In This Issue
-
News
Upward Mobility
The Max Climber 2000P-IPM rack and pinion personnel and material elevator by Beta Max Inc. uses little space while providing a safe and efficient means of access for workers performing maintenance work at high levels. The Max Climber 2000P-IPM easily attaches to scaffolding or a building exterior and is designed with a base system footprint […]
-
News
Plant Communication Link
Parker Hannifin’s Instrumentation Products Division introduced Pilot Pro, a new process sample conditioning system communications interface designed to provide a link between plant process control operations and analyzer maintenance networks, regardless of where the two are located. A sensor and solenoid administration module, Pilot Pro is designed to acquire, transmit, and manage real-time sample system […]
-
Commentary
The Obama Administration’s Energy Challenge
As the Obama administration takes office, energy resource allocation is both the most critical national security issue and the most critical economic issue facing us. It will be difficult to sustain and improve economic growth unless we implement policies that result in the more rational use of energy resources, especially those for which there is a finite supply.
-
Coal
TVA Containment Pond Bursts, Causing Massive Coal Ash Flood
Just after midnight on Dec. 22, 2008, a 40-acre pond holding coal combustion waste for a Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) steam power plant ruptured, sending a wave of wet ash across 300 acres of rural land in Harriman County, Tenn. It was the largest coal slurry spill in U.S. history — more than three times the size of the Martin Country, Ky., sludge spill of 2000, and about eight times that of the 1972 Buffalo Creek flood in West Virginia. Unlike that flood, which killed 125 people and injured scores others, this one, Tennessee authorities reported, resulted in no serious injuries or hospitalizations.
-
Nuclear
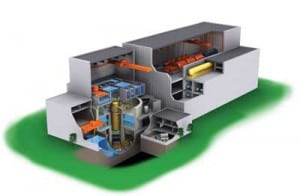
Exelon Drops ESBWR for Victoria Plant, Weighs Options
A year after Exelon Nuclear ceremoniously announced the selection of General Electric-Hitachi’s Economic & Simplified Boiling Water Reactor (ESBWR) design (Figure 2) as its preferred technology for a proposed two-unit nuclear facility in Victoria County, Texas, the operator of the largest nuclear power fleet in the U.S. — and the third-largest in the world — said it had reconsidered its decision. The company said it is now negotiating separately with Toshiba and GE-Hitachi, both vendors of the Advanced Boiling Water Reactor (ABWR), and with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries for its U.S. Advanced Pressurized Water Reactor (US APWR).
-
Engineers Week Is Feb. 15–21
I just renewed my professional society membership dues for the umpteenth year, and while writing the check, I paused to consider if I was getting good value from them. I expect to receive another "suitable for framing" certificate this year, as the number of my membership years ends with a zero, but I wondered if there were other, more tangible benefits.
-
Nuclear
China’s Nuke Power Boom
China has put its nuclear power plans on a fast track, kicking off a construction frenzy worth billions of dollars. In the latter months of 2008, the nation inaugurated construction of seven reactors, and in 2009, work will begin on another 10.
-
-
Nuclear
Eastern Europe Prepares for Nuclear Revival
Despite hostilities that linger as a result of the 1986 nuclear nightmare at Chernobyl, Ukraine, and pressure from the European Union to shut down older-generation plants, Eastern European countries from the Baltic to Bulgaria are renovating existing nuclear plants or building new ones. If these projects become reality, the region will be able to secure its power supplies as well as cover the ongoing shortages in countries such as Greece, Macedonia, and Albania.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Oil—Unsafe at Any Price
A confluence of circumstances promised to make 2008 a transformative year for renewable energy in the U.S. States enacted additional, and more demanding, renewable portfolio standards, promoting accelerated and sustained development of "green" energy resources. Increasing concerns about global warming and climate change prompted some of this activity. However, the unprecedented escalation of oil prices to almost $150 a barrel (translating into prices at the pump in excess of $4) was the largest impetus for demands that this nation end its addiction to fossil fuels.
-
Solar
New Technologies Could Improve Solar Cell Efficiencies
Declining oil prices, supply issues, and dwindling financing may have battered solar energy in recent months, but the industry seems to have sparred well in the research arena. An assortment of institutions separately announced breakthroughs in their quests to boost the efficiency of solar cells. The technological advancements ranged in approach, from the development of an antireflective coating to the formulation of more efficient solar cell materials, but all point to promising possibilities for the industry.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
ISA POWID: Where Power Computing Professionals Meet
Which new and emerging technologies will be essential to your power plant’s success? Our special cover story series gives you a glimpse into the future of advanced distributed controls, wireless applications, and automation technologies.
-
Business
An Energy-Generating Door
An energy-generating revolving door installed at Driebergen-Zeist railway station in the Netherlands is the latest experiment in eco-building. Dutch company Royal Boon Edam Group Holdings designed the manual door to match the newly refurbished station’s sustainable technology theme, while keeping in mind that the station — converted into a multifunctional area featuring restaurants and a tourist information and visitor center — holds 8,500 commuters at capacity.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Distributed Control Technology: From Progress to Possibilities
The past decade has seen an explosion of technology that has significantly altered the process control industry. The adoption of commercially available technology driven by desktop computing has allowed suppliers to focus on applications to enhance the process and deliver ever-greater value to the user.
