Gas
-
Coal
Wisconsin Utility Doubled Its Gas Burn in 2012
Wisconsin Energy nearly doubled its natural gas burn for power generation in 2012, from 23.9 billion cubic feet (bcf) in 2011 to 46.5 bcf in 2012. Gale Klappa, CEO, said during a January 30 earnings conference call that natural gas units at the company’s 1,150-MW Port Washington generating station operated at a 46% capacity factor in 2012. This compares with a 23% capacity factor in 2011.
-
Coal
Federal Court Declines to Bind EPA to New Source MATS Deadline
A federal appeals court last week denied a motion from developers of new coal- and oil-fired power plants to force the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to finalize its reconsidered Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS) for new sources by March and help them avoid a regulatory Catch-22 posed by a looming rule to curb greenhouse gas emissions in new plants.
-
Coal
EPA Rules, Economy, Natural Gas Prices Prompt Georgia Power to Retire 2 GW of Coal, Oil Power
Georgia Power on Monday said it was seeking state regulatory permission to decertify and retire 15 coal- and oil-fired generating units—a total capacity of 2,061 MW—citing several factors, including costs to comply with existing and future environmental regulations, economic conditions, and lower natural gas prices.
-
Coal
EPA Finalizes Standards for Industrial Boilers, Certain Incinerators
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Dec. 20 finalized changes to a specific set of adjustments to Clean Air Act that apply to a coal, oil, natural gas and biomass boilers and certain solid waste incinerators.
-
Coal
World Energy Outlook Foresees Distinct Generation Shift
Global generating capacity is poised to soar by more than 72%, to 9,340 GW, by 2035 from 5,429 GW in 2011, despite retirement of about 1,980 GW, the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts in its World Energy Outlook 2012, released in November.
-
O&M
Emerging Technologies Enable “No Regrets” Energy Strategy
Achieving a balance between affordable and sustainable electricity while improving reliability is a challenge unlike any the electricity sector has faced since its inception. Technology innovations in key areas such as energy efficiency, smart grid, renewable energy resources, hardened transmission systems, and long-term operation of the existing nuclear and fossil fleets are essential to shaping the future of electricity supplies.
-
Coal
Slow Growth Ahead—with Unexpected Flares of Activity
North American shale gas was supposed to realign the generation fleet here and abroad (thanks to anticipated exports) far into the future. Turns out, that’s not exactly how the near term is shaping up. Despite stagnant (and even putrid) economies and legislative bodies in the U.S. and EU, there promises to be sufficient market volatility to keep everyone alert.
-
Coal
Coal Battered Early, Later Rebounds
For the first time, U.S. generation from coal and natural gas was equal in 2012, although just momentarily. Gas dominated early in the year, but as gas prices rose in response to supply and demand forces, coal use rebounded. Expect more of the same give-and-take in 2013.
-
Gas
Natural Gas–Fired Plants Continue Rollercoaster Ride
The availability and low price of natural gas enticed many U.S. utilities to fuel switch on a grand scale in 2012. Increased demand has put upward pressure on prices, moving coal back to the top of the dispatch order in some regions. Expect the price momentum to shift often in 2013.
-
History
The Russian Power Revolution
Exports of natural resources have given Russia increased global political and economic clout. But domestically, the world’s fourth-largest generator of electricity has had to embark on the most ambitious reforms ever undertaken to modernize dilapidated Soviet-era power infrastructure and incentivize a massive capacity expansion to support a revived economy.
-
Coal
Report: Fuel for Power Generation to Lead Energy Growth Through 2040
Fuel for power generation will account for about 55% of demand-related energy growth through 2040, ExxonMobil forecasts in its freshly released annual energy forecast. Like several other forecasters, the Irving, Texas–based oil and gas company also predicts that natural gas will emerge as the leading source of electricity generation by 2040. Among key findings in […]
-
Coal
Silicon Valley Funds Ontario Inventor’s Atmospheric Vortex Engine
Maybe it’s time to start talking about the “POWER bump.” Over two years ago, POWER magazine published a story about a new concept for generating power from waste heat. Today, Sarnia, Ontario’s AVEtec Energy Corp. announced that Silicon Valley entrepreneur and venture capitalist Peter Thiel will fund a prototype Atmospheric Vortex Engine (AVE) invented by the company’s president, Louis Michaud. The technology holds promise for low-cost thermal plant efficiency gains by generating power from waste heat.
-
Coal
Report: LNG Exports to Have Net Economic Benefits, Impact Domestic Power Sector
Allowing unlimited U.S. exports of liquefied natural gas (LNG) would increase marginal costs of supply and raise domestic natural gas prices, but it would have "net economic benefits" across a range of scenarios ranging from relatively normal conditions to stress cases with high costs of producing natural gas in the U.S. and exceptionally large demand for U.S. LNG exports around the world, a report prepared for the Department of Energy and released on Wednesday suggests.
-
Coal
EIA Projects Faster Growth of Natural Gas Production, Gas Generation
Compared to projections from last year, an Early Release Overview of the Energy Information Administration’s (EIA’s) Annual Energy Outlook 2013 (AEO2013) released on Wednesday foresees higher gas production and, with it, a higher share of gas generation by 2040. The outlook also projects a growing share of renewable and nuclear power, but dampened future coal use.
