Latest
-
Nuclear
China Nuclear Plant Construction Gets Boost—With Technology Transfer
China’s nuclear power plant building spree got a little more frenzied this January, as the country kicked off its 21st project at Ningde 3.
-
Gas
Brazil Beings Operation of Ethanol Power Plant
Brazil’s state-owned oil producer, Petrobras, on Dec. 31, 2009, said it had inaugurated the world’s first power plant to run exclusively on ethanol.
-
Coal
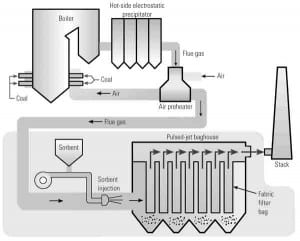
NETL, We Energies Successfully Complete TOXECON Demonstration
A three-year demonstration of the TOXECON process, a technology to reduce mercury emissions while increasing the collection efficiency of particulate matter (PM), was last year successfully completed at a Michigan coal power plant, the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Energy Technology Laboratory (NETL) reported in January.
-
Hydro
Ethiopia’s New Hydro Plant Boosts Region’s Generating Capacity
Ethiopia in mid-January officially inaugurated the 420-MW Gilgel Gibe II hydropower project, the second hydropower plant to be opened since November 2009, when the 300-MW Tekezé project began operations.
-
News
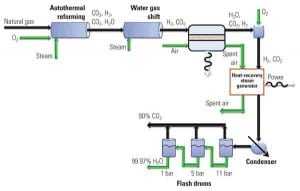
MIT Researchers Propose Solid Oxide Fuel Cells for Natural Gas Power
A new power generation system that uses solid oxide fuel cells in conjunction with natural gas and promises lower carbon emissions would not use any new technology, according to researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), but rather would combine existing components in a novel configuration.
-
O&M
Restraining Torsional Vibration
All rotating equipment power trains found in a power plant have some amount of vibration, usually caused by mechanical unbalance of the rotating system, shaft misalignment, or weakness in the bearing support.
-
Commentary
Copenhagen: The Case for Climate Adaptation
The U.S. Congress won’t pass anything that looks like a cap-and-trade or carbon tax approach to global warming anytime soon. What’s left? Adaptation, the low-tech, low-cost, slow-cooking, most-sensible policy approach.
-
Commentary
TREND: Water, Water Everywhere—But Not in the U.S.
Although hydro power in the U.S. is politically incorrect, even though it generates no greenhouse gases and is by far the largest renewable resource in the country’s generating mix, the rest of the world often has a more sanguine approach to using water to generate electricity. For example…
-
Finance
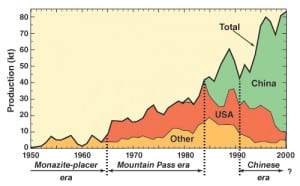
Rare Earth and Lithium Supplies Cloud Renewables
Ensuring an adequate supply of rare earth elements and minerals may be a hurdle in the renewable energy supply chain. The metals and their compounds are used in battery technologies, windmills, catalysts, and communications technologies. Add lithium (not a rare earth) to that mix, as Latin American politics could cloud the prospects for new lithium supplies.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Computing in the Clouds, Part II: It’s About Security
What do Gmail, YouTube, Twitter, and Facebook have in common? All are examples of cloud computing. All present serious data security challenges.