Coal
-
O&M
The Coal Patrol: Looking Back at 2006
To borrow shamelessly from Charles Dickens, one of my favorite authors, for coal in 2006, "It was the best of times, it was the worst of times." No Escape The year began in horror. On January 2, most likely a result of a severe lightning strike, methane gas in the International Coal Group’s Sago Mine […]
-
Coal
PRB Tech Notes: Give Coal Handling the Priority It Deserves
Over the past 17 years — dating back to the 1990 Clean Air Act Amendments and including the introduction of retail competition — coal-fired power plants have become much cleaner and more efficient. Utilities have spent many billions of dollars to install pollution controls for regulatory reasons, and only slightly less to upgrade turbine-generators and […]
-
O&M
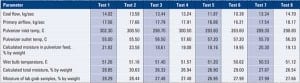
Coal Plant O&M: Elemental Analyzer Checks Quality of Delivered Coal in Real Time
When you receive a shipment, you don’t wait weeks to see whether you got what you paid for — do you? J.M. Stuart Generating Station doesn’t, but it used to. Since coming on-line in the early 1970s, the big plant, on the Ohio River near Aberdeen, Ohio, mechanically sampled coal shipments as they reached the […]
-
Coal
Coal Plant O&M: Coal Drying Reduces Pulverizer Start-up Costs
If coal leaving a pulverizer isn’t dry, it may plug up the coal pipes leading to the boiler. The coal-drying process in a pulverizer is similar to that used by flash dryers. Certain coals should be preheated to make them more combustible. Generally, preheating is done on higher rank coals — those with a low […]
-
O&M
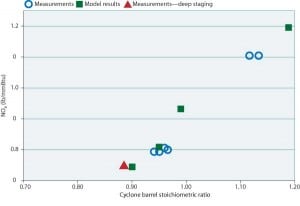
Emissions Control: Layered NOx Reduction on a 500-MW Cyclone-Fired Boiler
Historically, cyclone-fired boilers have been characterized as big emitters of NOx due to the very high temperatures in their primary combustion zone. Uncontrolled levels from 0.8 to 1.9 lb/mmBtu have been typical. The design of cyclone-fired units makes them impossible to retrofit with standard low-NOx burners. Prior to 1997, the conventional wisdom was that cyclone […]
-
-
Coal
Expert systems optimize boiler performance, extend plant life
Slagging and fouling of furnaces and boilers’ convective pass top the list of costly coal plant O&M problems. Although sootblowing is a tried and true solution, running sootblowers too often can erode boiler tubes. Lehigh University’s Energy Research Center has developed an "expert" sootblowing system that has outperformed experienced operators’ "seat of their pants" sootblowing procedures on two head-to-head field tests.
-
Coal
Utilities split on readiness of IGCC
For some gencos, the dearth of operating experience for integrated gasification combined-cycle plants adds too much uncertainty to the risk/reward equation for new-capacity technology options. For others, the possibility of being able to comply with air pollution limits as far out as 2018, as well as to meet all-but-certain CO2 caps, makes IGCC well worth investing in—now.
-
Coal
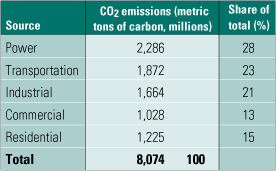
Technology options for capturing CO2
Concerns about global climate change have prompted interest in reducing or eliminating the carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions of fossil fuel-fired power plants. Here’s a guide to the technology and economics of three CO2 capture methods: postcombustion separation of CO2 from flue gas (applicable to existing plants), and oxygen-fired combustion and precombustion capture (suitable for new coal-fired capacity, including IGCC plants).
-
Coal
Global Monitor (October 2006)
First live superconducting cable / Biggest CO2 storage project / Largest hydrogen-fueled plants / Record run for fuel cell cogen system / Largest PV plant still in Bavaria / Luz returns to U.S. / POWER digest
-
O&M
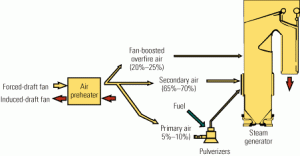
Apply the fundamentals to improve emissions performance
The O&M staff of AES Westover Station wisely took a holistic approach to optimizing combustion within Unit 8’s boiler in order to reduce its NOx emissions while maintaining acceptable levels of carbon-in-ash content. The results of major modifications—centered on the addition of a fan-boosted overfire air system—were a 60% reduction in NOx levels, improved unit reliability, and a project payback period measured in months rather than years. As this project proved, the whole is more than the sum of its parts.
