POWER
-
Nuclear
India’s Indigenous Nuclear Program Advances While U.S.-India Trade Stalls
Since a landmark 2008 deal that lifted global sanctions and allowed countries to conduct nuclear trade with India, the nation struggling to keep up with domestic power demand has signed deals with the U.S., France, Russia, Canada, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Argentina, Namibia, and, in August, South Korea, for construction of large nuclear power plants (in technical collaboration with foreign vendors) or for nuclear fuel.
-
Coal
Best Practices for Natural Gas Line Cleaning
As barriers to new coal-fired generation expand and enthusiasm for nuclear plants wanes, the commissioning of natural gas–fired plants promises to increase. However, gas plants pose hazards, too. An explosion last year that was caused by unsafe use of natural gas to blow residue from a gas pipeline during commissioning of a gas-fired power plant has focused regulator and industry attention on finding safer alternatives for this task. Fluor shares its gas pipeline cleaning best practices.
-
Solar
Spanish Power Tower Supplies 24 Hours of Electricity
In Spain this June, a new 19.9-MW concentrated solar power (CSP) tower in Fuentes de Andalucía, Seville, reached the unprecedented milestone of storing thermal energy to its fullest capacity and supply power for an uninterrupted 24-hour period.
-
Gas
Who Pays for Firming Up Variable Energy Resources?
The major economic hurdle for renewable power generation technologies continues to be substantial installation costs. But another cost is associated with continuous load-balancing, made possible by backstopping that variable generation with dispatchable generators that typically consume expensive fossil fuels. Bottom line: Who pays for the capacity firming or backstopping resources?
-
Hydro
Commercial Oscillating Water Column Marine Power Plant Commissioned
One of the world’s first breakwater wave power stations was commissioned this July by Ente Vasco de Energia (EVE), an energy agency in the northern Basque region of Spain. The €2.3 million ($3.3 million) project in Mutriku uses oscillating water column technology developed by Voith Hydro’s Wavegen, based in Inverness, Scotland. The technology is integrated into a concrete power station built on a breakwater or coastal protection project.
-
News
Close-Coupled Pumps for Low-Flow Applications
Moyno introduced the Moyno 2000 WA and WB close-coupled pumps designed for lower-pressure, lower-flow applications that do not require the full features and benefits of the Moyno 2000 GI pump. The Moyno 2000 WA (shown here) and WB models are ideal for municipal and industrial applications that require the transfer of highly viscous fluids and […]
-
News
Novel Nanotube Applications for Power Generation
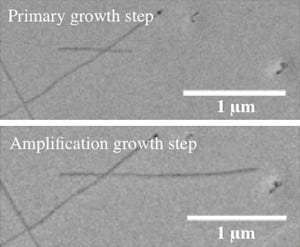
As it does for sectors such as global defense and transportation, nanotube technology holds great promise for the energy sector—and, in particular, for power generation. This July, researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) said carbon nanotubes showed potential as an innovative approach to storing solar energy, and Rice University scientists claimed they were closer to developing a unique wire that could transmit power with few losses.
-
News
Glycol Pumps for Gas Dehydration
Cat Pumps launched a new series of glycol pumps developed to supply triethylene glycol for natural gas dehydration systems. System reliability, especially of the pump, is essential to minimize production interruptions and costly equipment failures. The TEG triglycol pumps have been field-proven in the most rigorous dehydration systems, Cat Pumps says. The electric engine–driven TEG […]
-
Coal
POWER Digest (September 2011)
Australia Pursues Carbon Tax. Australia’s Prime Minister Julia Gillard on July 10 laid out an ambitious plan to cut national greenhouse gas emissions by 5% of 2000 levels by 2020 by imposing a A$23 (US$23.4) per metric ton carbon tax, starting next year. If parliament approves the plan before year-end, the carbon tax will increase […]
-
News
Equipment Line for Industrial Gas Applications
Air Liquide America Specialty Gases equipment group recently announced the introduction of a comprehensive line of “industrial grade” equipment for use with gases commonly used in welding, cutting, and other industrial applications, as well as with liquid cryogenics. The equipment is ideally suited for use with Air Liquide brands of industrial gases such as ALIGAL, […]
-
O&M
Advanced Coatings Protect Plant FGD Systems
Now that many flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems are reaching middle age, corrosion repairs of structural and process vessels are becoming more common. Corrosion is caused by condensates of acids formed during the FGD process, which accelerate pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly in scrubbers where high sulfate solutions are present. Scrubbers lined with 2205 duplex stainless steel are among the most vulnerable to pit or crevice corrosion, from both chlorides and fluorides.
