Solar
-
Solar
Sunny Days Ahead for Solar
In the U.S., developers of thermal and photovoltaic solar plants face a number of challenges in their efforts to deploy more utility-scale solar power. Some trends, however, are helping solar proponents move this renewable energy source closer to becoming a mainstream generating option.
-
Solar
Countries Abandon Subsidies for Renewables en Masse
Stricken by the economic crisis and forced to implement austerity measures, several countries around the world have been forced to abandon or slash subsidies for renewable power producers.
-
Coal
Spain: A Renewable Kingdom
Spain has served as both exemplar and scapegoat when it comes to renewable energy policy. Though power policy must necessarily accommodate specific national resources and goals, Spain’s experience as an early and eager adopter of renewable energy technologies and subsidies is a cautionary tale of how the best intentions can have unintended consequences.
-
Solar
Interest, Funding Buoys Floating Solar Power Plants
Like most forms of generation, solar power has its disadvantages. Two cited most by critics of photovoltaic (PV) or concentrating solar power facilities are that they require large expanses of land and that solar cell fabrication and maintenance costs are high. Several companies have been assessing a new approach to tackling these factors: installing solar plants on water.
-
Coal
China’s Five-Year Plan Is Heavy on Non-Fossil Generation
The People’s Republic of China’s Congress approved a much-anticipated draft of the country’s 12th Five-Year Plan (2011–2015) on March 14. Along with key objectives that included boosting its gross domestic product (GDP) by 7% annually on average, the country for the first time in a five-year plan established targets to tackle climate change. It plans to reduce carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP by 17% from 2010 levels by 2015 and to reduce energy consumption per unit of GDP by 16% from 2010 levels by 2015.
-
Solar
Energy Storage Enables Just-in-Time Generation
One of the main criticisms of renewable energy facilities is that they are unable to dispatch electricity when it’s needed. The great game-changer is low-cost energy storage, which would enable renewable energy production to be stored and rapidly released when needed. Here are seven promising distributed energy storage technologies that could be commercialized in the near future.
-
Solar
The Smart Grid and Distributed Generation: Better Together
Electricity grids are slowly getting smarter. Simultaneously, the use of distributed generation is increasing. Though smart grid advocates tout the ability of a smarter grid to enable greater deployment of distributed resources, the benefits could flow in both directions.
-
Coal
Canada’s “Clean” Image Extends to Clean Power
Canada’s extensive natural resources are the driver of its powerful economy, and energy is Canada’s single most important export. Yet policy makers across the nation are currently dealing with the consequences of a generation of under-investment in the electricity system and deciding what the new grid and supply mix should look like. Several provinces are competing to lead the charge in renewable energy and grid intelligence. Policy makers hope that such efforts will not only provide for Canada’s electricity needs but also create the green economy jobs that will drive the nation’s next generation of economic development.
-
Coal
Canada’s Provincial Power Strategies
In Canada, as in the U.S., where you live determines the type of generation technology that provides your power. Here’s how the four most energy-intensive provinces in Canada are responding to the challenge of providing reliable and cheap power in a sustainable way.
-
Solar
DOI Approves Nine Solar Projects on Federal Land—So Far
U.S. Interior Secretary Ken Salazar in late December approved—for the ninth time since October 2010—a solar power project to be built on federal lands.
-
Coal
IEA: Global Power Demand to Surge 2.2% Annually Through 2035
Though electricity generation has entered a key period of transition—as investment shifts to low-carbon technologies—world electricity demand is set to grow faster than any other “final form of energy,” the International Energy Agency (IEA) says in its latest annual World Energy Outlook.
-
Legal & Regulatory
Solving the Renewable Integration Puzzle
In November, California voters overwhelmingly rejected an initiative that would have put the brakes on AB 32, the state’s ambitious greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction law. Given the role that California has played in climate change policy, that such a vote took place only four years into the law’s implementation process and 10 years before the emissions reduction targets were to be met was a reality check on climate change policy for those on both sides of the issue.
