Coal
-
Coal
Globalization: The new millennium’s "invisible hand"
Participants in the CEO Roundtable at Electric Power 2006 raised a plethora of issues affecting decisions on future electric power generation. Representing a cross section of power producers, the industry leaders made clear that, although globalization has lost its luster in the power generation sector, its impact on the domestic industry remains profound. Ten years […]
-
Coal
Safety still Job No. 1 for PRB users
If coal is to be “America’s energy future” (see p. 42), the work of the Powder River Basin Coal Users’ Group (PRBCUG) will have a lot to do with making it so. Since 1999, the PRBCUG (see sidebar) has fostered the safe, efficient, and cost-effective use of the fuel as it watched its membership swell […]
-
Coal
Cover Story: Coal-fired Electric Power Capacity Continues to Increase
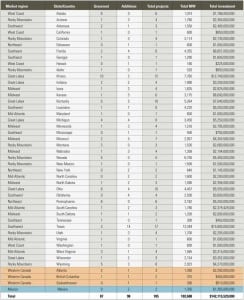
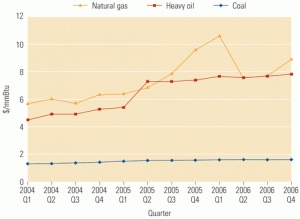
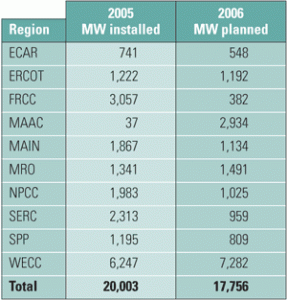
In the U.S. electric power industry, coal is making a comeback as a fuel of choice for new generation projects. During the construction boom that occurred from 1999 to 2003 about 90% of new electric generation utilized natural gas – fired combustion turbines. Unfortunately, over the past few years natural gas supplies have tightened and […]
-
Coal
Editorial: Industrial Perspectives
Is the U.S. supply of coal sufficient to meet the increased demand for coal-fired generation? With the increasing demand for coal to generate electricity, the big question is, How reliable is the supply and transportation of the fuel? Currently, Industrial Info Resources (IIR) is tracking 185 new coal-fired power projects, and if all were to […]
-
O&M
Projects
Kansas City Power & Light Installing SCR at La Cygne Generating Station Kansas City Power & Light (KCP&L), a subsidiary of Great Plains Energy, has awarded The Babcock & Wilcox Company (B&W) a contract for the installation of new emissions control equipment on Unit 1 at its La Cygne Generating Station. When completed, the selective […]
-
Coal
Pollution-Control Technologies: Multi-Pollutant Removal Systems Are a Clean Coal Technology
The first power plants were built about 130 years ago. Coal was then, and is still today, the major fuel used for power generation. Currently, about 1,400 pulverized coal – fired units, with an average age of more than 30 years, generate over 50% of U.S. electric power. The use of low-sulfur coal and improved […]
-
O&M
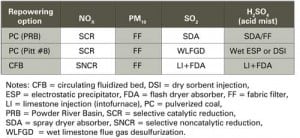
Project Planning: Repowering or Replacement: What Is the Solution?
