In This Issue
-
Gas
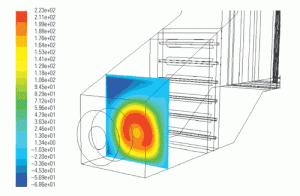
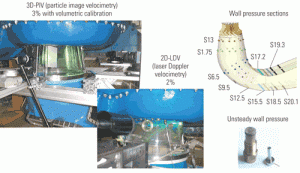
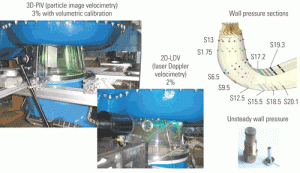
Fluid dynamics of the HRSG gas side
Designers of heat-recovery steam generators are using computational fluid dynamics software as one tool to reveal the invisible forces affecting the flow over, under, around, and through structures such as inlet ducts, distribution grids, and guide vanes.
-
Coal
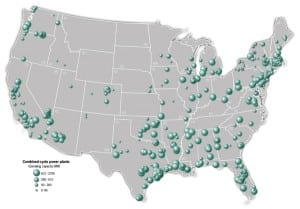
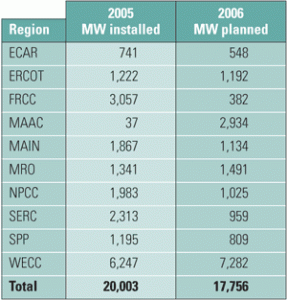
Map: Combined-cycle plants constitute about 20% of U.S. generating capacity
Copyright 2006 Platts, a Division of the McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved. 800-PLATTS-8. Data Source: Platts Energy Advantage www.maps.platts.com
-
Coal
Designing wet duct/stack systems for coal-fired plants
A multitude of variables must be accounted for during the design and development of a wet-stack flue gas desulfurization system. The five-phase process detailed below has proven effective on more than 60 wet-stack system design studies. A basic understanding of these concepts will help inform early design decisions and produce a system amenable to wet operation.
-
Coal
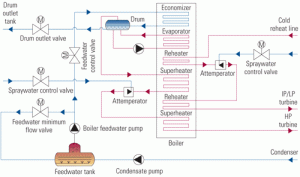
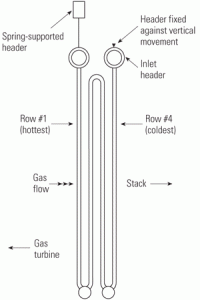
Designing HRSG desuperheaters for performance and reliability
Increased cycling of combined-cycle plants has made precise control of attemperator spray water within heat-recovery steam generators more important if damage to their hardware and piping is to be avoided. Complicating the issue is the industry’s still-limited experience with cycling and the fact that demands on the attemperator and turbine bypass of cycled plants are more stringent than those on baseloaded units.
-
-
Poor priorities
I couldn’t help but marvel at the synchronicity of two unrelated events over the past few weeks. The first, on January 12, was the rare cancellation of a major military acquisition program with problems called “too expensive to fix.” It takes an Act of Congress to kill most military contracts due to the pork flowing […]
-
-
Gas
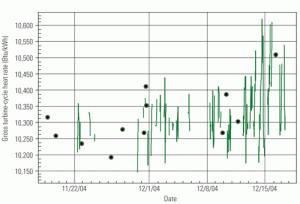
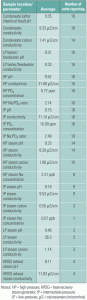
Fleetwide standardization of steam cycle chemistry
Nearly five years ago, a major IPP began standardizing steam cycle chemistry feed, control, and monitoring across its combined-cycle fleet. This article discusses the steps taken, the costs incurred, and the technical and financial benefits achieved. Although the project focused on non-cogeneration plants, the findings detailed below are broadly applicable to other kinds of plants. However, the specific implementations (especially of the chemistry standards) described may have to be modified slightly for application to cogen plants.
-
-
News
Poor Priorities
I couldn’t help but marvel at the synchronicity of two unrelated events over the past few weeks. The first, on January 12, was the rare cancellation of a major military acquisition program with problems called “too expensive to fix.” It takes an Act of Congress to kill most military contracts due to the pork flowing […]
-
Coal
Gas turbine "refueling" via IGCC
The jury is still out on the economic and technical feasibility of burning gasified coal to generate electricity. Gasification technology has yet to be proven on a utility scale, especially with Powder River Basin coal as the feedstock. And on the generation side, there are more questions than answers about the capital cost and availability of integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) plants. But with natural gas prices high and rising, it’s definitely worth examining whether it would be economically and technically feasible to convert the existing U.S. fleet of gas-fired combined-cycle plants to burn gasified coal.
