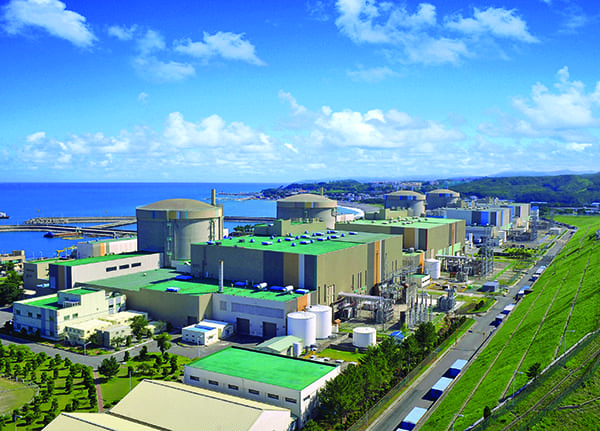
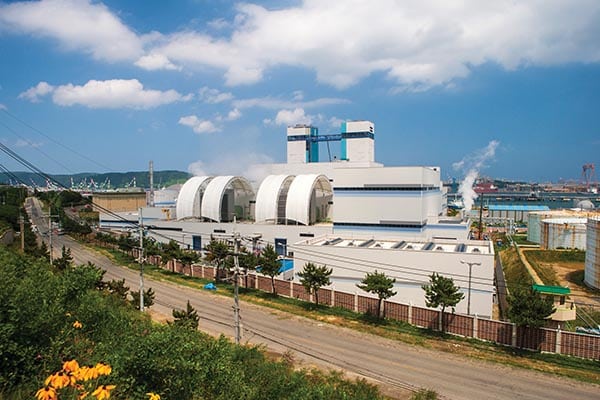
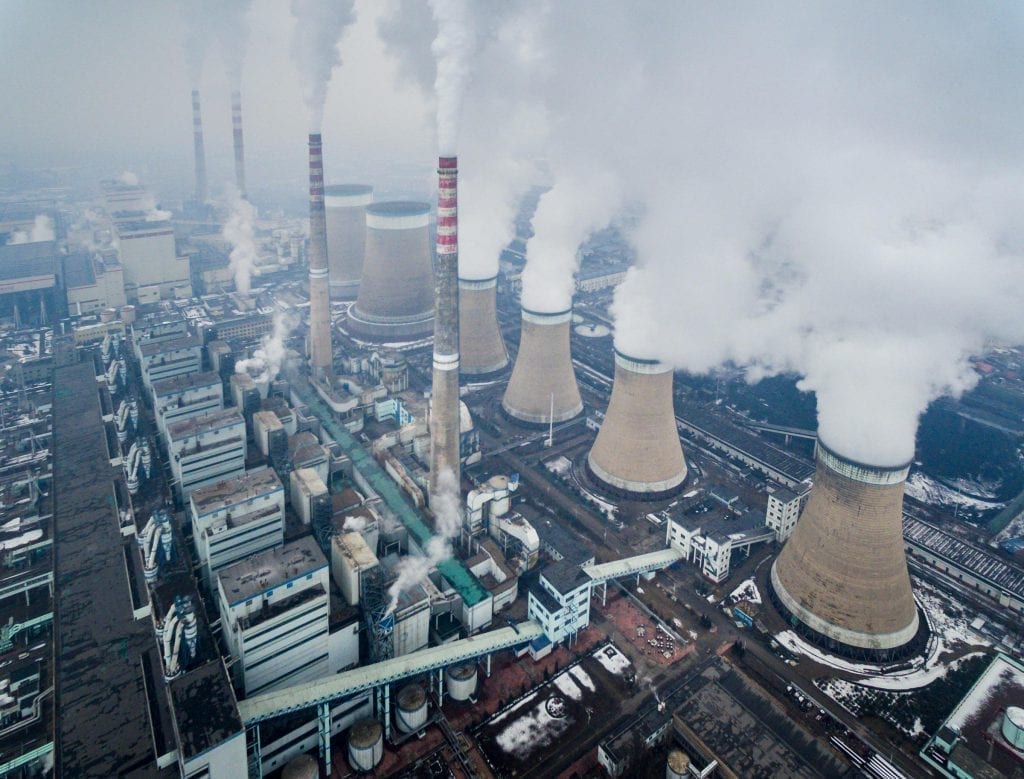
The South Korean government said the country’s coal-fired power generation hit a new high in 2017, helped by three thermal power plants that came online with combined generation capacity of 5.3 GW. The country also suspended operations at 11 of its 24 nuclear reactors, which meant coal generation supplied an even higher percentage of South Korea’s power, reaching 43.2%, up 3.6 percentage points from 2016.
Statistics released in late February by state-run Korea Electric Power Corp. (KEPCO) said South Korea’s coal-fired generation totaled 217,037 GWh from January through November 2017, exceeding the previous record of 213,803 GWh across the first 11 months of 2016. Nuclear power supplied 27.5% of the country’s generation, followed by liquefied natural gas (LNG) at 20.8%.
The increase in coal-fired generation (Figure 1) comes even as the administration of President Moon Jae-in has said it wants to increase its use of wind and solar power, as outlined in the country’s latest energy plan, released in December 2017. Pak Won-ju, the country’s deputy energy minister, in late February 2018 met with Anton Inyutsyn, Russia’s deputy minister of energy, as the countries discussed increasing their cooperation on energy matters, including renewable energy development. Doing business with Russia is part of Jae-in’s “New Northern Policy,” which seeks to broaden economic opportunities in Russia, and Northeast and Central Asia. Russia and South Korea already cooperate on joint projects for LNG and gas-fired power generation. KEPCO also is working with Rosseti, the Russian energy grid, on an agreement for power grid development; KEPCO has pushed for a multinational grid interconnection among South Korea, Russia, China, and Japan. Jae-in earlier in February met with Lithuanian President Dalia Grybauskaite to discuss cooperation on energy-related matters.
Construction of the three coal plants that began commercial operation last year began during the previous administration of President Park Geun-hye, who served from February 2013 until March 2017, when she was impeached and forced from office. Jae-in won a special presidential election and took office in May 2017, running on a pledge to move the country away from coal and nuclear power and increase the use of renewables. During his campaign he said his goal was to increase electricity production from renewable sources—currently at about 6%, according to government figures—to 20% by 2030, a number that was confirmed in the country’s latest energy plan.
The latest plan calls for an increase in installed capacity of renewable power generation to 58.5 GW by 2030, up from 11.3 GW in 2017, a jump of almost 420%. The country’s energy ministry said the plan is to add about 31 GW of solar power generation capacity and more than 16 GW of wind power capacity by 2030. The new plan would drop coal-fired generation’s share of the country’s electricity output to about 36% in 2030, with nuclear falling to about 24%. The government has said most of the changes will not be introduced until after 2022. Jae-in had said his administration would review existing plans to build nine new coal plants and eight nuclear reactors; in the plan announced in December, the energy ministry said it would convert at least two of the planned coal-fired plants to gas, increasing their generation capacity to 1.9 GW, up from 1.2 GW. The ministry also said it would convert four existing coal-fired plants to natural gas. The country still plans to add two new nuclear reactors by 2022 after a poll of the country’s citizens in October 2017 showed support to resume construction of Units 5 and 6 at the Shin Kori plant, where the president had ordered a halt to construction in July 2017 as part of his administration’s review of the country’s reactors.
—Darrell Proctor is a POWER associate editor.