-
Solar
MIT Researchers Invent Self-Renewing PV Technology
Scientists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have a created a set of self-assembling molecules that can turn sunlight into power, and which can repeatedly be broken down and reassembled by adding or removing solution. The scientific breakthrough—inspired by a natural process used by plants to renew light-capturing molecules that have been degraded by the sun—could mean that researchers are closer to creating a self-healing photovoltaic (PV) technology that can keep repairing itself to avoid loss in performance.
-
Solar
Top Plant: DeSoto Next Generation Solar Energy Center, DeSoto County, Florida
The forecast is looking sunny for the 25-MW DeSoto Next Generation Solar Energy Center, which has more than 90,000 photovoltaic (PV) panels and is the largest solar PV plant in the U.S. Completed in October 2009, it is a sustainable energy solution with minimal maintenance costs. The site uses no fuel, consumes no cooling water, has no air emissions, and creates no waste products.
-
Solar
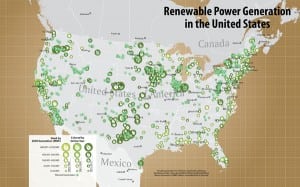
Map of Renewable Power Generation in the United States
For a full-size map, contact Platts. Courtesy: Platts Data source: POWERmap All rights reserved. No reproduction allowed.
-
Solar
A Winning Combination: Government and Utilities Partner on Renewable Energy Projects
Recent mandates require government facilities to develop energy policies that enable energy conservation, increase the use of renewable energy, and improve energy security. Utilities with government facilities in their service territory may have opportunities to develop solar and other renewable energy projects that help them meet state renewable portfolio standards while increasing a government facility’s usage of renewable energy. The key to such a win-win proposition is careful structuring of the project agreement to leverage each party’s assets.
-
Hydro
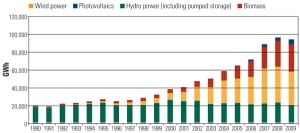
The Rush to Renewables
In 2010 investment in wind power continued to accelerate, particularly in California and Texas. California also entered several solar projects in the race for financing. The finish line that renewable power developers and their partners are racing to meet is a December 31 deadline to qualify for federal cash grants.
-
Commentary
While Congress Bickers, Solar Industry Holds Its Breath
Energy is the most regulated sector of the American economy, making public-private partnerships essential to scaling the solar industry. Such partnerships have helped other energy sectors to reach scale over the past hundred years.
-
Gas
Smart Power Generation at UCSD
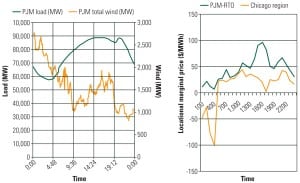
The University of California, San Diego has been accumulating awards for its savvy use of a constellation of power generation and energy-saving technologies. The campus already controls a fully functioning microgrid—including a cogeneration plant—and, as befits a research institution, is constantly looking for new ways to make its energy system smarter. This “living laboratory,” as campus leaders like to call it, demonstrates what it takes to build a smarter grid and why the effort is worth it.
-
Solar
The Global Smart Grid Scene
Presenters at the inaugural GridWise Global Forum in Washington, D.C., September 21 to 23 had a lot to say about the prospects for smarter grids. This synopsis of facts and opinions shared at the event, which attracted several smart grid A-listers, looks at the major challenges ahead, especially for the U.S.
-
Solar
Australia Fires Up Solar-Diesel Hybrid Plant
Australian company Horizon Power opened the country’s first hybrid solar-diesel power station in August near Marble Bar, and it is readying another for operation in the neighboring town of Nullagine, Western Australia—a region infamous for extremely hot temperatures. The power stations are the first “high penetration, hybrid solar-diesel systems” in the world, claims Horizon, adding […]
-
Solar
What Utility Executives Think About the Smart Grid
This summary of results from a recent Platts/Capgemini survey of North American utility executives looks at what respondents had to say about all things related to the smart grid. Nearly half of respondents’ utilities have a smart grid strategy in place, while the other half said their utility has one in development.
-
Coal
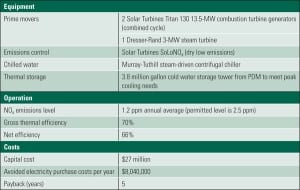
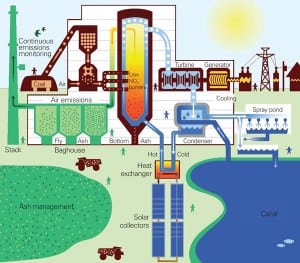
Xcel Energy Fires Up Solar/Coal Hybrid Demonstration
At the end of June, Xcel Energy fired up a demonstration project that integrates a 4-MW parabolic trough solar technology with an existing 44-MW coal-fired power plant.