-
News
Environmental quandary shuts Mohave plant
Southern California Edison (SCE, Rosemead, Calif.) closed the 1,580-MW coal-fired Mohave Generating Station in Laughlin, Nev., on December 31. In a filing with the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC), SCE said it expects the plant to remain off-line for four years—the time it will take for the utility and the plant’s other owners to battle […]
-
O&M
O&M staff keep their cool at Alaskan plant
Operating a combined-cycle power plant profitably is no walk in the park, even under ideal conditions. But the extreme conditions at the Beluga Power Plant—from isolation to volcanoes—challenge its staff every day in ways that operators in the lower 48 can only imagine.
-
News
Fluor completes Texas project
Fluor Corp. (Aliso Viejo, Calif.) has finished building and commissioning the 620-MW Jack County power plant (Figure 2) near Jacksboro, Texas, for Waco-based Brazos Electric Cooperative Inc. The natural gas–fired, combined-cycle plant officially came on-line on February 1. 2. Texas 2 x 1 step. The gas-fired, 620-MW, combined-cycle Jack County Generation Plant was built and […]
-
O&M
Include generators and exciters in your outage inspections
Generators and exciters don’t get much respect during scheduled outages. If yours fall into that category, a strategy that includes regular inspections and routine maintenance is all the more important for identifying incipient problems that could bring a plant down. Read on to learn how to keep your generator or exciter from suffering any of the problems shown in the dramatic photos.
-
News
Russia says "da" to floating nukes
The Russian Federation plans to start building a floating nuclear power plant this year. According to the country’s atomic energy agency (Rosatom), the first plant will be small (3 MW) but could lead to the development of offshore plants with capacities of several hundred megawatts. The pioneering plant will be sited off the coast of […]
-
-
News
Pearl Harbor cable links past, future
A new, mile-long submarine transmission cable in Pearl Harbor (Figure 3, p. 10) will facilitate the U.S. Navy’s plan to renovate and expand historic Ford Island. Honolulu-based Hawaiian Electric Co. Inc. (HECO) recently laid two new 46-kV lines beneath the bridge connecting the island to Oahu. The trickiest part of the installation was avoiding the […]
-
-
News
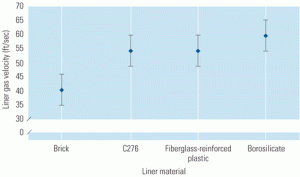
A breakthrough in hydroturbine design
One of the distinguishing characteristics of deregulated power markets is variable demand. The ability to operate efficiently at partial loads can determine whether a plant is profitable or not. This need creates special challenges for hydroelectric turbines, because at partial loads they often exhibit strong swirl in the draft tube at the outlet of the […]
-
-
Legal & Regulatory
Get involved!
The Combined Cycle Users’ Group (CCUG) was formed to address issues of importance to users, particularly the interactions among the major systems of combined-cycle power plants: the steam turbine, combustion turbine(s), and heat-recovery steam generator. The added value of becoming a CCUG member is the opportunity to interact with other operators, as well as designers, […]
-
-
-
Legal & Regulatory
Hybrid generation markets endanger competition and innovation
Competition in power generation fosters technical innovation, cleaner power plants, and downward pressure on prices. Before the 1980s, such competition was almost nonexistent: vertically integrated utilities built and operated the vast majority of U.S. plants with oversight by state regulators. The Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act of 1978 and the Energy Policy Act of 1992 […]
-
Gas
Designing HRSGs for cycling
With U.S. combined-cycle plants increasingly being cycled—rather than being run continuously, as they were designed to do—owner/operators worry that units expected to last two or three decades may survive only a few years without an expensive overhaul. Cycling takes as much of a toll on heat-recovery steam generators as it does on gas turbines. Whether you’re procuring a new HRSG or adapting an existing one for cycling service, robust design features should be what you’re looking for.
-
Coal
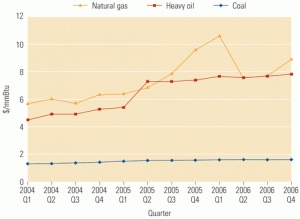
Stressed merchant industry hopes for better days
The U.S. power generation industry is changing at warp speed, via regulatory changes, consolidation, mergers, and sales of assets at yard-sale prices. New players have entered the market and become major players overnight, while several mainstays have gone bankrupt. Though many of the latter blamed high gas prices for their woes, well-diversified merchants enjoyed a record year. Whatever changes are in store for the business of combined-cycle generation, you can be sure that innovations in plant design and O&M such as those described in this special section will keep pace with them.