Coal
-
Coal
EPA Extends Deadline for Four Corners Decision as Ariz. Re-Examines Deregulation
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) last week gave Arizona Public Service Co. (APS) six more months to decide on the future of its 2-GW coal-fired Four Corners Power Plant near Farmington, N.M., recognizing "uncertainties" posed by Arizona’s recent move to consider deregulation of the state’s electric sector.
-
Coal
Binz to Be Nominated for FERC Chairman Position (Updated)
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) said on June 27 that President Barack Obama has announced his intent to nominate Ronald Binz as FERC commissioner. It had been widely anticipated that Binz would be named the new chair of the regulatory body.
-
Coal
EPA Settles with Deseret to the Tune of $35,000
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced a Clean Air Act settlement with Utah-based Deseret Generation & Transmission Co-operative (Deseret) resolving alleged violations at the coal-fired Bonanza Power Plant.
-
Coal
DOE to Offer Up to $8B in Loan Guarantees for Advanced Fossil Energy Projects
Last week, the Department of Energy (DOE) announced a draft loan guarantee solicitation for “innovative and advanced” fossil energy projects that “substantially reduce greenhouse gas and other air pollution.”
-
Coal
FirstEnergy to Shutter 2 GW of More Coal Capacity on MATS Cost Concerns
FirstEnergy Corp. plans to shutter two coal-fired power plants in Pennsylvania this fall—a total capacity of 2,080 MW—citing high costs of compliance with current and future environmental rules and a "continued low market price for electricity."
-
Coal
Hawaii Power Companies to Deactivate Oil Plants, Ramp Up Renewables
Three Hawaiian power companies plan to deactivate a total of 226 MW of oil-fired generating units, convert remaining baseload plants to cycling duty, and substantially ramp up use of renewables by 2016.
-
O&M
The Case for Utility Boiler Fuel Delivery System Upgrades
A vital part of any coal-fired unit is its fuel delivery system (FDS). A newly formed subcommittee of the ASME Research Committee on Energy, Environment, and Waste has investigated potential FDS upgrades on three typical 500-MW wall-, tangential-, and cyclone-fired boilers. The subcommittee has produced a series of suggested upgrades that have a simple payback of no more than two years.
-
Coal
Gas-Electric Integration “Swamps” All Other Issues
Panelists at the ELECTRIC POWER 2013 Keynote and Roundtable Discussion in Chicago in May were consumed by the need to ensure future reliability by more closely integrating the gas and electricity markets. Acknowledged less directly were distortions created by renewable energy subsidies and mandates, onerous regulations affecting coal, and “irreversible” demand destruction caused by the success of energy efficiency and demand management programs. The elephant in the room was the continued demise of electricity markets.
-
Coal
THE BIG PICTURE: Parched
Water scarcity as it relates to energy use is becoming a major concern.
-
Coal
Water Issues Challenge Power Generators
Drought and competing uses for water continue to challenge power plant operators worldwide. In response, innovative approaches for reducing water use are being explored from South Africa to China.
-
Coal
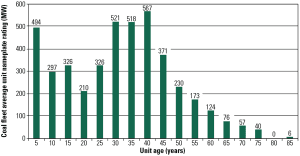
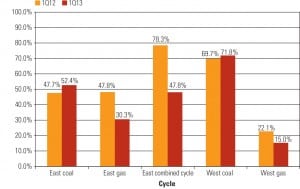
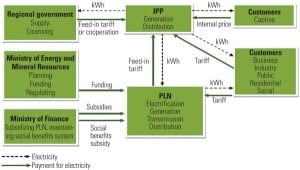
Indonesia: Energy Rich and Electricity Poor
Even though it enjoys sizeable coal and natural gas reserves, Indonesia struggles to provide electricity to its growing economy. Geography is its most obvious challenge. Others include evolving international markets and an energy sector that remains highly politicized.
-
Coal
Supreme Court Agrees to Review Vacated Cross-State Pollution Rule
The Supreme Court today granted a petition by health and environmental groups, 15 states, and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and agreed to review the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR), a Bush-era rule that a federal appeals court had previously vacated.
-
Coal
Your Guide to the White House Climate Action Plan
President Obama’s highly anticipated Climate Action Plan (CAP) released today outlines a wide variety of executive actions founded on three pillars: slashing U.S. carbon pollution through stringent rules for new and existing power plants while doubling renewables deployment and promoting fuel switching from coal to natural gas; preparing the U.S. for impacts of climate change; and leading international efforts to combat global climate change.
-
Coal
Obama: Climate Strategy to Be Driven by Natural Gas, Renewables
President Barack Obama’s landmark speech on Tuesday outlining executive actions to combat and prepare for climate change backed the growth of natural gas and renewable power in lieu of carbon-heavy coal power, but he mentioned nuclear power only once—and only in the context of energy security.
-
Coal
Reactions to Obama’s Climate Action Plan Swift and Varied
Amid the deluge of reactions to President Obama’s June 25 speech announcing wide-ranging executive actions to curb carbon emissions and prepare for climate change effects were some unexpected statements.
