O&M
-
O&M
Solving Fouling Problems with an HRSG Upgrade
Despite being located on the beautiful Hawaiian island of Oahu, the Kalaeloa Cogeneration Plant had trouble in paradise: Large amounts of ash from #6 low-sulfur fuel oil coated the finned tubes of its heat-recovery steam generators (HRSGs). The fouling added an extra $5 million dollars a year to the plant’s fuel bill. By retrofitting the HRSG with new panels and improved fin design, the plant overcame the fouling problems, stopped tube leaks, and cut fuel costs.
-
O&M
Nuclear: Realistic Simulation Assists in Nuclear Power Plant Certification
From the onset of the civilian nuclear era (marked by President Dwight Eisenhower’s "Atoms for Peace" speech to the United Nations in 1953), there has been a strong awareness of the importance of safety within the nuclear energy industry. Western experts have devoted much time and effort to ensuring the integrity of reactor cores and […]
-
O&M
A New Era in Power Plant Control Performance
Recent improvements in the performance of steam power plants have been achieved with advanced computerized controls. These new control schemes not only reduce fuel consumption and make the plant much more responsive, but they also can significantly decrease start-up commissioning time and cost.
-
O&M
Better Combustion Airflow Monitoring at the Hunan Yiyang Power Plant
Measuring combustion airflow in a coal-fired power plant can be problematic when using annubar instruments that feature small holes that can easily plug with coal dust. Sierra Instruments eliminates this big maintenance headache with its more-accurate, nonplugging thermal mass flow meter design.
-
O&M
Lessons Learned from a Hydrogen Explosion
On January 8, 2007, a hydrogen explosion at the Muskingum River Power Plant’s 585-MW coal-fired supercritical Unit 5 caused one fatality, injuries to 10 other people, and significant damage to several buildings. The explosion occurred during a routine delivery of hydrogen when a hydrogen relief device failed, which allowed the contents of the hydrogen tank to escape and be ignited by an unknown source. This article covers the findings of the incident investigation and the actions the plant has taken to prevent a reoccurrence.
-
O&M
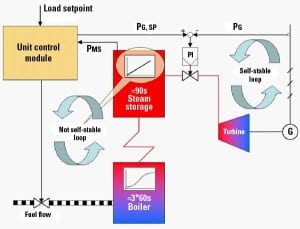
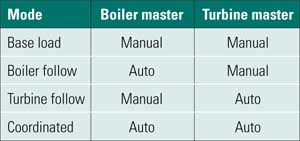
Boiler-Tuning Basics, Part II
Boilers have enormous thermal mass and are relatively slow to react. Turbines are nimble and quickly answer an operator’s command. Coordinating an entire plant requires an intimate knowledge of both systems and selecting the right logic tools to bring them together.
-
O&M
Hydrokinetic Plant Piggybacks on Existing Hydro Plant
Hydrokinetic energy — which generates power by using underwater turbines that harness moving water — is on the rise in the U.S. In January, the first U.S.-licensed, commercial, grid-connected hydrokinetic project installed the first of two 100-kW nameplate-rated turbines downriver from an existing run-of-river hydroelectric plant on the Mississippi River.
-
O&M
Fire Safety in Modern Hydroelectric Stations
It may seem counterintuitive, but fire can be a serious danger in hydropower plants. In some respects, the danger is even greater than in thermal power stations. Most U.S. hydro plants are 30 to 70 years old but can deliver another 20 or 30 years of service with upgrades — including state-of-the-art fire protection systems. The design options outlined here also apply in large part to other generating stations.
-
O&M
Making the Most of Thermal Imaging Data
This article discusses planning, operation, and documentation procedures designed to effectively use the thermal imaging camera as a critical element in an effective reliability program.
-
O&M
Reducing Millirem Exposure
Radioactive materials are clinging to the inside walls of reactor system components because of a noble metals injection process error some years ago at Cooper Nuclear Station (CNS). CNS has launched an aggressive, long-term program to remove the materials, but until the work is successfully completed, the station is also taking extensive measures to protect employees and reduce higher source term dose.