-
Solar
Solar Capacity Heats Up Worldwide
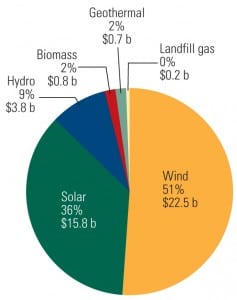
Spain in July inaugurated another major concentrated solar power (CSP) power station. The 50-MW La Florida parabolic solar trough plant in Alvarado Badajoz (in the west of the country), increases Spain’s solar nameplate capacity to 432 MW—beating out the U.S., which produces 422 MW from solar installations.
-
Solar
The Feed-in Tariff Factor
Most countries are trying to increase the percentage of their electricity supply that comes from renewable sources. But because capital costs for renewable generation still, in most cases, are higher per kilowatt-hour than for fossil-fueled power, governments are looking at all options for encouraging the development of greater renewable capacity. Feed-in tariffs (FITs) are one policy tool that has been used, most notably in Europe. Now North America is testing FITs as well.
-
Solar
Bulk Storage Could Optimize Renewable Energy
A defining challenge for the U.S. electricity industry is to economically integrate renewable energy facilities into grid operations without sacrificing reliability. Bulk energy storage options are commercially proven technologies that enable that integration most expediently. Existing and emerging national and state policy frameworks are supporting their application in projects under development throughout the country.
-
Solar
Feed-in-Tariffs Around the World
Feed-in-tariffs (FITs)—above-retail rates paid for renewable power that producers "feed" into the grid—are gaining momentum all over the world as a means of driving project growth. Here are some of those established and proposed FITs.
-
Solar
Abengoa Solar Begins Operation of 50-MW Parabolic Trough Plant
Abengoa Solar in early May began commercial operation of Solnova 1, the company’s first 50-MW parabolic trough plant. Covering 980,000 square feet with mirrors requiring an area totaling 280 acres (Figure 2), it is one of five planned concentrating solar power (CSP) plants to be built at the Solúcar Platform in Spain. All will use a technology developed by Abengoa with experience gained from a trough pilot built in 2007. Solnova 1 will also be equipped to burn natural gas if sunlight is weak.
-
History
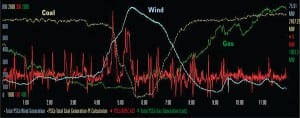
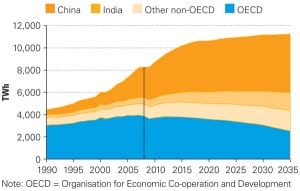
China: A World Powerhouse
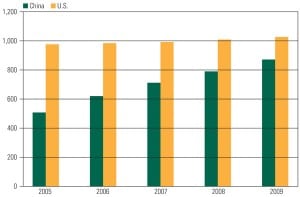
It’s no surprise that China leads the world in recent power capacity additions. What may surprise you is the precise mix of options this vast country is relying upon to meet its ever-growing demand for electricity. As a result, this ancient civilization is fast becoming the test bed and factory for the newest generation and transmission technologies.
-
Hydro
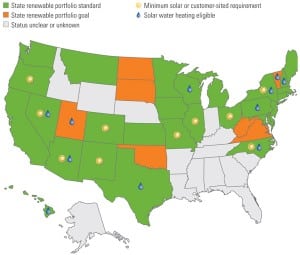
Utility Perspectives on Using Renewable Power
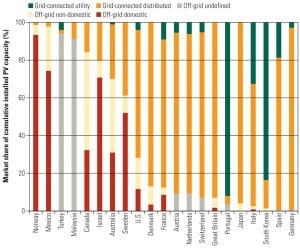
As U.S. utilities increase the percentage of renewable energy in their generation portfolio, they must deal with a number of key issues related to selecting specific technologies. Additionally, they must figure out what it will take to make renewables emerge as a mainstream generating option in the future.