-
Coal
USGS: U.S. Has Massive Carbon Storage Capacity in Geologic Basins
The U.S. has least 3,000 metric gigatons (Gt) of subsurface carbon dioxide storage capacity that is technically accessible below onshore areas and state waters—500 times more than previously estimated—the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) suggests in a new assessment released on Wednesday.
-
Coal
Energy and Water Spending Bill Proceeds with Deep Cuts for Renewables, ARPA-E
The fiscal year 2014 Energy and Water Appropriations Bill released by the U.S. House Appropriations Committee this week slashes $1.4 billion in funding to Department of Energy renewable energy and scientific research programs, including an 80% spending cut on the Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (ARPA-E) program.
-
Coal
House Energy Committee Advances Coal Ash Bill, Hears Moniz Testimony
The House Energy and Commerce Committee on Wednesday advanced a set of four bills that it said would "improve" environmental regulations and increase state authority, including legislation that would task states—not the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)—with the responsibility to set up coal ash disposal rules.
-
Coal
Edwardsport IGCC Project Start Marks Delayed, Costly Milestone for Coal Generation
Duke Energy’s long-awaited but controversial and cost-overrun-plagued integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) coal plant began commercial operation on June 7 in Knox County, Ind.
-
Coal
SCANA Delays New Reactor Startup, Accelerates Coal Plant Retirements
South Carolina Electric & Gas (SCE&G) last week announced that startup of the $6.3 billion nuclear extension under construction at its V.C. Summer plant could be delayed by up to a year owing to delivery issues. The SCANA Corp. subsidiary, which last year identified six coal-fired units that would be retired or switched to natural gas to comply with looming Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS), also said it plans to accelerate retirement of two units by the end of this year.
-
Coal
CRS Report: U.S. Energy Policy Debate Centers on Energy Security, Costs, and Environment
A report recently released by the Congressional Research Service (CRS) identifies policy goals—and their fundamental differences—identified in the 2012 presidential election and as highlighted in recent energy-related legislation. Among the nation’s energy priorities are to stabilize oil and gas markets, create natural gas pipeline infrastructure, dispose of nuclear radioactive waste, and replace conventional energy resources with renewables.
-
Coal
FERC Staff: Coal Generation Could See Comeback on Pricier Natural Gas This Summer
A much greater coal power burn is expected this summer in reaction to an anticipated rebound in natural gas prices, suggests a recent reliability assessment from staff at the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC). Among other key aspects of the new report is that while electric reliability for the rest of the nation will be adequate, Texas could see a significant chance of an energy emergency.
-
Coal
New Version of Coal Ash Legislation Introduced in the House
A new version of coal ash legislation introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives on Monday sets minimum federal standards for coal residuals from coal-fired power plants, but it gives states—not the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)—responsibility for crafting their own permit programs.
-
Coal
Coal-Heavy Indianapolis Getting a New Combined Cycle Plant
Faced with the need to upgrade its aging fleet, Indianapolis Power & Light is retiring a brace of coal-fired units and replacing them with a new combined cycle plant. -
Coal
EIA: Gas and Coal to Remain Competitive Through 2040
Despite the challenge of burgeoning gas supplies and sustained lower prices, the EIA projects that coal and gas generation will continue jockeying for the lead in the dispatch order for the next few decades. -
Coal
EIA Releases State-by-State Report on Energy-Related CO2 Emissions
In a report released on May 13, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) presents data on energy-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions for each state by year, fuel, sector, and other breakouts for the years 2000 through 2010.
-
Coal
AES Corp. to Retire 990 MW of Coal Capacity on Environmental Rule Concerns
AES Corp.’s subsidiary Dayton Power & Light (DP&L) plans to retire six coal-fired units representing about 390 MW at its 414-MW Hutchings coal-, gas-, and oil-fired plant in Miamisburg, Ohio, by June 2015 as a result of existing and expected environmental regulations, including the Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS). The news comes on the heels of Indianapolis Power & Light Co.’s (IPL’s) announcement that it plans to retire 600 MW of coal-fired capacity to comply with environmental rules.
-
Coal
Leadership Changes at Mississippi Power as Kemper IGCC Cost Overruns Soar
Cost overruns of nearly $1 billion to build the 582-MW Kemper integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC) plant in Kemper County, Miss., were underscored on May 20 as Mississippi Power’s Board of Directors took the dramatic step of replacing the Southern Co. subsidiary’s leadership.
-
O&M
Fire Protection Guidelines for Handling and Storing PRB Coal
Operators familiar with the unique requirements of burning Powder River Basin (PRB) coal will tell you that it’s not a case of “if” you will have a PRB coal fire, it’s “when.”
-
O&M
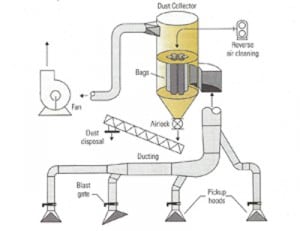
Give Your Plant a Dust Control Tune-Up
Every piece of equipment that transports or processes coal creates some level of particulate matter. Having a strategy for coal dust management in your plant is essential.