Coal
-
Coal
EIA: Gas and Coal to Remain Competitive Through 2040
Despite the challenge of burgeoning gas supplies and sustained lower prices, the EIA projects that coal and gas generation will continue jockeying for the lead in the dispatch order for the next few decades. -
Coal
Australia’s New Energy Paradigm
Investments into Australia’s power sector enable the industry to meet the collective goal of becoming a cleaner, greener nation. Download the report.
-
O&M
LADWP Harnesses LMS100 to Solve Once-Through Cooling Dilemma
Los Angeles sits alongside the world’s largest body of water, and naturally the city’s Department of Water & Power (LADWP) placed its generating stations along the shoreline to take advantage of that abundant resource for cooling. The LADWP built three coastal generating stations that provide the city with 2,162 MW, about 35% of the peak annual demand.
-
Coal
D.C. Court Dismisses Sunflower Appeal of Suit Delaying Holcomb Plant
The D.C. Circuit Court on Tuesday dismissed an appeal by Sunflower Electric Power Corp. of a ruling requiring environmental review of Sunflower’s proposed 875-MW coal-fired power plant in Holcomb, Kansas.
-
Coal
Leadership Changes at Mississippi Power as Kemper IGCC Cost Overruns Soar
Cost overruns of nearly $1 billion to build the 582-MW Kemper integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) plant in Kemper County, Miss., were underscored on Monday as Mississippi Power’s Board of Directors took the dramatic step of replacing the Southern Co. subsidiary’s leadership.
-
Coal
CBO: Carbon Tax Could Be Costly to Economy but Generate Trillions, Avert Climate Change Effects
A carbon tax or cap-and-trade programs could raise trillions of dollars within the first 10 years of their enactment and avert climate change effects, but without accounting for how these revenues will be used, they could take a toll on the U.S. economy, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) says in a report released on Tuesday.
-
Coal
AES Corp. to Retire 990 MW of Coal Capacity on Environmental Rule Concerns
AES Corp.’s subsidiary Dayton Power & Light (DP&L) plans to retire six coal-fired units representing about 390 MW at its 414-MW Hutchings coal-, gas-, and oil-fired plant in Miamisburg, Ohio, by June 2015 as a result of existing and expected environmental regulations, including the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS). The news comes on the heels of Indianapolis Power & Light Co.’s (IPL’s) announcement that it plans to retire 600 MW of coal-fired capacity to comply with environmental rules.
-
Coal
WTO Body Confirms Ontario’s Local Content Rules for Renewables Are Discriminatory
Domestic content requirements that require some generators to source up to 60% of equipment from the Canadian province of Ontario under its feed-in-tariff (FIT) program are inconsistent with international trade rules, officials from the World Trade Organization’s (WTO’s) highest court said on Monday.
-
Coal
Hearing Panelists Assess Grid Reliability Challenges Posed by Nat. Gas, Renewables
Panelists at a House hearing today refuted varied claims concerning if and how increased natural gas and renewables generation pose widespread challenges to the reliability of the electric grid. Some pointed to ineffective rules in the restructured wholesale power market and the failure of conventional power plants as being more of a threat to grid reliability.
-
Coal
Oregon Utility Weighs Gas Power Options as Coal Exports Loom
It’s not all coffee and hydropower in the Northwest, as Oregon’s largest utility looks toward natural gas to help it navigate the shifting shoals of regulation and renewable mandates. -
Coal
Summer Power Burn: Are Generators Headed Back to Coal?
Last year’s stampede toward gas in the power sector is moderating for 2013, as higher gas prices cut into the economic incentives supporting coal-to-gas switching.
-
Coal
Navajo Nation Signs New Navajo Station Lease
Navajo Nation President Ben Shelly signed a land lease extension on April 30 for the 2,250-MW Navajo Generating Station, but not before adding several amendments to the agreement. The early lease renewal with the Navajo Nation must be in place before plant owners could consider making future investment in expensive new air quality control equipment.
-
Coal
Power Sector Is Critically Vulnerable to Drought, Hearing Panel Testifies
Drought is a serious vulnerability for the power sector, witnesses testified at a full committee hearing held last week in the Senate to assess the impacts of drought on the power and water sectors. Members of the panel invited by the Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources offered a number of possible solutions for federal agencies and power companies that could mitigate adverse effects from drought.
-
Coal
India’s First Coal Mine–Integrated Supercritical Plant Synchronized
India’s Reliance Power in March synchronized the first of six 660-MW units of its Sasan Ultra Mega Power Plant (UMPP) in the state of Madhya Pradesh, readying it to supply power to 14 distribution companies across seven states. The plant (Figure 1) has been hailed as India’s first supercritical project to integrate a coal mine—an important achievement in a country that is battling chronic coal shortages. Though India has large coal reserves, domestic mining companies are struggling to keep up with demand needed to sustain its existing coal plants, which account for 55% of its generation.
-
O&M
Performance-Driven Maintenance
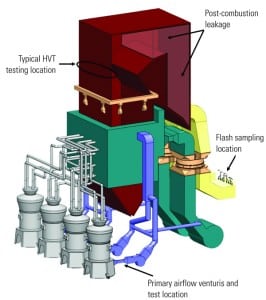
My career began as a results engineer testing large utility boilers. Ever since that first assignment, I have remained interested in the details of how the measurement and control of the furnace fuel and air inputs can make a huge difference in overall boiler performance. Given that plant operations and maintenance (O&M) budgets are slimmer today than in recent memory, my experience is that targeted performance testing can provide important feedback for prioritizing maintenance expenditures. The combination of plant testing and targeted O&M expenditures provide the best opportunity for efficient and reliable plant operations. I call this approach to plant efficiency improvement “performance-driven maintenace.”
