Environmental
-
Coal
House GOP Moves to Block EPA from Regulating Coal Ash as Toxic Waste
Continuing the House Republicans’ aggressive attack on Obama administration environmental proposals, a House subcommittee approved legislation in June to prevent the Environmental Protection Agency from regulating coal ash as a hazardous waste—one of two options the EPA is considering for tightening coal ash management regulations in response to a disastrous leak from a Tennessee Valley Authority ash impoundment in 2008.
-
Coal
Dominion to Convert Three Coal Plants to Biomass
Dominion Virginia Power has asked the Virginia Corporation Commission for approval to convert three aging and relatively small coal-fired plants to biomass, saying the move would provide substantial long-term savings to customers while cutting air emissions and creating hundreds of forest-related and trucking jobs in the state.
-
Commentary
Water Issues, Carbon, and Price of Power Top Utility Concerns
In a clear sign of growing industry unease about the availability of water for power plant operations, utility officials recently surveyed by Black & Veatch on a host of policy and business issues ranked water supply as their second-highest environmental concern and identified water management as the business issue that could have the greatest impact on the utility industry in the near future.
-
Commentary
Carbon Markets Take Flight (in Europe)
The European Union has adopted a greenhouse gas cap-and-trade system as part of its Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS). Beginning January 2012, aircraft flight engines will be added to the emissions sources regulated by the ETS. A Solutions Fellow at the Pew Center on Global Climate Change believes these regulations are an important step in regulating carbon emissions. You be the judge.
-
Coal
The Better Environmental Option: Dry Ash Conversion Technology
After the 2008 incident involving the failure of a large surface impoundment containing wet coal ash, the EPA began investigating all coal-fired power plants employing this wet coal ash management method. Now a new dry ash management technology offers coal-fired power plants an environmentally suitable alternative for handling coal ash that also increases energy efficiency.
-
Coal
Consolidation, Market Distortions Underlie Remarks by Industry Executives
If you needed additional proof that the power industry is changing, the ELECTRIC POWER keynote and panel discussions over the past few years have provided it—top-of-mind issues have been significantly different each year. For the 2011 keynote speaker and panelists, the challenges of reliability, regulatory compliance, financing, and getting the fuel mix right took center stage. In the wake of Japan’s nuclear crisis, safety also featured prominently.
-
O&M
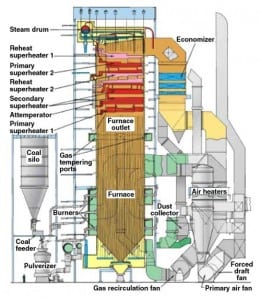
Solid Fuels: Moving Material and Managing Emissions
In today’s solid-fueled power plant, managing emissions and moving materials more defines the task than the traditional work of making megawatts. That’s the message that emerged from the coal and solid fuels track at this year’s ELECTRIC POWER.
-
Coal
Biomass Boiler Market Remains Unpredictable
Utilities struggling to meet renewable portfolio standards requirements have studied the conversion of existing coal-fired boilers to burn biomass. The results of those studies have been mixed, although test burns continue; the results of one such test are included. Overall, the market is tending toward smaller biomass projects, and the low price of natural gas is perhaps the biggest reason utility-scale projects are now few and far between.
-
Coal
Re-Industrializing America with Clean Coal Technologies
Balancing the rising energy needs of a globally expanding population (most of which lives in poverty) against the need to reduce increases in atmospheric emissions is a monumental problem. What role can clean coal technologies play?
-
O&M
Applying CFD to Optimize Furnaces Cofiring Biomass, and the Impact of Cofiring on SCR
The international policy framework regulating the emissions of greenhouse gases from industrial and utility boilers is in flux. Meanwhile, most boiler owners are evaluating potential strategies for when, not if, more stringent emissions reduction regulations are put in place. One of the most attractive compliance options is the cofiring of biomass in existing coal-fired boilers.