Between 1998 and 2002 the U.S. experienced an unprecedented power plant construction boom that consisted mostly of gas-fired, combustion turbine – based power plants. This surge in power plant construction had several driving forces, including electric power deregulation, the emergence of non-utility power producers, a sustained period of plentiful and inexpensive natural gas, and the […]
-
Coal
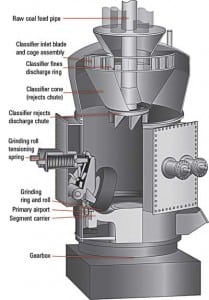
Case Histories: Pulverizer Upgrades Are Reducing Fuel Costs
St. Johns River Power Park (SJRPP) is a two-boiler, 2 x 660-MW station jointly owned by JEA (formerly Jacksonville Electric Authority) and Florida Power & Light (FPL). JEA is the plant operator. The Foster Wheeler boilers went into commercial operation in 1987 and 1988. Each boiler has seven OEM vertical spindle pulverizers (mills) and 28 […]
-
Coal
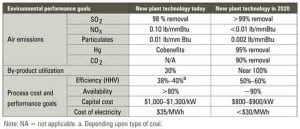
Clean Coal: Clean Coal Technology Is Not an Oxymoron
In the late 1980s, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), in conjunction with industry and state agencies, started the Clean Coal Technology (CCT) program. The aim of the CCT program was to develop technologies, increase efficiency, and reduce the environmental effects of burning coal in power plants. Today, pollution controls for new and existing plants […]
-
Coal
Coal Users Community: Capitalizing on Coal: The Challenges and Opportunities
Demand for energy in America continues to grow. So too does the challenge of generating it in a reliable, affordable, and an environmentally sensitive manner. Given the U.S.’s abundant coal reserves, the nation’s electric utilities are pursuing a variety of strategies to keep coal a key fuel source for generating electricity. Developing Technologies One approach […]
-
Coal
Coal Users Community: NCTA helping to resolve coal transportation infrastructure problems
The Mission of the National Coal Transportation Association (NCTA) is to provide education and facilitation for the resolution of coal transportation issues in order to serve the needs of the general public, industry, and all modes of transportation. This is accomplished through the sponsoring of educational forums and by providing opportunities for the lawful exchange […]
-
Coal
Controls: Building the Digital Power Plant of the Future
History has shown that the proper deployment of automation on new construction projects can make the difference between a moderate performer and an industry-leading unit, between average financial results and accelerated profitability. Given the magnitude of a new coal-fired plant construction project, automation is often viewed as just one of the many components essential to […]
-
Coal
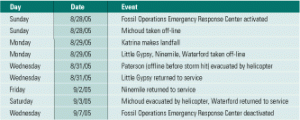
Preparation keyed Entergy’s responses to Katrina, Rita
With the 2006 hurricane season about to begin, climatologists are predicting that the Atlantic Ocean will spawn 17 “named” storms this summer and fall, with 9 categorized as hurricanes and 5 expected to be “intense.” Whether or not your plant lies in a vulnerable coastal area, you’d do well to learn a few lessons from Entergy’s unique experience last year.
-
Coal
Curbing the blue plume: SO3 formation and mitigation
Understanding why stack emissions become opaque leads to better choices of systems for controlling SO3 and other pollutants, based on current and future plant operating configurations.
-
Coal
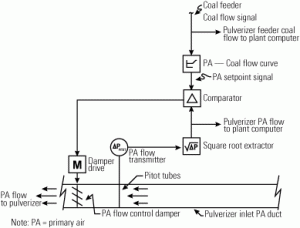
How accurate primary airflow measurements improve plant performance
Primary airflow has a major impact on the efficiency, capacity, and cleanliness of pulverized coal–fired generation. Inaccurate measurements that underestimate primary airflow levels can lead to negative operational outcomes that include increased boiler gas temperatures, flyash loss-on-ignition, excessive NOx emissions, and higher-than-necessary fan power consumption. We remind you how to avoid those headaches.
-
Coal
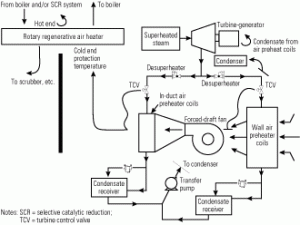
Designing and maintaining steam coil air preheaters for reliability and effectiveness
If engineered well and drained properly, a simple finned-tube heat exchanger can help maximize a fossil-fueled power plant’s combustion efficiency, capacity, and air pollution reduction. Use the guidelines in this article either to return a disabled steam coil air preheater to service or to improve the performance of a unit that may have been wasting […]
-
Coal
Big bucks for carbon sequestration
The California Energy Commission (CEC) recently awarded about $14 million for carbon sequestration projects to be overseen by the West Coast Regional Carbon Sequestration Partnership. Westcarb, as the partnership is known, is part of the U.S. DOE’s effort to deploy technologies through its Regional Carbon Sequestration Partnership (RCSP) program. New members Alberta and British Columbia […]
-
Coal
Why new U.S. supercritical units should consider T/P92 piping
T/P92 is being heralded as a superior and lower-cost alternative to T/P91 for new power plants with pressures above 3,600 psi and temperatures above 1,100F—such as the supercritical and ultra-supercritical units proposed to be built in the U.S. over the next few years. The switch from T/P91 to T/P92 would represent the next step in […]
-
Coal
Gas turbine "refueling" via IGCC
The jury is still out on the economic and technical feasibility of burning gasified coal to generate electricity. Gasification technology has yet to be proven on a utility scale, especially with Powder River Basin coal as the feedstock. And on the generation side, there are more questions than answers about the capital cost and availability of integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) plants. But with natural gas prices high and rising, it’s definitely worth examining whether it would be economically and technically feasible to convert the existing U.S. fleet of gas-fired combined-cycle plants to burn gasified coal.
