Environmental
-
Coal
Federal Court Rejects Challenges to EPA Industrial, Automotive GHG Rules
A three-judge panel of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit on June 26 ruled that the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was "unambiguously correct" in its interpretation of the Clean Air Act (CAA) to regulate carbon dioxide emissions. The federal agency’s endangerment finding that greenhouse gases (GHG), including carbon dioxide, are a threat to public health and welfare, and its decision to set limits for industrial and automotive emissions of GHGs, was "neither arbitrary nor capricious," the court ruled. The court, however, found that it lacked jurisdiction to review the timing and scope of the GHG rules that affect larger stationary sources, including new coal-fired power plants.
-
Coal
EPA Proposes Clean Air Standards for PM2.5
In response to a court order, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) proposed updates on June 15 to its national air quality standards for harmful fine particle pollution, including soot (known as PM2.5). The agency says that 99% of U.S. counties are projected to meet proposed standards without any additional actions.
-
Environmental
EPA Delays Issuance of Final Cooling Water Intake Rule by Nearly a Year
An amended settlement reached with environmental groups will allow the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to delay by nearly a year issuance of rules that would govern cooling water intake structures at existing power plants and mandate compliance under Section 316(b) of the Clean Water Act.
-
Coal
Federal Appeals Court Upholds EPA NAAQS Standards for NOx, SO2
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit last week handed the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) two legal victories over challenges from states and industry, affirming the agency’s revisions to the National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS) for nitrogen oxides (NOx) and upholding its revised final sulfur dioxide (SO2) standard.
-
Coal
EPA to Stay, Reconsider New Source Emission Standards in MATS Rule
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) intends to stay and reconsider new source emission standards contained in its February 2012-finalized Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS), a letter from the agency’s assistant administrator, Gina McCarthy, shows.
-
Environmental
EPA’s “Sue and Settle Rulemaking” Criticized in New Report, Congressional Hearing
A new report from the U.S. Chamber of Commerce claims that the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) uses a regulatory tactic dubbed “sue and settle rulemaking” to force states to relinquish their authority and accept agency-promulgated plans to mitigate regional haze that are much costlier to implement.
-
Environmental
Left-Right Cabal on Carbon Taxes?
Washington, D.C., July 14, 2012 — A group of mainstream conservatives and representatives from Washington environmental groups have been meeting over recent weeks to revive the idea of a U.S. carbon tax as a way to combat alleged man-made global warming. The aim is to have a package of proposed laws to bring up when […]
-
Environmental
EPA Promulgates Final Step 3 of GHG Tailoring Rule
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) last week promulgated a final rule that does not revise the greenhouse gas (GHG) permitting thresholds that were established in Step 1 and Step 2 of the GHG Tailoring Rule. The final rule, which comes just days after a federal appeals court ruled the EPA was “unambiguously correct” in its interpretation of the Clean Air Act to regulate carbon dioxide emissions, is the third step of the agency’s phased-in approach to GHG permitting under the Clean Air Act.
-
Environmental
New York Adopts Rules Curbing Carbon at New Plants, Requiring Environmental Justice Analysis
New York’s State Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC) last week adopted rules that set limits on carbon dioxide emissions from new power plants as well as require new or expanding electric generating facilities in that state to evaluate the potential disproportionate impacts on nearby environmental justice communities.
-
Coal
Settlement to Force Wisconsin Cooperative to Install Pollution Control, Close Coal Units
A settlement to resolve alleged violations of the New Source Review (NSR) provisions of the Clean Air Act reached between the Dairyland Power Cooperative (DPC), federal entities, and the Sierra Club will force the Wisconsin utility to invest about $150 million in pollution control technology, retire three coal units at its 210-MW Alma Station, and pay a civil penalty of $950,000.
-
Coal
EPA Grants PNM Stay on San Juan Pollution Control Mandate
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Tuesday granted PNM a 90-day stay in the effectiveness of the federal plan that would force the Albuquerque, N.M.–based utility to install pollution controls at its 1,800-MW San Juan Generating Station by September 2016 to meet visibility requirements of the Clean Air Act in New Mexico.
-
Environmental
South Korea Enacts Cap-and-Trade Program
The Republic of Korea’s National Assembly on May 2 passed legislation that will mandate cuts in greenhouse gases (GHGs) starting in 2015. The Act on Allocation and Trading of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Allowances passed with a near unanimous vote of 140-0, with three abstentions. It follows the country’s voluntary GHG emissions reduction target of 30% […]
-
Coal
Optimizing Catalyst Performance Lowers O&M Costs
Santee Cooper’s Cross Station has implemented a catalyst optimization program that reduces catalyst replacement cost while maximizing catalyst performance. This case study illustrates the economic advantages of taking a holistic approach to optimizing unit catalyst performance by controlling slag, fouling, sulfur trioxide, and ammonium bisulfate—key factors that lead to premature shortening of catalyst life. With catalyst costing $2 million a layer and up, there is plenty of economic motivation to find ways to improve its life.
-
Coal
New Technologies Advance Biomass for Power Generation
As U.S. utilities seek to increase the percentage of carbon-neutral biomass used in their generation portfolios, they must deal with a number of complex challenges unique to this fuel source. Several breakthrough technologies are poised to help promote greater use of biomaterials.
-
Coal
Clean Air, Dirty Water
Efforts by power producers to meet clean air rules mean that wastewater effluent streams now face revised EPA regulations. A skirmish involving a New Hampshire power plant could set the tone for the next battle over regulations.