-
Coal
ERCOT Predicts No Coal Retirements from EPA Rules
In surprising findings, given the state’s often-contentious relationship with the Environmental Protection Agency, a study released May 11 by the Texas grid operator concludes that a suite of looming EPA rules to reduce conventional and hazardous air pollution from power plants and to tighten power plant cooling water regulations likely would not force the retirement of any Texas coal plants.
-
Coal
Southern CEO Sees Federal "War on Coal"; Questions Dash to Gas
In a wide-ranging speech on U.S. electricity policy, Southern Co. Chairman, President, and Chief Executive Officer Thomas Fanning said that coal is "under attack" by the federal government, that natural gas may not be the panacea seen by some utilities facing environmental constraints on their coal plants, and that federal proposals to sharply reduce utility hazardous air pollution have unreasonable compliance deadlines that should be extended.
-
Coal
Proposed Clean Energy Agency Has Cost Issue
Even as Senate energy leaders gear up to re-introduce widely supported legislation to create the Clean Energy Deployment Administration, they have acknowledged that the bill faces a heightened problem this term: the need to find nearly $10 billion in offsets to pay for the new green energy financing authority at a time of overwhelming concern about the federal debt.
-
Coal
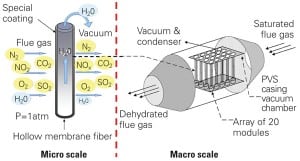
Large-Scale Tests Begin to Convert Flue Gas to Usable Water
Subsidized by the Dutch government, a number of Dutch utilities, the European Membrane Institute at the University of Twente, and Dutch consulting firm KEMA have, for over a decade, been testing membrane technology that promises to directly convert water vapor from power and other industrial plants’ flue gases into drinking water. The technology could provide a new source of large volumes of potable water.
-
Environmental
Researchers Develop Supercritical CO2 Brayton Cycle Turbines
Researchers at Sandia National Laboratories say a project that focuses on supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) Brayton cycle turbines is moving to the demonstration stage.
-
Gas
Sendai Plant Boosts Efficiency and Cuts Emissions
Located on the scenic Japanese coastline, Tohoku Electric Power Co., Inc.’s new 446-MW Sendai Thermal Power Station Unit 4 is a combined-cycle plant that replaces three 175-MW coal-fired units that had been in operation for more than 50 years. The new plant features the first application of MHI’s 50-Hz M701F4 gas turbine, which provides a thermal efficiency boost from the old plant’s 43% to more than 58%. This change substantially reduces CO2 emissions.
-
Solar
Energy Storage Enables Just-in-Time Generation
One of the main criticisms of renewable energy facilities is that they are unable to dispatch electricity when it’s needed. The great game-changer is low-cost energy storage, which would enable renewable energy production to be stored and rapidly released when needed. Here are seven promising distributed energy storage technologies that could be commercialized in the near future.
-
Coal
House Panel Hustles Through Bill Blocking EPA Climate Rules
In an anti-climactic markup that featured little new debate and no amendments by opposing Democrats, the House Energy and Power Subcommittee approved Republican legislation to block Obama administration action on climate change by stripping the Environmental Protection Agency of its Clean Air Act authority to regulate carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
-
Coal
EPA Requiring Three Oklahoma Coal Plants to Scrub or Use Gas
In an unusual ultimatum, the Environmental Protection Agency said that it is proposing to take over visibility portions of the Oklahoma Clean Air Act implementation plan to require three coal-fired power plants in the state either to switch to natural gas or install sulfur dioxide scrubbers within three years.
-
Coal
Air Rules Could Risk 11% of PJM Generation
Anticipated clean air regulations could force the retirement of as much as 19,000 MW of coal capacity in the Mid-Atlantic—or 11% of the region’s generation—unless power prices rise to levels that make operation of the plants profitable, according to the independent market monitor for PJM Interconnection.
