Hydro
-
Hydro
Osmotic Power Makes Headway
Statkraft began operating its 4-kW prototype osmotic power plant at Tofte, just outside Oslo, Norway, in 2009. Now the firm reports that it is close to developing a large-scale plant. In June, Statkraft and Japanese materials manufacturer Nitto Denko/Hydranautics signed an agreement for the development and supply of membranes specifically designed for use in large-scale osmotic power plants.
-
Hydro
Hydro: The Forgotten Renewable Rebounds
When President Obama unveiled his “clean energy standard” in the 2011 State of the Union address in February, and again when he spoke of his administration’s energy policy in late March, one form of electrical energy was conspicuous by its absence: hydropower. Hydro is the forgotten form, the politically incorrect renewable, the invisible generation. To borrow the complaint of comedian and Caddyshack movie star Rodney Dangerfield, hydro projects “don’t get no respect.”
-
Hydro
Carbon Trust: Marine Energy Has High Potential but Faces Several Challenges
In a an analysis released this May, nonprofit UK group Carbon Trust admits that there is “still considerable uncertainty as to whether wave and tidal systems will play a meaningful role in meeting global energy needs,” but it suggests, based on high and low scenarios, that up to 240 GW of marine capacity could be deployed globally by 2050. Roughly 75% of this capacity will come from wave and the remainder from tidal energy.
-
Hydro
Seven Charged in Siberian Hydropower Plant Accident
The Russian Investigative Committee has completed a probe into the August 2009 accident at the Sayano-Shushenskaya Hydro Power Plant in Siberia that killed 75 people. The committee has charged seven people—including the plant’s former head, Nikolai Nevolko, his deputies, and the plant’s former chief engineer, Andrei Mitrofanov—for violating safety rules. If found guilty, the officials could face five years in jail.
-
Coal
Spain: A Renewable Kingdom
Spain has served as both exemplar and scapegoat when it comes to renewable energy policy. Though power policy must necessarily accommodate specific national resources and goals, Spain’s experience as an early and eager adopter of renewable energy technologies and subsidies is a cautionary tale of how the best intentions can have unintended consequences.
-
Coal
China’s Five-Year Plan Is Heavy on Non-Fossil Generation
The People’s Republic of China’s Congress approved a much-anticipated draft of the country’s 12th Five-Year Plan (2011–2015) on March 14. Along with key objectives that included boosting its gross domestic product (GDP) by 7% annually on average, the country for the first time in a five-year plan established targets to tackle climate change. It plans to reduce carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP by 17% from 2010 levels by 2015 and to reduce energy consumption per unit of GDP by 16% from 2010 levels by 2015.
-
Hydro
China Dam Gets World’s First Self-Closing Ring Gate Control System
A major technical advance in hydroelectric dam safety was achieved this March as Alstom’s Chinese arm, the Tianjin Alstom Hydro Co. (TAH), delivered what it called “the world’s first self-closing electronic ring gate control system” to the Ahai hydropower project in China.
-
Hydro
New York City Backs Tidal Power
The Roosevelt Island Tidal Energy (RITE) pilot project used six full-scale hydrokinetic turbines to capture the power of river tides and currents and convert it into electricity. Located in New York City’s East River, it is the first and only grid-connected tidal array project in the world. RITE project developers are seeking approval to install up to 30 additional turbines in the near future.
-
O&M
Fire Protection Options for Air-Cooled Hydroelectric Generators
Fire protection systems for air-cooled hydroelectric generators have several special requirements due to these generators’ unique geometries. This survey of options will help plant owners and operators make the best equipment selections for their plants and thereby avoid unexpected surprises.
-
Hydro
Brazil Greenlights 11-GW Belo Monte Project
Brazil’s environment agency, IBAMA, in January issued a partial installation license that allows for construction of the controversial Belo Monte dam complex, an 11,233-MW project estimated to cost some 19.6 billion reals (US$11.7 billion), to begin on the margins of the Amazon’s Xingu River. Saying the project is needed to meet soaring electricity demand when completed, as planned in 2015, the government gave license to dam-building consortium Norte Energia to begin clearing 238.1 hectares (588 acres) of forestland.