-
Commentary
Advancing America’s Nuclear Infrastructure
It is fair to say that 2011 is bringing some uncertainty into the nuclear energy industry. The tsunami and subsequent events at Fukushima present Japan and our industry with new challenges but also serve as a catalyst for continuous improvement. In the U.S., we are learning from these events and improving our operations, designs, and emergency response approaches to make our plants safer, more efficient, and more environmentally friendly.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
NERC CIPS Update: The Advantages of an Integrated Factory Acceptance Test
When adding, modifying, or upgrading a system, many critical infrastructures conduct a factory acceptance test (FAT). A FAT includes a customized testing procedure for systems and is completed before the final installation at the critical facility. Because it is difficult to predict the correct operation of the safety instrumented system or consequences due to failures in some parts of the system, a FAT provides a valuable check of these safety issues. Similarly, because cyber security can also impact the safety of critical systems if a system is compromised, it makes sense to integrate cyber security with the FAT.
-
O&M
BIG PICTURE: Lights Out (Web Supplement)
A web supplement to the September issue with details of global power shortages.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Critics Get Crossways with New Cross-State Air Rule
From the East Coast to the Lone Star State, a number of elected officials and power industry representatives are bashing the new aggressive regulation aimed at controlling specific power plant emissions. Complying with a federal court mandate, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) finalized the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) on July 6. The new […]
-
Nuclear
The Fukushima Fallout: Six Months After the Nuclear Crisis
(WEB EXCLUSIVE) Much has transpired during the nearly six months following the Great East Japan Earthquake—a 3-minute, magnitude 9.0 temblor that generated a series of tsunami waves as tall as 38.9 meters (130 feet), killed more than 25,000 people, and set off the worst nuclear disaster in 25 years.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Adapazari Power Plant, Adapazari, Sakarya Province, Turkey
In 2010, the 2,310-MW Adapazari Power Plant achieved 99.8% availability, which is nearly 7% higher than the industry average and a global record in F-class gas turbine technology. The new turbine upgrade is helping ENKA Power bolster Turkey’s evolving economy by improving its energy sector’s efficiency and productivity.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Arvah B. Hopkins Generating Station, Unit 2, Tallahassee, Florida
Known for its progressive, pro-sustainability policies, the City of Tallahassee recently repowered a 30-year-old conventional steam plant unit, turning it into a new 300-MW facility. The utility redesigned the Arvah B. Hopkins Generating Station, Unit 2 as a 1 × 1 combined cycle plant in order to improve efficiency, switched the primary fuel from oil to natural gas, and thereby reduced fuel costs and emissions. The plant’s flexible design even will enable expansion to a 2 × 1 configuration when additional capacity is needed in the future.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Astoria II Combined Cycle Plant, Queens, New York
Managing construction of the 550-MW Astoria II Combined Cycle Plant in the midst of Queens, a densely packed New York City borough, required extensive off-site modular construction and a high level of logistical organization. Now the new Astoria II plant is operating successfully in conjunction with the Astoria Energy I plant as the largest natural gas–fired power plant in the Big Apple.
-
Gas
Top Plant: Emirates Aluminum Smelter Complex (EMAL), Al-Taweelah, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
The new 2,100-MW Phase 1 EMAL combined cycle power plant provides dedicated power with a high level of reliability to the Emirates Aluminum Smelter Complex, which is designed to be the world’s largest aluminum smelter upon completion. Located on the Persian Gulf, the gas-fired combined cycle plant uses seawater cooling towers to eliminate thermal stress on local marine life.
-
O&M
Systems Integration, Flexible Control Reduce Makeup Water Cost
Longview Power, a 695-MW coal-fired power plant now under construction in Maidsville, W.Va., is scheduled to begin commercial operation later this year. The $2 billion project reached 580 MW in early June, just a month after completing the “first fire on coal” schedule milestone. Testing and tuning of the controls and various systems continue.
-
O&M
Improving the Efficiency of Toronto’s District Heating Plant
Enwave Energy Corp.’s district heating plants in downtown Toronto will be operating cleaner and more efficiently before the fall 2011 heating season begins when boiler upgrades now under way are completed. Enwave hired Benz Air Engineering (BAE) to design and install upgrades to all eight boilers inside Enwave’s Pearl Street Station. When the $20 million project is completed, the retrofits will produce energy savings exceeding $5 million per year. In addition, the company will receive incentives of $100,000 per boiler from Enbridge, its natural gas provider.
