Coal
-
Coal
Gas Taxes: Carbon Taxes Around The World
A supplement to “The Big Picture: Gas Taxes” in our January 2012 issue.
-
Coal
Restructuring the South African Power Industry
South Africa is at a critical turning point. An uncertain environment for private investment, escalating electricity prices, and a lack of available power threaten South Africa’s position as an attractive investment destination for many of the country’s most important industries. Power has been placed at the forefront of the government’s agenda, but South Africa needs a collaborative effort to meet the country’s energy demands and diversify its generation portfolio in order to drive economic growth.
-
O&M
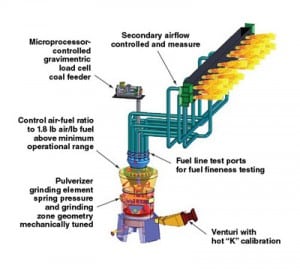
Pulverizers 101: Part III
Pulverizers prepare raw fuel for burning by grinding it to a desired fineness and mixing it with the just the right amount of air before sending the mixture to boiler burners for combustion. Part I of this three-part report examined the essentials of pulverizer design and performance; Part II discussed the importance of fuel fineness. This final article discusses the importance of air and fuel measurement.
-
O&M
Improved Performance from Priority-Based Intelligent Sootblower Systems
When sootblower operation frequency is too high, a plant risks losing power generation from tube leaks; but when sootblower frequency is too low, there is a risk of boiler pluggage. Intelligent sootblowing finds the right balance between tube erosion and plant economic operation.
-
Coal
EPA Moves Forward with GHG Regulations for Power Plants
The EPA’s proposed rules on limiting greenhouse gas emissions from new, modified, and existing power plants has taken another step forward.
-
Coal
California Adopts Final Cap-and-Trade Regulation
After three years of development, dozens of public workshops, and hundreds of meetings with stakeholders, the California Air Resources Board (ARB) on Oct. 20 adopted a final rule to cap California’s greenhouse gas emissions and put a price on carbon. The cap-and-trade program starts in 2013 for electric utilities and large industrial facilities.
-
Coal
Consultancy Group Downgrades Coal Plant Retirement Projections
ICF International, a consultancy group that earlier this year had predicted 68 GW of coal-fired power plants could retire by 2030 as a result of finalized and proposed regulations from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), downgraded its retirement projections to 50 GW this fall.
-
Coal
UK Pulls Funding for Flagship Longannet CCS Demonstration
Ditching the only project remaining in its £1 billion ($1.60 billion) carbon capture and storage (CCS) competition, the UK government declined to back the much-watched CCS project at the Longannet power station in Fife, Scotland, in October. The decision balances the UK’s low-carbon ambition with the need to ensure that taxpayer money is invested in “the most effective way,” the nation’s Department of Energy and Climate Change said. The funds are now expected be used to “pursue other projects” in both Scotland and England.
-
O&M
Wet Booster Fans Optimize Power Station Performance with FGD and Wet Stack
A Romanian lignite-fired power station wanted to minimize the operating cost of the flue gas desulfurization (FGD) system by placing the booster fans in the "wet position," between the wet FGD scrubber and the wet stack, where they would consume significantly less power. A number of combined environmental effects must be considered in this design.
-
O&M
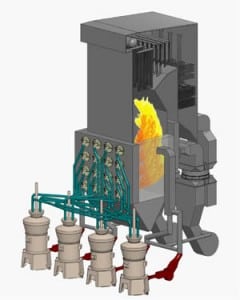
JEA Increases Power Output Through CFB Improvements
JEA’s Northside Generating Station in Jacksonville, Fla., Units 1 and 2 were built in 1966 and 1972, respectively, although the Unit 2 boiler had not operated since 1983. Both were heavy oil– and natural gas–fired steam units rated at about 300 MW. The utility “repowered” those two units by removing the old boilers and adding new circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers (Figure 1) that entered service in 2002. At that time, they were the world’s two largest CFBs, and the plant won POWER’ s Plant of the Year Award.