-
Environmental
U.S. Power Sector Meets 2020 Climate Change Target—for a Month
The failure of cap and trade seemed to have doomed the U.S. to missing greenhouse gas emissions cuts it committed to at the 2009 Copenhagen conference. But a funny thing happened on the way to the hothouse.
-
Environmental
Fracking Guidelines Expand as Technology Evolves
New federal regulations promise to change the fracking landscape in the coming years, perhaps substantially. But technology may be running ahead of the law, as improvements in the fracking process threaten to make some of the new rules unnecessary.
-
Coal
Callide Oxyfuel Carbon Capture Plant Retrofit Moves Forward
Oxyfuel technology has been retrofitted at a 700-MW coal-fired power plant in Queensland, Australia, and is now capturing carbon dioxide from one of the plant’s six steam boilers.
-
Environmental
Particulate Matter Air Quality Standards Continue to Evolve
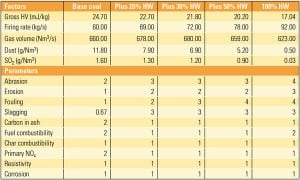
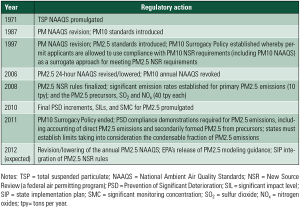
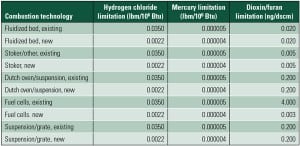
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has regulated particulate matter as an air pollutant for more than 40 years. Over time, PM regulations and testing methodologies have become more complex, with the focus shifting to smaller particle size fractions and the inclusion of the condensable form of PM. New developments make navigating the permitting and compliance process efficiently more important than ever.
-
Coal
Mercury and Air Toxics Standard, CSAPR Legal Pushback Mounts
Two Environmental Protection Agency rules are facing legal challenges. The Mercury and Air Toxics Standards is being challenged by half the U.S. states, while a decision in a case concerning the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule could be reached as soon as this summer.
-
Coal
EPA Sets Carbon Standards for New Coal Units, Compliance Options Limited
In late March, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) proposed its first-ever carbon pollution standard for new power plants, limiting carbon dioxide emissions from new fossil fuel–fired power plants. However, the technology options for complying wiith the proposed rule remain few and expensive, as recent developments demonstrate.
-
Coal
FERC: Coal Generation Losing Out to Natural Gas
Coal generation, as a percentage of total power output in the U.S., declined steadily to 39% at the end of 2011 from about 51% in 2002, while generation from natural gas–fired combined cycle plants grew to more than 20% from 10% over the same period, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) said in late April, as it released its annual assessment for U.S. energy markets.
-
O&M
Managing the Catalysts of a Combustion Turbine Fleet
Natural gas–fired fleets comprising diverse turbine unit types are operating their units more these days because of the historic low price of natural gas. With increased operating hours, fleet owners are challenged to find the best ways to manage their SCR catalyst systems.
-
Gas
An “Exploding Lake” Becomes a Power Source
Rwanda’s Lake Kivu has a nickname: “Killer Lake.” The shimmering 1,040–square mile body of freshwater on the western branch of the Great East African Rift that straddles the Democratic Republic of Congo and Rwanda has had a bloody history. Not only was it the site of atrocity during the 1994 Rwandan genocide, but scientists say that it is also one of three known “exploding lakes.”
-
Waste to Energy
Has Boiler MACT Improved the Future for Biomass Power?
The impact of recently released air emissions regulations has stirred heated debate about forced coal plant closures and the possibility of reduced grid reliability in some regions. Biomass power may be an unexpected beneficiary of the new rules.
-
Water
Clever “Helper” Tower Solves Cooling Water Dilemma
Gone are the days when ocean or river water for once-through cooling of a new power plant was assumed to be available. Today, more than 500 fossil-fueled and 38 nuclear plants use once-through cooling. However, regulators in several states are aggressively pushing what is essentially a ban on the use of once-through water cooling, forcing a conversion to closed-cycle cooling.
-
Coal
FirstEnergy, AEP, and GenOn Continue Trimming Coal-Fired Fleet Size
FirstEnergy Corp., AEP, and GenOn have all announced coal-fired plant closures, totaling over 13 GW, caused by the recently finalized Mercury and Air Toxics Standards.
-
Coal
EPA to Keep Thresholds in Step 3 of Tailoring Rule for GHG Permits
A proposed rule issued in late February by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) will not change the greenhouse gas (GHG) permitting thresholds for the Prevention of Significant Deterioration (PSD) and Title V Operating Permit programs. However, it includes revisions to the permitting program that would provide some flexibility in how compliance is achieved with GHG emission caps.
-
Coal
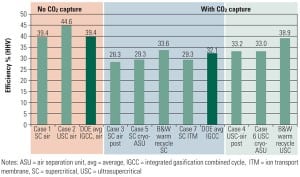
Design Features of Advanced Ultrasupercritical Plants, Part I
Advanced ultrasupercritical (A-USC) is a term used to designate a coal-fired power plant design with the inlet steam temperature to the turbine at 700C to 760C. In Part I of a three-part report, we introduce the A-USC boiler. Future reports will discuss the metallurgical and boiler design challenges.
-
Coal
Coping with Coal Dust
Plants can no longer sweep coal dust under the rug and ignore the health and safety hazard it presents, because a single spark can cause a dust explosion that could put a plant out of service, perhaps permanently. Managing dust in a power plant begins with good housekeeping, followed by retrofits using properly designed equipment.