-
Coal
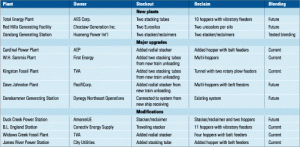
Designing and upgrading plants to blend coal
Fuel flexibility isn’t free. Whether you’re equipping a new power plant to burn more than one type of coal or retrofitting an existing plant to handle coal blends, you’ll have to spend time and money to ensure that all three functions performed by its coal-handling system—unloading, stockout, and reclaim—are up to the task. The first half of this article lays out the available options for configuring each subsystem to support blending. The second half describes, in words and pictures, how 12 power plants—both new and old—address the issue.
-
Coal
Global Monitor (September 2006)
Demand records fall nationwide;
GE’s ABWR to be STP’s edge; Entergy buys Palisades plant; Dithering over desert disposal; Tourist trash-to-energy plant;
Brooklyn says "Yo!" to microturbines; POWER digest -
Coal
Tri-State Generation and Transmission Association’s Springerville Unit 3 earns POWER’s highest honor
It’s said that pioneers take the arrows. In the case of Springerville Unit 3—a 418-MW (net) expansion of a Tucson Electric Power facility in Arizona and the first pulverized coal–fired unit built in the U.S. in more than a decade—the arrows were many. Although Tri-State (the developer), Tucson Electric (the host), and Bechtel Power (the EPC contractor) were wounded by delayed deliveries of major equipment, bankruptcy of a major supplier, and a labor shortage, the companies showed their pioneering spirit and completed the project ahead of schedule. For ushering in a new generation of clean and desperately needed baseload capacity, Springerville Unit 3 is POWER magazine’s 2006 Plant of the Year.
-
Coal
Nova Scotia Power’s Point Aconi plant overcomes CFB design problems to become rock of reliability
Point Aconi’s circulating fluidized-bed boiler experienced erosion, corrosion, and fouling problems from the day it went on-line in 1993. After several frustrating years of unreliable operation, in late 1999, Nova Scotia Power discovered the right combination of engineering and fuel modifications. Today, after a switch to 80% petroleum coke and major boiler modifications, Point Aconi’s output exceeds its original nameplate rating. For having the vision and fortitude to plan and execute a multiyear, $20 million project to revitalize North America’s first in-service utility CFB boiler, Nova Scotia Power’s Point Aconi plant is the well-deserved winner of POWER magazine’s 2006 Marmaduke Award for excellence in O&M.
-
Coal
How accurate are your reported emissions measurements?
Complying with permitted emissions limits may be the most significant operations risk for a power plant. As limits are slowly ratcheted downward, understanding the accuracy and variation of measured pollutant levels becomes even more important. To avoid misunderstandings, regulators and plant owners should factor measurement uncertainty into air quality permit numbers both as the permit is formulated and preceding any subsequent modifications.
-
Coal
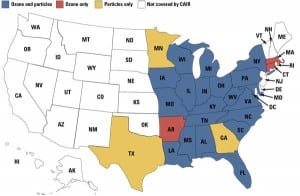
Emissions: Clean Air Interstate and Clean Air Mercury Rules: An Overview
Utility customers depend on and expect reliable, affordable electricity for virtually every aspect of their lives. At the same time, electricity producers in the United States are faced with finding cost-effective methods to meet ever-increasing demand and more stringent environmental regulations. Though it’s not a new trend, the frequency with which new regulatory air quality […]
-
O&M
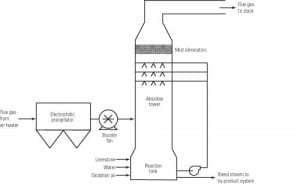
Scrubbing: Optimizing Flue Gas Desulfurization Technologies Is Essential
New flue gas desulfurization (FGD) units are being installed at utilities in many parts of the U.S. and a large percentage of the new scrubbers are of the wet limestone type. Although wet limestone scrubbing is a well-developed technology, it may be unfamiliar to employees at plants that have previously not required scrubbers. This article […]
-
O&M
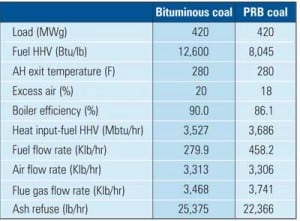
Boiler Conversion: Converting a Boiler from Burning Bituminous Coals to PRB Coals Can Be a Challenge
Design techniques and operating experience with Powder River Basin (PRB) coals have advanced significantly over the past 35 years for boilers that were originally designed for this fuel. Today, boiler installations looking to effectively utilize PRB coals fall into two primary categories: units that were initially designed for bituminous or other coals and units that […]
-
O&M
Case Histories: Co-Firing Coal and Oat Hulls Reduces Emissions at University Power Plant