-
Coal
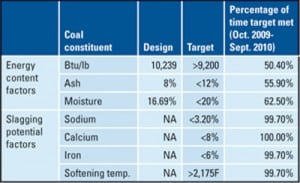
Top Plant: Coffeen Energy Center, Montgomery County, Illinois
Situated in predominantly rural central Illinois, the 1,000-MW Coffeen Energy Center has installed a number of controls in recent years and achieved significant environmental performance. For example, in 2010 a new scrubber facility was added that reduces SO2 from combustion gases coming from the plant’s two coal-fired boilers. The plant personnel’s continuing commitment to protecting the environment helps to promote a strong relationship between the plant and the local community.
-
Coal
Top Plant: J.K. Spruce 2, Calaveras Power Station, San Antonio, Texas
CPS Energy, the largest municipally owned utility in the U.S. providing both natural gas and electric service, implemented an energy plan in 2003 that required energy conservation measures, use of available renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, and additional coal-fired generation. The $1 billion 750-MW Spruce 2 fits into that plan by being one of the cleanest coal-fired plants in the country.
-
Coal
Top Plant: John Twitty Energy Center Unit 2, Springfield, Missouri
Utilities of Springfield elected to add a 300-MW coal-fired plant to its fleet to meet rising demand for electricity. It was the first coal plant constructed by the utility since 1976. An extremely competitive construction market required the utility to adopt new contracting practices to meet a tight project schedule, an approach that proved very successful. The $555 million plant commissioned in January 2011 is expected to cover system growth at least through 2024.
-
Coal
Top Plant: Masinloc Power Plant, Zambales Province, Philippines
In April 2008, AES Philippines purchased the Masinloc coal-fired power plant in Zambales Province in the Luzon region. Originally constructed in 1998 as a two-unit, 600-MW plant, the facility uses coal from a variety of sources in the Pacific Rim. After AES finished overhauling much of its equipment, the expanded 660-MW (gross) plant’s availability increased from 48% to 74%, which enabled net electricity production to jump by 129% by 2010.
-
Coal
Top Plant: Plum Point Energy Station Mississippi County, Arkansas
The new 665-MW Plum Point Energy Station is energizing the Arkansas Delta, an area that is ready to supplement its farming heritage by promoting new jobs that offer residents a higher standard of living. But first, the plant’s construction team had to overcome a number of significant challenges related to building a facility in the New Madrid fault zone.
-
O&M
Enhanced Capture of Mercury Using Unique Baghouse Filter Media
Several states have already instituted mercury emission limits in expectation of tightening mercury emission rules that will require reductions of up to 91%. Coal-fired plants searching for an economical way to meet the new limits may need to look no further than replacing their baghouse filter elements.
-
Coal
Top Plant: St. Johns River Power Park, Jacksonville, Florida
A recent NOx reduction project added selective catalytic reduction equipment to each of the two 640-MW, mixed coal–fired units at the St. Johns River Power Park. The selection of precisely the right catalyst required extensive long-term testing with “mini” reactors. Once the right catalyst formula was identified, the actual retrofit project was completed in a mere 23 months, an aggressive project schedule that required overcoming many design and construction challenges.
-
Coal
Luminant, AEP to Mothball Coal Units, Implement Derates on CSAPR Compliance Concerns
Dallas-based Luminant, Texas’ largest power generator, on September 9 filed a legal challenge against the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) Cross State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) but said the newly finalized rule that will require generators to dramatically reduce sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions from power plants had forced it to idle two coal-fired units and reduce capacity at three other units. This decision follows a similar decision made by American Electric Power to shutter 6GW of coal-fired plants in June.
-
Coal
CWA 316(b) Update: Fish Guidance and Protection
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has proposed new Clean Water Act section 316(b) regulations for once-through cooling water intake structures. Comments on the proposed rules closed in August, and a final rule is expected mid-2012. The EPA estimates that at least half of the power plants using once-through cooling will be required to implement a best technology available solution in coming years. That typically means barriers and screens, but you may want to consider other options.
-
Coal
EPA Indefinitely Delays Power Plant Greenhouse Gas Rules
Just two weeks after the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) withdrew its smog rule, the agency confirmed it would not meet a Sept. 30, 2011, deadline for issuing proposed New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) to limit greenhouse gas emissions from new, modified, and existing power plants. The agency did not specify a new deadline for proposing the rule.
