama’s Second-Term Agenda
Among the surprises in President Barack Obama’s second Inaugural Address on Monday was his promise to address the challenges of climate change and sustainable energy. An independent draft report released about a week earlier on climate change and its impacts in the U.S. may have helped to fuel his renewed resolve on these intertwined issues.
-
Coal
DOE, EPA Nab 25th Settlement for Emission Control under Clean Air Act New Source Review
A settlement reached with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Department of Justice to resolve alleged violations of the Clean Air Act will require Wisconsin Public Service (WPS) to invest about $300 million in pollution control technology, pay a civil penalty of $1.2 million, and spend $6 million on environmental mitigation projects.
-
Environmental
A Continuing Wave: The Debate Over Regulation of Fracking Rolls On
Shale gas production continues to surge as demand for cheap gas grows. But will state and federal regulation and a wave of local bans choke off the boom?
-
Environmental
EPA Admin Lisa Jackson to Step Down
Environmental Protection Agency Administrator Lisa Jackson on Thursday announced she would step down after President Obama’s state of the union address later this January.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Calif. Cap-and-Trade: Bull or Bear Market?
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) recently kicked off a new era in its cap-and-trade program designed to reduce greenhouse gases (GHG) when it held its first GHG emissions allowance auction on November 14. While CARB pronounced the auction a success, the low price and lukewarm demand for allowances evidences market reticence to fully embrace the program.
-
O&M
Emerging Technologies Enable “No Regrets” Energy Strategy
Achieving a balance between affordable and sustainable electricity while improving reliability is a challenge unlike any the electricity sector has faced since its inception. Technology innovations in key areas such as energy efficiency, smart grid, renewable energy resources, hardened transmission systems, and long-term operation of the existing nuclear and fossil fleets are essential to shaping the future of electricity supplies.
-
Coal
EPA Tightens Fine Particulate Matter NAAQS
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Friday issued a final rule that strengthens its National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS) for fine particulate matter (PM2.5) to 12.0 micrograms per cubic meter (μg/m3) but declared it would not finalize a proposal to update separate secondary PM2.5 standards. The final rule’s issuance was lauded by environmental and public health groups, though industry groups opposed it, citing concerns that nonattainment areas would suffer economic setbacks.
-
Coal
UPDATE: EPA’s First GHG Permitting Violation Reaps $34,000
Major oil and gas production company Vintage Production California and its subsidiary OXY USA last week agreed to pay $34,000 to resolve the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) first greenhouse gas (GHG) permitting violation case.
-
Coal
Reserve Margins in Texas Barely Healthy Again, ERCOT Says
Texas could again see tight power supplies in the summer of 2013 and beyond—with reserve margins dropping to 2.8% by 2022—even though the outlook has improved, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) warned in its latest long-term outlook released on Monday.
-
Coal
NRDC Urges EPA to Cut GHGs from Existing Fleet via Flexible Approach
The Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC) on Monday made public a proposal that calls for the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to use its authority under the Clean Air Act (CAA) to set greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions standards for existing power plants. The NRDC approach would have the EPA create “systemwide standards” rather than ones based on individual generating units.
-
Coal
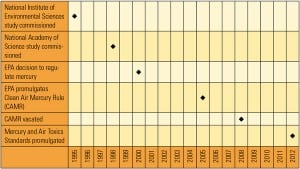
Mercury Regulations Up in the Air
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency efforts to regulate mercury emissions from coal- and oil-fired power plants have spanned nearly two decades. In February of this year the agency promulgated the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards, but changes to the standards continue.
-
Coal
China Leads the Global Race to Cleaner Coal
Coal used for power generation has been the cornerstone of economic development, social progress, and a higher quality of life around the globe and is now fueling the 21st-century economic miracle rapidly unfolding in China. Meanwhile, China is leading the world in coal-fired plant efficiency and the deployment of clean coal technologies.
-
O&M
Duke Prepares for Testing at Edwardsport IGCC Plant
Duke Energy said in mid-October that testing was under way in preparation for commercial operation next year of its 630-MW integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) Edwardsport power plant in Knox County, Ind.
-
Coal
Lawmakers to EPA: Consider MATS Subcategory for Waste Coal Plants
A bipartisan delegation of lawmakers from Pennsylvania on Oct. 15 urged the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to consider creating a separate subcategory for power plants that convert coal refuse into energy in its final Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS). Though waste coal plants made an important environmental contribution by reducing coal refuse piles, the hydrochloric acid (HCl) standard in the MATS rule could push them out of business, they said.
-
Coal
EPA Petitions Full Federal Court to Rehear CSAPR Appeal
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Oct. 5 appealed a federal court decision handed down on Aug. 21 that vacated the agency’s July 2011–finalized Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) because, the court said, it violated federal law. The EPA is now seeking a rehearing en banc that would involve all eight judges that serve at the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit.
-
O&M
EPRI: Generation Sector Research Update
This synopsis of today’s most interesting research related to power generation gives you a glimpse of what’s possibly coming to your plant in the not-so-distance future. Research under way today will surely determine how power plants are designed, operated, and maintained for many years to come.
-
O&M
Jinzhushan 3: The World’s First PC-Fired Low Mass Flux Vertical Tube Supercritical Boiler, Part 2
The world’s first supercritical pulverized coal–fired low mass flux vertical tube Benson boiler is Jinzhushan 3, located in Hunan Province of the People’s Republic of China. The 600-MW Babcock & Wilcox Power Generation Group Inc. once-through boiler burns Chinese anthracite using downshot pulverized coal (PC) technology. Part 2 of this three-part article discusses the boiler technology. The third and final part will review the plant’s performance test results.
-
Coal
Ohio State Develops CO2 Capture Membranes to Lower Energy Penalty Costs
In a project funded by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Office of Fossil Energy (OFE), researchers at The Ohio State University have developed what they call a groundbreaking new hybrid membrane that combines the separation performance of inorganic membranes with the cost-effectiveness of polymer membranes. The breakthrough technology has vast commercial potential for use at coal-fired power plants with carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS), a key element in national efforts to mitigate climate change.
-
Hydro
Hawaii’s Largest Wind Project Online as State Struggles to Integrate Renewables
On Monday, as First Wind announced its 69-MW Kawailoa Wind Project had gone into commercial operations on Oahu, other news underscored the difficulty the island state faces in trying to substitute renewables for expensive, imported fossil fuels.
-
Coal
EPA Proposes Slightly Modified MATS for New Power Plants
A reconsidered proposal issued by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Friday sets out slightly weakened emission limits for mercury, particulate matter (PM), acid gases, and certain individual metals for future coal- and oil-fired power plants.
-
Coal
Arizona Protests EPA-Imposed Regional Haze Limits at Three Coal Plants
A decision by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to impose new pollution limits on three coal-fired power plants in Arizona on Friday drew criticism from state officials, who said that the costly measure, which overrides the state’s regional haze plan, is designed to protect visibility, not public health.
-
Environmental
California Debuts Cap-and-Trade Program Amid Legal Challenge
Despite a last-minute lawsuit filed by California’s Chamber of Commerce, the state on Wednesday held its first auction of carbon emissions permits, kicking off the nation’s first state-implemented cap-and-trade program that limits the amount of greenhouse gases (GHGs) emitted by power plants, oil refineries, and other entities.
-
History
FuelCell Energy Claims Largest Order in Industry’s History
FuelCell Energy Inc. on Monday announced an order from its South Korean partner, POSCO Energy, for 121.8 MW of fuel cell kits and services to be manufactured at the FuelCell Energy production facility in Torrington, Conn. The company said this represents the largest order for both its company and the fuel cell industry.