The University of Iowa (UI) Biomass Fuel Project has produced significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, regulated boiler stack emissions, and purchased energy costs. The project utilizes a renewable, biomass fuel source and provides an opportunity for UI to partner with a local industry. UI was approached by Quaker Oats Co., Cedar Rapids Facility in […]
-
O&M
Case Histories: Asheville Power Station’s Retrofit First to Meet North Carolina’s Clean Smokestacks Act
Asheville Power Station’s Unit 1 in Arden, North Carolina, was the first coal-fired unit to be modified with a flue gas desulphurization (FGD) system and placed in service to meet the clean air requirements of the state’s Clean Smokestacks Act. As of November 16, 2005, at least 97% of the sulfur dioxide that had been […]
-
O&M
Case Histories: Synthetic Oil and Enhanced Filtration Reduce Wear and Extend Gear Life
A coal-fired power plant operating in the western U.S. was experiencing short gearbox life in its coal-pulverizing operation. After an annual gearbox inspection, oil analysis results indicated that the AGMA 6EP (ISO 320) gear oil recommended by the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) had failed to provide adequate lubrication and protection. This conclusion was based on […]
-
Coal
Coal Users Community: Growth Is the Byword for Gasification
The Gasification Technologies Council (GTC, www.gasification.org) was created in 1995 with a straightforward mission: to promote the greater use of gasification as an environmentally and economically preferred alternative for the production of power, fuels, and chemicals from low-value energy sources. Those energy sources include high-sulfur coal, petroleum coke, and wastes. Since that time the GTC […]
-
O&M
Projects
Reliant Energy Commits $350 Million for Environmental Upgrades at Two Key Facilities Reliant Energy has announced plans to install state-of-the-art emission control systems at two Pennsylvania power plants, a major step in the company’s strategy for maximizing the long-term value of its power generation assets while reducing air emissions. The utility, Reliant Energy, estimated it […]
-
Coal
Editorial: Tax Credits Should Help Promote Coal-Based Power Generation Technologies
In order to promote coal-based technologies, the U.S. Department of Energy will be assisting the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the selection of projects to receive tax credits. According to the DOE’s Office of Fossil Energy, recent legislation has been designed to advance cleaner coal-based power generation and gasification technologies. The Energy Policy Act of […]
-
Coal
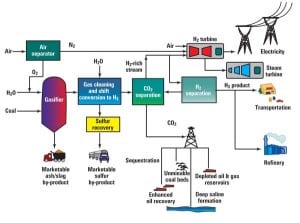
Cover Story: FutureGen: Zero-Emission Power Plant of the Future
In early 2003 the United States announced its plans to build a zero-emission prototype of the fossil fuel power plant of the future called FutureGen. It is one of the boldest steps toward a pollution-free energy future ever taken by the U.S. It has the potential to be one of the most important advances in […]
-
Coal
Bethlehem Energy Center, Glenmont, New York
A great location, a fish-friendly cooling system, and the extent of environmental remediation needed to permit it distinguish this repowering project on the Hudson River just south of the New York State capital.
-
Coal
Currant Creek Power Plant, Mona, Utah
Commercial operation of PacifiCorp’s first new power plant in more than 20 years coincided with the company’s acquisition by MidAmerican Energy Holdings Company this past March. Currant Creek treads lightly on the environment, provides needed power to PacifiCorp’s eastern control area, and has demonstrated its commitment to be a good corporate citizen of the local community. By any account, Currant Creek is a model for how to develop a power project.
-
Coal
Monticello Steam Electric Station, Mount Pleasant, Texas
Why does Monticello, a 30-year-old plant, deserve recognition as one of POWER’s Top Plants of 2006? Because TXU has been blending Powder River Basin (PRB) coal with local lignite at the plant for the past decade, and steady reductions in air-pollutant emission rates have been the result. That positive experience has made the company confident enough to propose building nearly 9,100 MW of new coal- or lignite-fired capacity in Texas by 2010 at a cost of $10 billion. Read on to share some of the lessons that TXU has learned about handling PRB coal safely.
-
Coal
Coal: The cornerstone of America’s energy future
In April 2005, U.S. Secretary of Energy Samuel W. Bodman asked the National Coal Council to develop a “report identifying the challenges and opportunities of more fully exploring our domestic coal resources to meet the nation’s future energy needs.” The council has responded with eight specific recommendations for developing and implementing advanced coal processing and combustion technologies to satisfy our unquenchable thirst for energy.