-
Coal
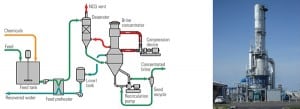
Fundamentals of Zero Liquid Discharge System Design
Power plants often produce wastewaters that contain salts, such as those from wet gas scrubbing, coal pile run-off, and leachate from gypsum stacks. Evaporation of those liquid wastes in a modern zero liquid discharge system produces clean water that is recycled into the plant plus a solid product suitable for landfill disposal. Here are the options to consider.
-
Coal
Obama Shelves Smog Rule on Concerns About Regulatory Burdens, Uncertainty
President Obama has scuttled the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA’s) smog rule, saying that he had underscored the importance of reducing regulatory burdens and uncertainty. The decision has dealt a blow to environmental groups—which are contemplating legal action—and won the Democratic president praise from Republicans and industry groups.
-
Legal & Regulatory
New EPA Rule Calls for Flexibility
Quin Shea, vice president, environment for the Edison Electric Institute, comments on the Utility MACT rule that is expected to be finalized in November.
-
O&M
Pulverizers 101: Part II
Pulverizers prepare the raw fuel by grinding it to a desired fineness and mixing it with the just the right amount of air before sending the mixture to boiler burners for combustion. In Part I of this three-part report, we examined the essentials of pulverizer design and performance. In the second part, we discuss the importance of fuel fineness. In the final article, we will discuss the importance of air and fuel measurement.
-
Coal
An SCR Can Provide Mercury Removal Co-Benefits
Complying with various state (and expected federal) requirements governing mercury removal from the stack gas of coal-fired power plants has usually been achieved by adding an expensive activated carbon injection system. Now there is another alternative: a catalyst that features higher mercury oxidization activity than conventional catalysts while maintaining the same SO2 to SO3 conversion activity—and all at a lower operating cost. Full-scale installations are under way at several Southern Company plants that burn a variety of coals.
-
O&M
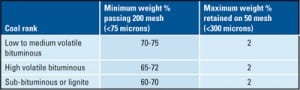
Improved Coal Fineness Improves Performance, Reduces Emissions
Utilizing engineering ingenuity and today’s developing computational fluid dynamics tools, a new classifier design is now available that significantly improves fineness from pulverizers without the heavy costs associated with dynamic classification or any downsides on pulverizer capacities, maintenance, and parasitic power. Instead, operational flexibility and improved emission control options are enhanced.
-
Coal
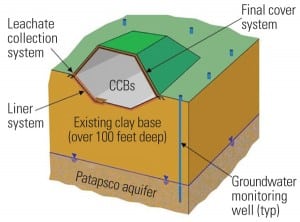
Constructing Maryland’s First Permitted Landfill for Coal Combustion By-products
Constellation Power Source Generation Inc., which owns and operates three coal-fired power plants in Maryland, has contracted with Charah Inc., an ash management company, to build a landfill to strict environmental requirements for the disposal of its plants’ coal combustion by-products that can’t be recycled for other uses.
-
Commentary
Shaping America’s Energy Policy
America’s energy and environmental policies have been dysfunctional for decades. Obsessively moving toward “green” has made America weaker and has damaged our economy. During POWER’ s first 100 years (1882–1982), the magazine chronicled the U.S. growing into the strongest industrialized economy in the world. America designed and built products for the world using raw materials and energy from within our own borders. Now we are in a recession and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) “War on Coal” continues. Does anyone get the connection? Ever-worsening regulations are killing jobs by the thousands.
-
Coal
U.S. Coal-Fired Power Development: Full Employment for the Lawyers
The EPA began rolling out its long-anticipated power plant regulations this year, causing some utilities to shutter some older coal-fired plants. Other utilities paused, perhaps hoping that a neighbor’s closure decisions would allow continued operation of some of their own older, smaller, less-efficient plants. As the nation sweated through a scorching summer, air conditioners hummed thanks to coal-fired power plants built 50 or more years ago. How many of them will be retired, and over what timeframe?
-
O&M
BIG PICTURE: Lights Out (Web Supplement)
A web supplement to the September issue with details of global power shortages.