-
Coal
Canada’s “Clean” Image Extends to Clean Power
Canada’s extensive natural resources are the driver of its powerful economy, and energy is Canada’s single most important export. Yet policy makers across the nation are currently dealing with the consequences of a generation of under-investment in the electricity system and deciding what the new grid and supply mix should look like. Several provinces are competing to lead the charge in renewable energy and grid intelligence. Policy makers hope that such efforts will not only provide for Canada’s electricity needs but also create the green economy jobs that will drive the nation’s next generation of economic development.
-
Coal
Illinois Lawmakers Block Clean Coal Plant
Ringing what may be the death knell for the $3.5 billion Taylorville IGCC project, the Illinois Senate voted 33-18 in early January against authorizing construction of a coal gasification and power generating plant proposed in the state by Tenaska.
-
O&M
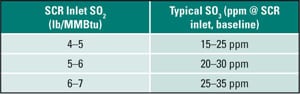
Continuous SO3 Monitoring Can Reduce Sorbent Consumption
An unintended consequence of employing selective catalytic reduction and wet flue gas desulfurization to reduce nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide levels at coal-fired power plants has been unwanted sulfur trioxide (SO3) emissions. Picking the right sorbent in the right amount can eliminate that problem.
-
Coal
Coal Groups Blast Colorado’s Dash to Natural Gas
In a decision blasted by the coal industry as making the state "dangerously reliant" on natural gas, the Colorado Public Utilities Commission has approved an emissions-reduction plan for Xcel Energy that further expands the utility’s already extensive shutdown of coal-fired power plants in favor of gas-fueled generation.
-
Coal
The U.S. Power Industry 2011: The Sequel
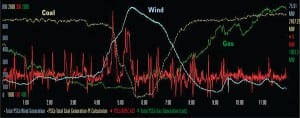
If Hollywood were scripting the power industry story for 2011, it would be a sequel to 2010—more of the same, but just not quite as good. Natural gas gets top billing and the accolades, wind power drops to a supporting role, and new nuclear answers the casting call but has yet to get a speaking part. Coal is like Mel Gibson—a talented Oscar winner unlikely to get another leading role. In this, our fifth annual industry forecast report, the story may be familiar, but the price of admission is going way up.
-
O&M
EPRI Identifies Four Breakthrough Technologies for 2011
The Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) has identified four breakthrough technologies and funded them through its Strategic Research and Development Portfolio. EPRI expects to accelerate development of these innovations because they are likely to have significant effects on how electricity is generated and delivered.
-
Coal
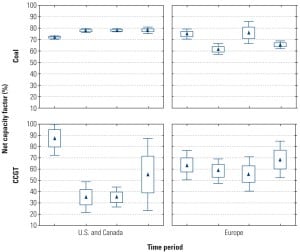
Coal Plants Challenged as Gas Plants Surge
European carbon trading is gradually pushing down coal-fired capacity factors, and operating costs are rising. The U.S. may not have a carbon market, but increasing regulatory requirements are having the same effect on coal-fired generation capacity factors and operating costs. In the meantime, gas-fired assets are enjoying increased usage and lower unit costs.
-
Coal
Oxy-Combustion: A Promising Technology for Coal-Fired Plants
For more than a decade Babcock & Wilcox Power Generation Group Inc. and Air Liquide have been developing oxyfuel technology with the goal of using it to concentrate CO2 from pulverized coal-fired power plants and achieve up to 90% CO2 capture and storage. This technology was recently selected for demonstration as part of FutureGen 2.0.
-
Commentary
Anticipating the New Utility MACT Rules
It’s been almost three years since the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit issued its decision vacating the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Revision Rule and the Clean Air Mercury Rule. Since then, the utility industry has been in a holding pattern with respect to the control of hazardous air pollutant (HAP) emissions.
-
Coal
Efficiency Favored in EPA Greenhouse Guidance To States
A long-awaited Clean Air Act regulatory guidance document released by the Environmental Protection Agency recommends that state air regulators strongly emphasize energy efficiency in determining the most cost-effective and technically feasible greenhouse gas control technologies that must be used by utilities and other major industrial emitters when expanding existing facilities or building new ones.