-
Coal
Canada’s “Clean” Image Extends to Clean Power
Canada’s extensive natural resources are the driver of its powerful economy, and energy is Canada’s single most important export. Yet policy makers across the nation are currently dealing with the consequences of a generation of under-investment in the electricity system and deciding what the new grid and supply mix should look like. Several provinces are competing to lead the charge in renewable energy and grid intelligence. Policy makers hope that such efforts will not only provide for Canada’s electricity needs but also create the green economy jobs that will drive the nation’s next generation of economic development.
-
Hydro
Transmission and Distribution in Canada
Like its neighbor to the south, Canada faces enormous costs to upgrade and expand its transmission and distribution system. The desire to integrate more renewable power into the grid, build a smarter grid, and export more power are providing the rationale for action, but capital and political will lag behind.
-
Coal
Canada’s Provincial Power Strategies
In Canada, as in the U.S., where you live determines the type of generation technology that provides your power. Here’s how the four most energy-intensive provinces in Canada are responding to the challenge of providing reliable and cheap power in a sustainable way.
-
Hydro
Laos Inaugurates Major Revenue-Generating Hydropower Plant
Lao People’s Democratic Republic (PDR), the tiny landlocked country in Southeast Asia of just 6.3 million people, in December inaugurated the 1,070-MW Nam Theun 2 Power Station, a hydropower project in Khammouane Province.
-
Hydro
Marine Power Developments Move Forward in North America
In early January, Verdant Power—a decade-old company based in New York—made headlines for filing an application with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) for a project that could allow it to install up to 30 new tidal power turbines in the East Channel of the East River in New York City.
-
Hydro
German Researchers Develop Cost-Efficient Small Hydro Plant
Researchers at Germany’s Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM) claim to have developed a small-scale hydroelectric power plant that is capable of operating profitably even at modest dam heights while minimizing impact on waterways.
-
Coal
IEA: Global Power Demand to Surge 2.2% Annually Through 2035
Though electricity generation has entered a key period of transition—as investment shifts to low-carbon technologies—world electricity demand is set to grow faster than any other “final form of energy,” the International Energy Agency (IEA) says in its latest annual World Energy Outlook.
-
Hydro
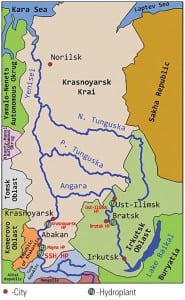
Construction of Tibetan Dam Sets Off Cross-Border Tensions
China in mid-November embarked upon building the first massive hydropower project in Tibet, a 6 x 85-MW plant straddling the middle reaches of the mighty Yarlung Tsangpo River (Figure 2). According to the Hunan Daily, a Chinese state-owned enterprise, Sinohydro began damming the river in Shannan Prefecture, Tibet, on Nov. 8, kicking off the 7.9 billion yuan ($1.2 billion) “run of the river” project that is estimated to generate electricity for the surrounding region by 2014.
-
Hydro
UK Cancels Tidal Barrage Plans, Approves Key Nuclear Sites
The UK government in late October shelved plans to build the Severn barrage—a project that would have involved building a 10-mile dam across the mouth of the Severn River—after a two-year-long feasibility study failed to convince ministers to use public funds to build it. The Department of Energy and Climate Change instead gave its long-awaited approval to eight sites for new nuclear reactors, saying that private companies could begin building the country’s new fleet of reactors, provided no public subsidy is involved.
-
Hydro
Massive Energy Storage Facility Planned for Mexico-U.S. Border
Dubai-based energy firm Rubenius in October proposed to build a $4 billion energy storage facility based on sodium sulfur (NaS) technology on a 345-acre site in the Mexican state of Baja California, close to the U.S. border. If it comes to fruition, the facility—dubbed a “mega region energy warehouse” by Mexico’s President Felipe Calderon—will feature 1,000 MW of battery storage and offer “storage space” to energy companies and utilities in both Mexico and the U.S.
-
Hydro
Investigating the Sayano-Shushenskaya Hydro Power Plant Disaster
The destruction of the turbines and auxiliary equipment at Russia’s Sayano-Shushenskaya Hydro Power Plant in August 2009 claimed the lives of 75 workers and wrecked an indispensable source of electricity that will take years to fully restore. The disaster, as this report explains, was predictable and preventable.