-
-
Coal
Stressed merchant industry hopes for better days
The U.S. power generation industry is changing at warp speed, via regulatory changes, consolidation, mergers, and sales of assets at yard-sale prices. New players have entered the market and become major players overnight, while several mainstays have gone bankrupt. Though many of the latter blamed high gas prices for their woes, well-diversified merchants enjoyed a record year. Whatever changes are in store for the business of combined-cycle generation, you can be sure that innovations in plant design and O&M such as those described in this special section will keep pace with them.
-
Coal
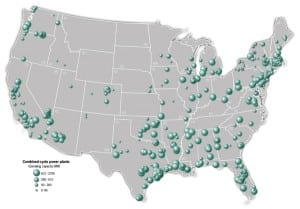
Map: Combined-cycle plants constitute about 20% of U.S. generating capacity
Copyright 2006 Platts, a Division of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. 800-PLATTS-8. Data Source: Platts Energy Advantage www.maps.platts.com
-
Coal
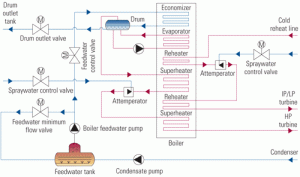
Designing HRSG desuperheaters for performance and reliability
Increased cycling of combined-cycle plants has made precise control of attemperator spray water within heat-recovery steam generators more important if damage to their hardware and piping is to be avoided. Complicating the issue is the industry’s still-limited experience with cycling and the fact that demands on the attemperator and turbine bypass of cycled plants are more stringent than those on baseloaded units.
-
Coal
Designing wet duct/stack systems for coal-fired plants
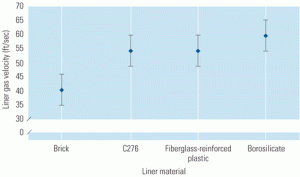
A multitude of variables must be accounted for during the design and development of a wet-stack flue gas desulfurization system. The five-phase process detailed below has proven effective on more than 60 wet-stack system design studies. A basic understanding of these concepts will help inform early design decisions and produce a system amenable to wet operation.
-
Coal
Constant and sliding-pressure options for new supercritical plants
Sliding-pressure, supercritical plants are all the rage. They generally include certain design features developed for markets and operating environments outside the U.S., where new coal-fired plants have been built in recent decades. U.S. market conditions are different, and considerable capital cost savings—with negligible operating cost differences—are possible if technology options are considered for the next wave of supercritical and ultra-supercritical steam plants.
-
Coal
CCPI bears first fruit
In 2002, the Bush administration launched the Clean Coal Power Initiative in the hope that it would develop the missing technology piece of the cleaner energy puzzle. Four years and two rounds later, the U.S. electric power industry is seeing the first usable clean coal technologies emerge before its eyes.
-
Coal
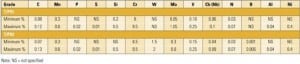
Estimating SCR installation costs
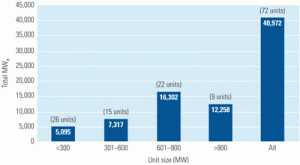
The EUCG surveyed 72 separate installations of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems at coal-fired units totaling 41 GW of capacity to identify the systems’ major cost drivers. The results, summarized in this article, provide excellent first-order estimates and guidance for utilities considering installing the downstream emissions-control technology.
-
Coal
Honduras’ big new oil-fired plant
The 267-MW Pavana III power plant (Figure 1) was officially inaugurated on January 28 by Honduran President Ricardo Maduro. It was built by Helsinki-based Wärtsilä Corp. for Tegucigalpa-based independent power producer (IPP) Luz y Fuerza de San Lorenzo S.A. (Lufussa). 1. From Finland to Central America. The new 267-MW Pavana III power plant […]