-
Coal
Ontario Goes Coal-Free in a Decade
By the end of 2013, one year ahead of its goal, the province of Ontario will be virtually coal-free—a first for a North American jurisdiction. How did the most populous part of Canada go from 25% to 0% coal-fired generation in just a decade, and what does this phaseout mean for the rest of the world?
-
Coal
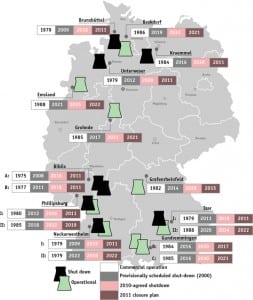
Germany’s Energy Transition Experiment
Germany has chosen to transform its energy system within a few decades—an ambition that has evoked equal admiration and confusion. Has Europe’s largest economy embarked on a rational path to an energy future that will make it the bellwether for global acceptance of renewables, or will the complex array of current challenges encumber its grand transformation?
-
Coal
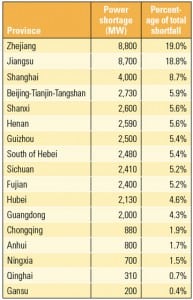
China Wrestles with Power Shortages
China has gone through three periods of nationwide power shortages since 1978. The previous two shortages were mostly caused by the lack of installed generation capacity. However, the third—which has severely restricted economic development—is a consequence of institutional problems that must be corrected.
-
Coal
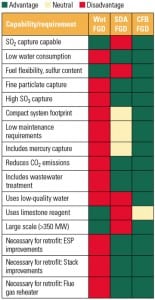
CFB Scrubbing: A Flexible Multipollutant Technology
The number of regulated air emission constituents is increasing while the acceptable amounts for release are decreasing. In the long run, picking the most flexible multipollutant technology is surely the least cost option.
-
Coal
Settlement Between Feds, Wisconsin Utilities Mandate More Coal-Plant Retirements
A settlement between the federal government, the Sierra Club, and Wisconsin Power and Light Co. (WPL) on Monday could require the Madison-based Alliant Energy subsidiary and other defendants to invest more than $1 billion in pollution controls and retire and refuel at least four units at three Wisconsin coal-fired power plants to resolve alleged Clean Air Act New Source Review violations.
-
Coal
EPA Proposes Revisions to Steam Electric Power Plant Effluent Guidelines
Revisions proposed on Friday by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to technology-based effluent limitations guidelines and standards could set the first federal limits on the levels of toxic metals in wastewater discharges from steam electric power plants. The proposed rule would help reduce pollutants in U.S. waterways from coal ash, air pollution control waste, and other power plant waste, but they could come at a cost of between $185.2 million to nearly $1 billion a year, the agency said.
-
Coal
Lawmakers Push for Financing Parity for Renewable Projects
Bipartisan legislation introduced on Wednesday by a bicameral group of lawmakers seeks to give renewable energy project investors access to an existing corporate structure whose tax benefits are now only available to investors in fossil fuel–based energy projects.
-
Coal
EPA Nominee Says Environmental Protection Is a Nonpartisan Issue
Gina McCarthy, who has served for the past four years as assistant administrator for the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Office of Air and Radiation, responded to questions from a Senate committee on April 11 in a hearing on her nomination to become the next administrator of the EPA.
-
Coal
EPA Delays GHG Emissions Decision and Adds to FutureGen Challenges
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) deadline for placing greenhouse gas (GHG) emission limits on new fossil-fueled power plants has come and gone. Comments from EPA staff indicate little urgency in setting a new deadline. Meanwhile, prospects for FutureGen 2.0, originally developed with GHG limits in mind, are looking bleaker.
-
Coal
IEA: Carbon Mitigation Efforts Have Stalled Despite Rapid Renewables Expansion
The carbon intensity of the global energy supply has barely budged in more than two decades despite otherwise successful efforts in deploying renewable energy, the International Energy Agency (IEA) warns in an annual report submitted to the Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) on Wednesday.
-
Coal
EIA Projects Coal Generation Gains Due to Increasing Gas Prices
The increasing cost of natural gas relative to coal is expected to increase coal’s share of total generation from 37.4% in 2012 to 39.9% in 2013, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) April release of its Short-Term Energy Outlook (STEO). Though that would leave coal’s percentage below its 42.3% share in 2011, it indicates that gas may not be on an inevitable path to overtake a significantly greater share of the generation pie.
-
Coal
Polish Coal Plant Scrapped, Renewable Subsidies Adjusted
Polish utility PGE scrapped plans to build two 900-MW coal-fired power units worth $3.6 billion at a plant near the southwestern city of Opole, citing falling electricity prices and weak demand.
-
Coal
DOE Nominee Moniz Gets Bipartisan Support in Senate Hearing
Dr. Ernest Moniz, President Obama’s nominee for the next Secretary of Energy, appears poised for easy confirmation after responding to questions from the Senate Energy & Natural Resources Committee on April 9. His remarks indicated support for, among other things, small modular reactors, carbon capture technology research, and moving forward with the recommendations of the Blue Ribbon Commission on America’s Nuclear Future.
-
Coal
Proposed 2014 Budget: More Funds for the DOE, Less for the EPA
The proposed 2014 federal budget that President Obama submitted to Congress on Wednesday includes increases for the Department of Energy in general and for DOE-sponsored research and development (R&D) in particular. It also shows a slight decrease in funding for the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
-
Coal
EPA Updates MATS for Power Plants
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on March 28 finalized updates to emission limits for new power plants under the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS). The rule includes emission limits for mercury, particulate matter (PM), sulfur dioxide (SO2), acid gases, and certain individual metals.