-
Hydro
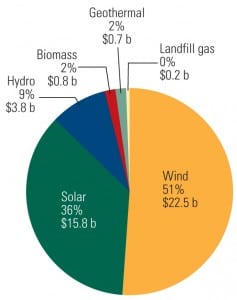
The Rush to Renewables
In 2010 investment in wind power continued to accelerate, particularly in California and Texas. California also entered several solar projects in the race for financing. The finish line that renewable power developers and their partners are racing to meet is a December 31 deadline to qualify for federal cash grants.
-
Hydro
UK Installs Hub to Test Wave Energy Projects
A £42 million marine power infrastructure project that will function as an “electrical socket” in waters 50 meters (m) deep and nearly 16 kilometers (km) off the coast of Cornwall in South West England set sail toward its proposed location this July.
-
Hydro
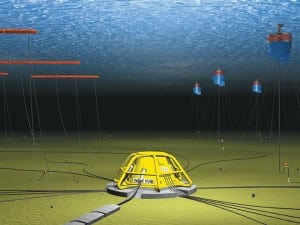
Wave Energy Device to Tap Marine Energy in Gulf of Mexico
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers earlier this year awarded its first Section 10 permit ever to a commercial wave-powered demonstration facility planned for installation in the Gulf of Mexico. The novel offshore platform, dubbed the SEADOG, will use a buoy and piston mechanism combined with a water wheel to generate electricity and desalinate water.
-
Hydro
Australia Gets Hydropower from Wastewater
An Australian sewage plant this April began using treated wastewater falling down a 60-meter (m) shaft to produce its own power.
-
Hydro
Integrating Wave and Wind Power
While Europe’s offshore wind sector has taken off, interest is resurging in marine energy. The UK’s Crown Estate took the major step this March, for example, of awarding leasing rights to 10 wave power projects to develop generation in Scotland’s Pentland Firth and Orkney waters of the North Sea.
-
History
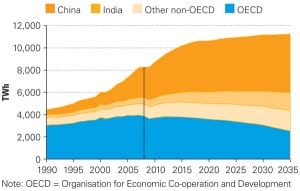
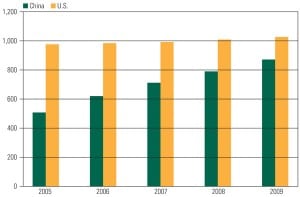
China: A World Powerhouse
It’s no surprise that China leads the world in recent power capacity additions. What may surprise you is the precise mix of options this vast country is relying upon to meet its ever-growing demand for electricity. As a result, this ancient civilization is fast becoming the test bed and factory for the newest generation and transmission technologies.
-
Hydro
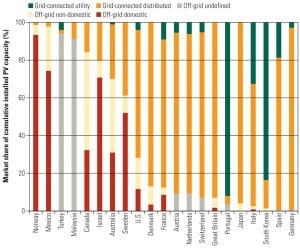
Utility Perspectives on Using Renewable Power
As U.S. utilities increase the percentage of renewable energy in their generation portfolio, they must deal with a number of key issues related to selecting specific technologies. Additionally, they must figure out what it will take to make renewables emerge as a mainstream generating option in the future.
-
Hydro
Hoover Dam Contracts for Low-Water Hydroelectric Turbine
Growing water demand and reduced runoff due to drought has depleted waters feeding many hydroelectric power plants around the world—sometimes causing severe power shortages, such as in Brazil and New Zealand. The 2,080-MW Hoover Dam (Figure 4), a facility that generates power for more than a million people in Arizona, Nevada, and Southern California, is not immune to this phenomenon. According to a recent study by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography, the Colorado River system, which includes Lake Powell and Lake Mead (both manmade reservoirs), is suffering a net deficit of nearly one million acre-feet of water per year.
-
Hydro
The Backpack Power Plant
Soldiers could one day carry 600-W power plants on their backs, or set up arrays of up to 20 kW in streams deeper than 4 feet, if a prototype being developed by California-based Bourne Energy comes to fruition.