-
O&M
Fighting Pipe Abrasion
Steel piping systems used to convey coarse materials, often over long distances, are under constant attack from abrasion. In power plants, the materials are usually coal and limestone slurry. The common industry solution has been to install abrasion resistant (AR) pipe that is much harder on the Brinnell Scale than standard steel pipe. The harder the inner wall, studies have shown, the better it resists the gouging or plowing action of abrasive sliding particle flow.
-
Legal & Regulatory
New Approach Needed for Renewable Integration
It is time for the renewable integration discussion to move beyond simply identifying the challenges of ensuring reliability in a nation increasingly served by intermittent renewable resources and toward developing real-world solutions to these challenges.
-
Coal
Plant of the Year: KCP&L’s Iatan 2 Earns POWER’s Highest Honor
Kansas City Power & Light (KCP&L) began engaging stakeholders in 2003 to develop consensus on a regional energy plan designed to balance customers’ desire for low electricity costs with system reliability needs and environmental requirements. The culmination of that plan was the completion of Iatan 2, which entered service in August 2010. For executing an innovative energy plan that reduced overall fleet emissions, ensuring the region’s future electricity supply, and completing an approximately $2 billion project in time for the summer 2010 peak load by using innovative contracting and project controls, KCP&L’s Iatan 2 is awarded POWER’s 2011 Plant of the Year Award.
-
O&M
Marmaduke Award: CFE Extends CTG Universidad Unit 2’s Life with Conversion to Synchronous Condenser
CTG Universidad is a two-unit combustion turbine plant commissioned in late 1970 by the Comisión Federal de Electricidad (CFE) on the north side of Monterrey, Mexico’s third-largest city and an important industrial center. By the 1990s, the two 14-MW turbines were obsolete, used sparingly, and slated for demolition in 2010. However, by 2002, portions of Monterrey began experiencing power restrictions caused by a lack of sufficient reactive power production, and that situation presented an opportunity for the plant. By repurposing an old combustion turbine for use as a synchronous condenser to provide local reactive power, CFE significantly reduced local power supply limitations. For that savvy plant repurposing, CFE’s CTG Universidad Unit 2 is the winner of POWER’s 2011 Marmaduke Award for excellence in power plant problem-solving. The award is named for Marmaduke Surfaceblow, the fictional marine engineer and plant troubleshooter par excellence.
-
Smart Grid
Smart Grid Award: Vermont Electric Cooperative Takes Wise Approach to Smart Grid Projects
A cooperative in northern Vermont serving a largely rural area has proven that even small utilities can achieve great smart grid results by planning wisely. For improving service to its members by developing a grid modernization strategy before “smart grid” was a buzz phrase, Vermont Electric Cooperative is the winner of the first POWER Smart Grid Award.
-
News
Fracking Problems
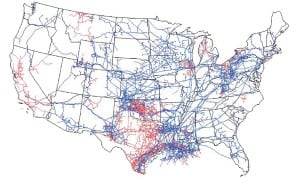
By most estimates, natural gas is likely to become the dominant power generation fuel in the U.S. within perhaps a decade. The rapid growth in natural gas supplies follows advanced drilling techniques that can economically tap large shale gas reserves located deep beneath Earth’s crust. Unfortunately, it only takes one outlaw drilling company to frack it up for the rest of us.
-
O&M
Make Your Plant Ready for Cycling Operations
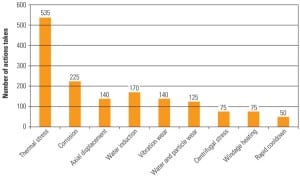
Cycling your steam power plant is inevitable, so now is the time to learn how to minimize equipment damage and assess the true costs of cycling. Whether cycling is required by the grid operator because of renewable integration or other factors, you must be proactive about updating operating processes and upgrade equipment so the transition to cycling operation goes smoothly.
-
Nuclear
THE BIG PICTURE: Underground Nuclear Waste Disposal
According to the International Atomic Energy Commission, deep disposal in stable geological formations is the only sustainable way to safely manage spent fuel and high-level waste (HLW) from nuclear power reactors. No permanent geological repository has yet been built, but some countries have found a location for a future repository. Others are researching the option…