-
Gas
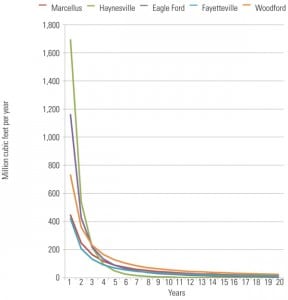
Is Shale Gas Shallow or the Real Deal?
The de facto U.S. energy policy is to burn more gas, much of it produced using “fracking” technology. Huge volumes of low-priced natural gas have caused coal plant shutdowns, slowed renewable development, and undercut new nuclear plant development. Using more gas has also sent the nation’s carbon dioxide emissions into a downward spiral. Is the glut of natural gas too good to be true?
-
History
FuelCell Energy Claims Largest Order in Industry’s History
FuelCell Energy Inc. on Monday announced an order from its South Korean partner, POSCO Energy, for 121.8 MW of fuel cell kits and services to be manufactured at the FuelCell Energy production facility in Torrington, Conn. The company said this represents the largest order for both its company and the fuel cell industry.
-
Gas
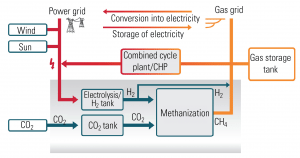
Progress for Germany’s Power-to-Gas Drive
Germany’s E.ON this August began construction of a new pilot plant in Falkenhagen in northeast Germany that will convert excess wind energy into synthetic natural gas that can then be fed into the regional gas grid, where it can be used to produce heat and power.
-
Coal
Coal Burn Rebounds in the Third Quarter, but Economics Still Favor Natural Gas
Natural gas–fired generation gave up some ground to coal during the third quarter, and coal producers are optimistic that higher natural gas prices will benefit coal, especially coal sourced from the Powder River Basin in Wyoming. Even so, at least one Midwest utility expects natural gas to power what could be as much as 1,500 MW of new generating capacity it may add over the next several years.
-
Coal
Potential Impacts of Closed-Cycle Cooling Retrofits at U.S. Power Plants
The Clean Water Act Section 316(b) rule changes regarding cooling water intake structures that are expected next year could affect up to 428 power plants, representing 1,156 individual units, according to the Electric Power Research Institute. Depending on plant size and the complexity of the retrofit project, retrofit capital costs could range from very low to over $500 million for large nuclear plants. The power industry total cost is projected to be over $100 billion.
-
Gas
Blowing Sunshine
The influx of cheap Chinese-manufactured solar panels has upended the solar industry in more ways than one. The saga offers some lessons on what to do about LNG exports.
-
O&M
Major Noise Sources and Mitigation Cost Estimates for Gas-Fired Power Facilities
Natural gas–fired power plants can generate substantial amounts of noise. With proper planning and foresight during the design phase, major noise sources can be effectively mitigated, while failing to plan can be very expensive in the long run.
-
Coal
Replacing Coal: U.S. Combined Cycle Development Trends, Challenges
There’s plenty of uncertainty in gas-fired power these days, with low prices and impending coal plant retirements. Even so, many generators are forging ahead with some ambitious projects and plans for the future.
-
Gas
Why EDF Is Working on Natural Gas
Many environmental groups are calling for a ban on hydraulic fracturing and are even lobbying to end natural gas development altogether. The Environmental Defense Fund is not. The EDF energy program chief counsel explains why.
-
Gas
New Study Advocates Shift Toward Long-Term Gas Supply Agreements
Current low gas prices offer a unique opportunity to lock in savings for years to come—but only if utilities, gas suppliers, and regulators have the vision to commit to a new way of doing business.
-
Gas
Global Prospects for Gas-Fired Power Generation
Driven by the decline of coal in the developed world, new sources of production, broadening availability, and expanding LNG development, installed capacities of gas-fired plants should rise strongly worldwide.
-
Gas
Tomato or To-mah-to? GE Gas Engines Do Triple Duty in California Hothouse
Growing hothouse tomatoes might not be the first application that comes to mind for a natural gas–fueled combustion engine, but that’s exactly what an innovative grower in Southern California is doing, with some help from General Electric (GE).
-
O&M
Upgrading Legacy Gas Turbines’ Fuel Control Systems
Relatively simple upgrades to legacy turbine systems can yield big payoffs in efficiency and reduced maintenance.
-
Coal
Are Economics Trumping Regulation?
The fate of coal-fired generation remains fluid as owners weigh environmental rules, the effect of low natural gas prices, and the shifting cost of investing in emissions control technology. An analysis of generating unit data suggests that smaller, older, less-efficient, and less-frequently dispatched assets are most vulnerable to retirements. Recently accelerated retirement dates for some units indicate that economic factors are a more important determining factor than pending environmental mandates
-
Gas
TOP PLANTS: University of Iowa Research Park Tri-Generation Power Plant, Iowa City, Iowa
As part of the University of Iowa Research Park’s efforts to promote renewable energy use, the new campus power plant’s engine generators are designed to operate primarily on landfill gas when the pipeline from the Iowa City Landfill is completed, with natural gas as a secondary fuel source. To make it more efficient, the plant’s waste heat recovery system captures waste heat from the gas engine generator’s cooling and exhaust systems to produce hot water for heating, or chilled water for cooling, campus facilities.
-
Coal
Chile’s Power Challenge: Reliable Energy Supplies
Droughts, unreliable gas imports, and protests against proposed projects have hampered the Chilean power sector and its largest economic driver, the copper-mining industry. Recent policies designed to foster more reliable supplies are a move in the right direction, but remaining obstacles are formidable.