-
Coal
Sri Lanka Commissions Major Thermal Power Plant
The Sri Lankan government in December commissioned the first phase of the 300-MW Kerawalapitiya Thermal Power Plant, the nation’s biggest combined-cycle power plant project. The $300 million plant in the western part of the country commenced operations by generating 200 MW (Figure 7). In its second phase, it will expand to 300 MW. Per government estimates, power produced by the plant is priced at about 20 rupees or $0.18/kWh.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Optimize Your Plant Using the Latest Distributed Control System Technology
Distributed control systems are powerful assets for new and modernized power plants. Thanks to three product generations of technology innovations, these systems now provide new benefits — including improved O&M efficiency, greater plant design flexibility, and improved process control and asset reliability — that help competitive plants advance in the game.
-
O&M
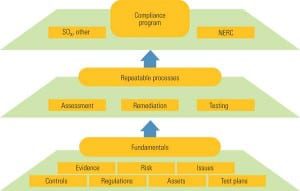
FERC Focuses on Internal Compliance Programs
By now, most electric industry participants are aware of the mandatory reliability standards required by the Energy Policy Act of 2005 and managed by the North American Electric Reliability Corp. (NERC). Bulk-power system users, owners, and operators (known as NERC registered entities) are responsible for complying with the set of standards that are applicable to their operations in their specific region. Compliance is monitored by the NERC regions (Texas Regional Entity, Western Electric Coordinating Council, Reliability First Corp., Midwest Reliability Organization, SERC Reliability Corp., Florida Reliability Coordinating Council, Northeast Power Coordinating Council, and Southwest Power Pool) through spot checks, self-certifications, audits, and investigations.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Power Plant Automation: Where We Are and Where We’re Headed
Over the past decade, power plant control systems have evolved from DCS-centered platforms with proprietary software, to open systems using industry standard hardware and software, and then to totally integrated plant automation systems with almost unlimited connectivity and the ability to interrogate field instruments from many different manufacturers. What’s next?
-
O&M
Preventing Boiler Code Violations Creates a Safer Work Environment
Nearly 10% of boilers and pressure vessels inspected in the second quarter of 2008 were slapped with violations, which means that the violations put workers and equipment in danger, according to a quarterly report released by the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Enhancing Plant Asset Management with Wireless Retrofits
Wireless technology is a mostly untapped resource in the power generation industry that can have a significant impact on the way business is done. It enables a greater degree of connectivity among devices for enhanced monitoring and asset utilization and has led to the development of new applications that improve productivity, uptime, and overall business performance.
-
O&M
Converting a Pump to Use Mechanical Seals
Wear and leakage are common maintenance problems that result in pump discharge pressure dropping below optimum levels and reduced pump efficiency. Converting pumps to mechanical seals eliminates fretting or grooving of the shaft and provides for easier pump maintenance. By converting to mechanical seals, a plant also avoids incurring expenses associated with the replacement of sleeves and shafts.
-
Instrumentation & Controls
Wireless Technology Unlocks Possibilities
Modern wireless systems improve productivity, monitoring activities, and safety at power plants by enabling the right people to be at the right place at the right time. Wireless technology can put hard-to-access process and asset information at your fingertips, wherever you are, to enable more accurate and timely decisions.
-
News
A Documenting Calibrator
The latest documenting process calibrator from Beamex is the MC4, a compact-sized device that calibrates various process parameters, such as pressure and temperature, and then automatically stores results in the MC4’s memory. The instrument data can also be sent from computer to MC4, or calibration results can be uploaded from the MC4 to a computer […]
-
Coal
New Laser Technology Helps Reduce Coal-Slagging Headaches
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy is starting to light the way for power plant operators who want to reduce coal ash deposition in their boilers.
-
News
Economical Positive Displacement Pump
SPX Process Equipment last December introduced the ProCam SMART, a Bran + Luebbe positive displacement pump capable of a wide range of metering duties at a low initial investment. Available in four models offering flow rates ranging from 1.3 gph to 132 gph and suitable for pressures up to 290 psi, the ProCam SMART is […]
-
Business
HTS Cables Speed up the Electric Superhighway
High-temperature superconducting cables deliver up to 10 times as much power as conventional electric power transmission cables. They are poised to help to reduce grid congestion as well as installation and operating costs.
-
News
Vortex-Shedding Flowmeters
Universal Flow Monitors launched the P420 Series, a set of plastic, vortex-shedding flow rate transmitters designed to process corrosive fluids, water, brine, and low-viscosity fluids in water treatment, chemical, and desalination applications. The series features plastic flowmeters that have no O-ring seals or other moving parts that can stick, bind, or coat processing water or […]
-
Business
NERC Drives Development of Sustainable Compliance Programs
Compliance with reliability standards has moved beyond the "check the box" phase to one of regulations with real deliverables and fines for noncompliance. Utilities that aren’t vigorously evaluating and refining their compliance procedures today may find NERC’s 2009 audit cycle much more challenging.
-
News
Repairing Water Pipes with Ice Plugs
Facilities facing emergency plumbing repairs are typically forced to shut down and then drain the entire water system. RIDGID’s new SF-2500 SuperFreeze pipe-freezing unit is designed to avoid this costly and inconvenient process by quickly isolating sections of copper or steel pipe with ice plugs. Plugs are formed in as little as five minutes in […]